Does The Debtor Have An Absolute Right To A Discharge
No, the debtor does not have an absolute right to a discharge. If there is an objection to the debtors discharge, a case may be filed by a creditor, trustee in the case or by the U.S trustee. Then, the creditos will receive a notice that has all the important information with dates and deadlines to meet for the case. If there is an objection, the creditor may file a complaint with the court bankruptcy court before the state deadline for timeliness.;
Additionally in some cases, the bankruptcy court may deny a discharge for a debtors lack of compliance with rules or procedure. For example, if you defraud creditors, the court may not discharge your debts, even though they are otherwise dischargeable. Moreover, creditors, the bankruptcy trustee, or the U.S. Trustee are allowed to object to your discharge. However, the bankruptcy court will have the final say.
Discharges may also be denied if you file bankruptcy too frequently within a short time period. For example, if you file successive Chapter 7 cases, you will not receive a discharge in the second case if it is within eight years of the filing date for your first case.
When you are filing under two different chapters, the order determines the duration for when to receive a discharge in the second case. For example, if you file for Chapter 13, you cannot file under Chapter 7 and obtain a discharge within six years from the date you filed your Chapter 13 case. This is generally the case but there can be certain exceptions.;
What Bankruptcy Can Do
Bankruptcy allows people struggling with debt to wipe out certain obligations and get a fresh start. The two primary bankruptcy types filedChapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcyeach offer different benefits and, in some cases, treat debt and property differently, too. You’ll choose the chapter that’s right for you depending on your income, property, and goals.
Here are some of the things you can expect regardless of whether you file for Chapter 7 or 13.
What Only Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Can Do
Chapter 7 and 13 each offer unique solutions to debt problems. The two bankruptcy types work very differently. For instance, how quickly your debt will get wiped out will depend on the chapter you file:
- Chapter 7 bankruptcy. This chapter takes an average of three to four months to complete. Learn more about erasing your debt in Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
- Chapter 13 bankruptcy. If you file for Chapter 13 rather than Chapter 7, you’ll likely have to pay back some portion of your unsecured debts through a three- to five-year repayment plan. However, any unsecured debt balance that remains after completing your repayment plan will be discharged. Find out how to pay off or discharge your debts in Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
Chapter 7 is primarily for low-income filers, and therefore, it won’t help you keep property if you’re behind on payments. But, if you have enough income to pay at least something to creditors, then you’ll be able to take advantage of the additional benefits offered by Chapter 13.
Here are some of the things that Chapter 13 can do.
Stop a mortgage foreclosure. Filing for Chapter 13 bankruptcy will stop a foreclosure and force the lender to accept a plan that will allow you to make up the missed payments over time. To make this plan work, you must demonstrate that you have enough income to pay back payments and remain current on future payments. Learn more about your home and mortgage in Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
Don’t Miss: Which Of The Following Phrases Best Summarizes Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
What Is Secured Debt And Unsecured Debt
A bankruptcy usually discharges only unsecured debt, that is, debt that is not secured by collateral. Unsecured creditors cant take your property to satisfy debts. Usually, they must file a lawsuit against you and prevail with that lawsuit before they may begin collection proceedings.
Bankruptcies usually will not discharge secured debt, although there may be some narrow exceptions. A secured debt is a debt secured by property, which the creditor may seize if you default.
Things To Consider Surrendering Of Secured Assets
When you claim bankruptcy, you must surrender your assets, such as your home or your vehicle. This might not make sense if youve built up a fair amount of equity. For example, if you have $200,000 of net worth in your home, it doesnt make sense to give it up. Instead of filing for bankruptcy, youre likely better off with a consumer proposal, which allows you to hold on to your assets.
An exception to this would be if you did not have sufficient equity in your home or your car. There is an allowable amount of equity by which you can maintain these assets, but it varies slightly in each province. For example, if you are the sole owner of a home in Manitoba, you are only permitted to hold onto $2500 of equity in the property. If you own a car in Alberta, the maximum value, or equity, is $5000.
Recommended Reading: How To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
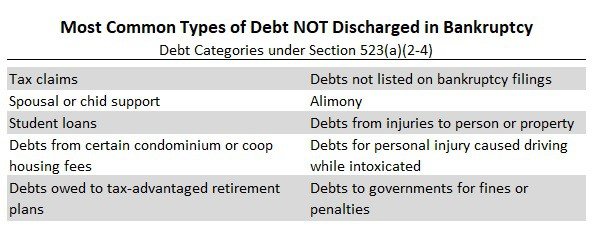
Debts That Are Always Nondischargeable In Chapter 7
Some types of debts are deemed nondischargeable without the need for a hearing if they fall within one of a list of prescribed categories. Unless the debtor can demonstrate extraordinary circumstances, the following debts are automatically nondischargeable:
- unscheduled debts , unless the creditor had actual notice or knowledge of the bankruptcy filing. Also, many jurisdictions allow