Breakup Of Northern Securities
In 1902, President Theodore Roosevelt ordered the Justice Department to break up the Northern Securities Company. This holding company controlled the main railroad lines from Chicago to the Pacific Northwest.
Roosevelt took the position that the company was an illegal monopoly. The company appealed the move, and the case went all the way to the Supreme Court, which ruled in favor of the federal government.
National debt: $2.3 billion
Hurricanes Katrina And Rita Growth Of China And India
In August of 2005, Hurricane Katrina hit the Gulf Coast, nearly destroying New Orleans and becoming one of the largest natural disasters in U.S. history. Hurricane Rita followed soon after.
The two storms caused more than $2 billion in damage, destroyed 275,000 homes, eliminated 400,000 jobs, killed over 1,000 people, and displaced hundreds of thousands of Americans.
This was also the year that China and India rose as world financial powers. For years, the U.S. had been outsourcing work to these countries because they offered cheap labor. Eventually, the strategy shifted to tapping these workforces for highly educated and skilled technical talent.
National Debt: $7.933 trillion
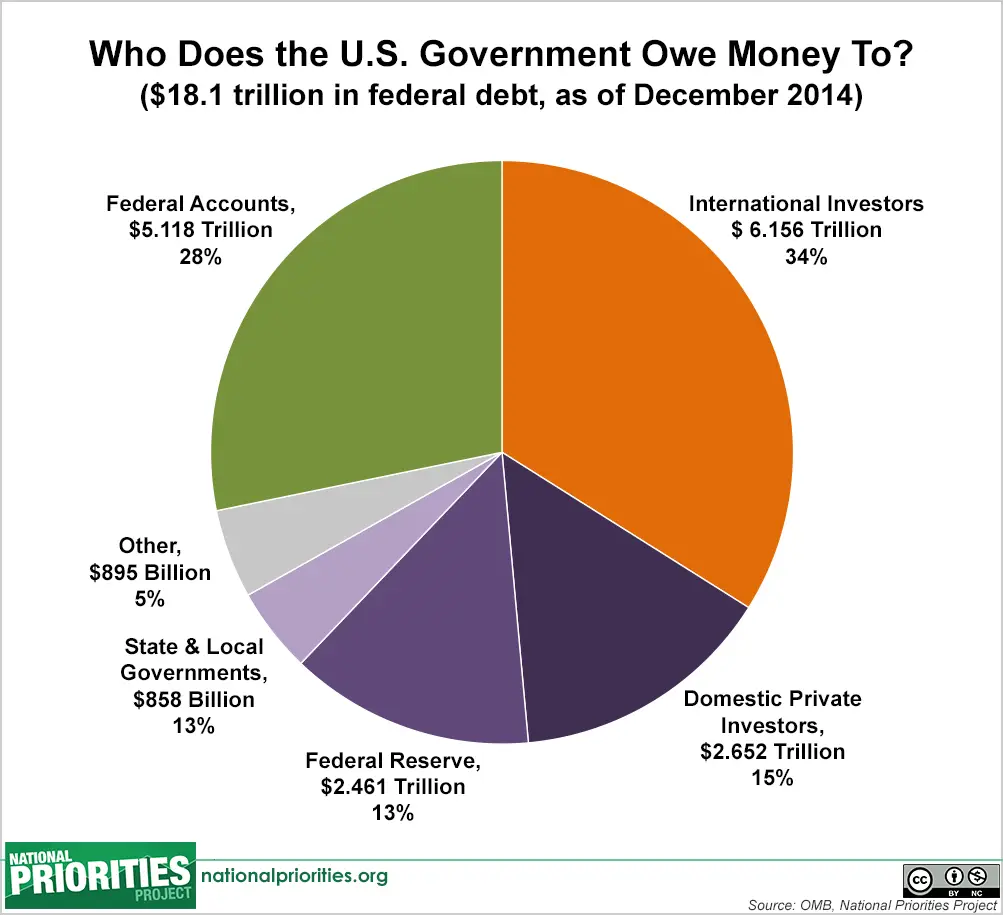
How Much Do Other Countries Owe The Us
Public debt makes up three-quarters of the national debt, and foreign governments and investors make up one-third of public debt. As of , the countries with the most debt owed to the U.S. are Japan, China, the United Kingdom, Luxembourg, and Ireland.
Though China had been the long-standing top placeholder for the country with the most debt owed to the United States, Japan currently holds $1.3 trillion worth of U.S. debt. The second place holder, China, currently holds $1.1 trillion in Treasury holdings. Together, they hold 31% of all foreign-owned U.S. debt.
Recommended Reading: Can Irs Debt Be Discharged In Bankruptcy
Why Does The National Debt Matter
What makes America strong is our willingness to build and leave a better future for the next generation. Unfortunately, our growing debt is doing the opposite.
America faces many challenges including rising inequality, unaffordable healthcare, a changing climate, failing education, crumbling infrastructure, and unpredictable security threats. To address these challenges we will need significant resources. Every dollar that goes toward interest payments means less resources available to build a stronger, more resilient future.
Being irresponsible with our budget is simply not fair to our kids and grandkids, who will inherit this debt.
RISING INTEREST IN THE BUDGET
Each business day, the U.S. Treasury Department reports the amount of total debt outstanding as of the previous business day. Our debt clocks are updated daily based on this number. In addition, our formula uses the debt projections from the Congressional Budget Office , to estimate the rate at which the debt is currently growing. Those CBO projections are updated 2-3 times per year.
Debt per person is calculated by dividing the total debt outstanding by the population of the United States, as .
The $30 trillion gross federal debt equals debt held by the public plus debt held by federal trust funds and other government accounts. Learn more about different ways to measure our national debt.
MORE RESOURCES
Less To Spend On Other Government Initiatives

The more money the U.S. has to spend on meeting its debt obligations as interest rates increase, the less financial capacity it could have to fund programs focused on education, veterans benefits and transportation.
This breakdown of the 2019 Federal Budget from the Council on Foreign Relations shows how the budget pie is only so big, so when one area increases , another must decrease.
Also Check: When Should A Company File For Bankruptcy
How Did The Debt Get Where It Is Today
More on:
The United States has run annual deficitsspending more than the Treasury collectsalmost every year since the nations founding. The period since World War II, during which the United States emerged as a global superpower, is a good starting point from which to examine modern debt levels. Defense spending during the war led to unprecedented borrowing, with the debt skyrocketing to more than 100 percent of gross domestic product in 1946.
Debt Grows Into The Trillions During 1980s And 1990s
At the start of the 1980s, an increase in defense spending and substantial tax cuts continued to balloon the federal debt. The national debt at the end of the Ronald Reagan era was $2.7 trillion.
The era under President Bill Clinton was marked with tax increases, reductions in defense spending and an economic boom that reduced the growth of debt, but it still reached a staggering $5.6 trillion by 2000.
Recommended Reading: How To File For Personal Bankruptcy In New York
The Birth Of Public Debt
George Washington,portrait by Gilbert Stuart
“No pecuniary consideration is more urgent than the regular redemption and discharge of the public debt: on none can delay be more injurious, or an economy of the time more valuable.”
George Washington, 1793, Message to the House of Representatives
The public debt of the United States can be traced back as far as the American Revolution. In 1776, a committee of ten founders took charge of what would become the Treasury, and they helped secure funding for the war through “loan certificates” with which they borrowed money for the fledgling government from France and the Netherlands. This committee morphed over the next decade into the Department of Finance. Robert Morris, a wealthy merchant and Congressman , was chosen to lead a new Department of Finance in 1782.
As the new Superintendent of Finance, Morris was the first committee member to order a reporting of the total government debt owed. This marked the beginning of annual Treasury reports to the President. On January 1, 1783, the public debt of the new United States totaled $43 million.
How This Presidential Bet Plans To Erase Debt
Kenyan presidential candidate George Wajackoyah attends a campaign rally in Gatundu, Kenya, August 3, 2022. REUTERS
NAIROBI Sexagenarian reggae aficionado and presidential candidate George Wajackoyah is convinced he has the right medicine for the ills troubling Kenyas voters: a dose of marijuana and some hyena testicles.
East Africas wealthiest country is holding elections on August 9. A tight race between the two leading presidential candidates veteran opposition leader Raila Odinga and Deputy President William Ruto has thrust a spotlight on Wajackoyahs small but committed band of followers, who could force a runoff if neither side gets more than 50 percent of the vote.
Voter registration among young people has fallen sharply, with many saying conventional politicians have failed to tackle rampant corruption, runaway inflation or joblessness.
Wajackoyahs bid for the presidency has caught the imagination of younger voters. The gravedigger-turned-adjunct-law-professor is trailing a distant third in the polls at around 2 percent but he could tip the balance if he endorses one candidate, or takes enough votes from another.
Read Also: How To Remove Chapter 7 Bankruptcy From Credit Report
Twin Towers Attacks Corporate Scandals And Wars In Afghanistan And Iraq
The terrorist attack of September 11, 2001, led to the War in Afghanistan, and eventually, the invasion of Iraq in March of 2003. The war lasted more than eight years, ending on December 18, 2011.
The stock market had experienced a brief slide after the terrorist attacks. But after rallying, the market began to fall again in March of 2002, partially due to corporate fraud scandals of 2001, such as Enron, Tyco, and WorldCom.
National Debt: $6.783 trillion
The National Debt Dilemma
- The pandemic has taken the U.S. national debt to levels not seen since the 1940s.
- The United States is in a unique position because it holds the worlds reserve currency, allowing it to carry debt more cheaply than other countries.
- Some experts argue that the United States can safely continue to sustain high levels of debt, while others warn that it will eventually have to face the consequences.
The U.S. national debt is once again raising alarm bells. The massive spending in response to the COVID-19 pandemic has taken the budget deficit to levels not seen since World War II. This expansion follows years of ballooning debttotaling nearly $17 trillion in 2019that will now be even more difficult to reduce. Raising the debt ceiling, the legal limit on government borrowing, has become a perennial fight in Congress.
Read Also: How To File Bankruptcy In Az On Your Own
What Is The National Debt Costing Us
As the debt grows, so does the interest we pay.
Similar to a home or car loan, interest payments represent the price we pay to borrow money. As we borrow more and more, federal interest costs rise and compound. Rapidly growing interest payments are a burden that hinders our future economy.
Interest will become the fastest growing part of the federal budget.
In ten years, our interest will nearly triple from where it is today.
What Is A Cds Spread
Credit default swaps are a type of derivative that provides a lender with insurance in the event of a default. The seller of the CDS represents a third party between the lender and borrower .
In exchange for receiving coverage, the buyer of a CDS pays a fee known as the spread, which is expressed in basis points . If a CDS has a spread of 300 bps , this means that to insure $100 in debt, the investor must pay $3 per year.
Applying this to Ukraines 5-year CDS spread of 10,856 bps , an investor would need to pay $108.56 each year to insure $100 in debt. This suggests that the market has very little faith in Ukraines ability to avoid default.
Read Also: Can You Get A House Loan After Filing Bankruptcy
Who Decides How Much Interest The Us Pays On Its Debt
Supply and demand. In other words, the marketplace. When the government needs to raise debt financing, it sells debt securities in an auction. Bidders offer to buy the debt for a specific rate, yield, or discount margin, and all successful bidders receive the highest yield or discount the Treasury accepts. Government debt buyers may include central banks, though their goal is typically to foster sustainable economic growth rather than to finance deficit spending.
National Debt For Selected Years
| Fiscal year | |
|---|---|
| 130.6% | 21,850 |
On July 27, 2018, the BEA revised its GDP figures in a comprehensive update and figures back to FY2013 were revised accordingly.
On June 25, 2014, the BEA announced: “n addition to the regular revision of estimates for the most recent 3 years and for the first quarter of 2014, GDP and select components will be revised back to the first quarter of 1999.
Fiscal years 19402009 GDP figures were derived from February 2011 Office of Management and Budget figures which contained revisions of prior year figures due to significant changes from prior GDP measurements. Fiscal years 19502010 GDP measurements were derived from December 2010 Bureau of Economic Analysis figures which also tend to be subject to revision, especially more recent years. Afterwards the OMB figures were revised back to 2004 and the BEA figures were revised back to 1947.
Fiscal years 19401970 begin July 1 of the previous year fiscal years 19802010 begin October 1 of the previous year. Intragovernmental debts before the Social Security Act are presumed to equal zero.
19091930 calendar year GDP estimates are from MeasuringWorth.com Fiscal Year estimates are derived from simple linear interpolation.
Audited figure was “about $5,659 billion.”
Audited figure was “about $5,792 billion.”
Audited figure was “about $6,213 billion.”
Audited figure was said to be “about” the stated figure.
Audited figure was “about $7,918 billion.”
Audited figure was “about $8,493 billion.”
You May Like: Can You Rent An Apartment After Bankruptcy
Which President Created The Most Debt
In terms of percentages, President Franklin Delanor Roosevelt added the most debt with a 1,048% increase in national debt from his predecessor President Herbert Hoover. With $236 billion added to the national debt, President Roosevelt served as president during the time of the Great Depression which largely depleted the countrys revenue. To combat this, he set up the New Deal which included relief programs and government spending to address unemployment, severe droughts and agriculture disruptions, and bank failures. The largest part of the addition to the national debt was World War II – the war cost the country $209 billion from 1942 to 1945.
A Brief History Of Us Debt
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
Nearly all national governments borrow money. The U.S. has carried national debt throughout its history, dating back to the borrowing that financed the Revolutionary War. Since then the debt has grown alongside the economy, as a result of increased government responsibilities, and in response to economic developments.
Read Also: How To Find Out If A Company Filed Bankruptcy
Major Events And The Impact On Us Debt
It helps to consider the national debt in context. During times of war, the U.S. increases military spending. When the economy is down, the federal government uses spending and tax cuts to spur growth. When these expansionary fiscal policies boost economic growth, higher tax revenues can be used to pay back the debt.
Here’s a timeline of the national debt by year, and how it compares to national events.
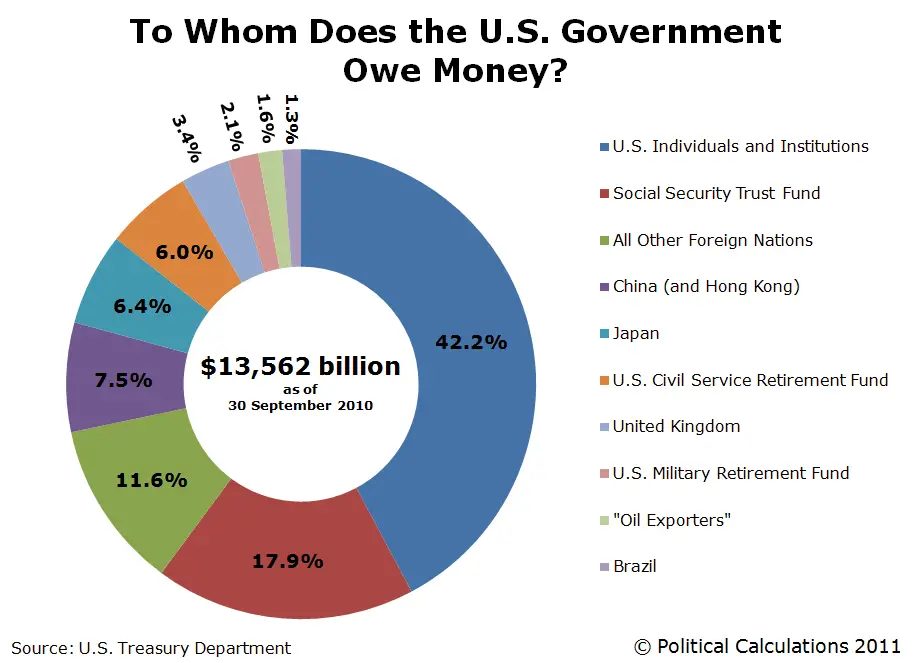
Who Owns Most Of Us Debt
The largest percentage of US debt is held by foreign investors. International investors hold 29.5% of all US debt. However, these investors hold 40% of all debt held by the public, which amounts to about $6.7 billion. In terms of countries, the US Treasury department lists Japan and China as the largest foreign investors, holding 18% and 15%, respectively, of all foreign securities.
You May Like: Can You File Bankruptcy On Traffic Tickets
Negative Real Interest Rates
Since 2010, the U.S. Treasury has been obtaining negative real interest rates on government debt, meaning the inflation rate is greater than the interest rate paid on the debt. Such low rates, outpaced by the inflation rate, occur when the market believes that there are no alternatives with sufficiently low risk, or when popular institutional investments such as insurance companies, pensions, or bond, money market, and balanced mutual funds are required or choose to invest sufficiently large sums in Treasury securities to hedge against risk. Economist Lawrence Summers states that at such low interest rates, government borrowing actually saves taxpayer money and improves creditworthiness.
In the late 1940s through the early 1970s, the U.S. and UK both reduced their debt burden by about 30% to 40% of GDP per decade by taking advantage of negative real interest rates, but there is no guarantee that government debt rates will continue to stay this low. Between 1946 and 1974, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio fell from 121% to 32% even though there were surpluses in only eight of those years which were much smaller than the deficits.
How Has The Covid
According to the Congressional Budget Office, debt held by the American public will rise to 98% of GDP due to the economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic and legislative actions taken as a result. The CBO says that the main driver of the increased debt is a federal budget shortfall of $3.3 trillion, the largest since 1945.
You May Like: What Does Foreclose Mean
Preventing This Situation In The Future
Without further intervention, after President Biden cancels some amount of student loan debt, students will continue to take out loans and, once again, accumulate debt. Colleges and universities will continue to take in billions of taxpayer dollars without sufficient justification for the prices they charge or for increases in tuition year after year. And many institutions will confer low-quality degrees that leave their holders with little economic opportunity.
In order to prevent a situation where another round of broad-based debt cancellation is needed in the future, Congress must address the root causes of student loan debt by increasing grant aid, controlling the actual cost of higher education, and implementing stronger institutional accountability measures.
First, aid: Expanding the availability of financial aid programs
As the purchasing power of the Pell Grant and other financial aid programs has declined relative to the cost of college over the years, more students have relied on federal student loans to cover outstanding costs. While states and institutions have important roles to play in expanding need-based grants, federal financial aid programs are the cornerstone of college affordability. If Congress wants to prevent another student debt crisis from emerging in the future, it must ensure that funding for grants and work-study outweighs the funding provided for new loan volume.
According to the Department of Education:
Also read
United States National Debt: What Affect Does Hiding $5 Trillion From The Books Have On The Us Debt Clock
The United States is one of the world’s most eager consumers of national debt. Due to the high volume of new US national debt being added on an irregular basis, this clock is regularly updated.
US Treasury & USA.gov website. US national debt statistics include Intragovernmental Holdings.
July 21, 2022
Disclosure:
In this guide to the United States National Debt, we discuss the amount of the countrys debt, whats included in it, who manages the debt, the countrys debt ceiling, how it raises loans, and who holds the US debt.
Read Also: How Will Filing Bankruptcy Affect My Credit Score
How Bad Is National Debt
Americans living with high levels of government and private debt tend to see saving in a positive light, while treating borrowing as a problem. In fact, they go hand in hand since borrowings come from savings and provide savers with the interest they earn from deferring consumption.
U.S. national debt provides corresponding low-risk assets for pension funds and families, and enables consumption in excess of production for the country as a whole.
At the same time, nothing more than simple arithmetic is required to see the pace of the recent growth of government debt as unsustainable. That’s the term the U.S. Treasury used in the Financial Report of the U.S. Government for Fiscal Year 2021, after calculating that under prevailing trends the federal debt-to-GDP ratio would increase from 100% in 2021 to 701% by 2096.Economists and policy analysts on the left often differ from those on the right in evaluating the tradeoffs between the everyday utility of government debt and its growing risks amid rapid accumulation.
Critics of public debt often contend it can crowd out private investment, a theory not supported by U.S. credit markets developments in recent decades. In contrast, economists using Modern Monetary Theory argue government borrowing can improve economic outcomes if it fosters public investment that expands the economy’s productive potential.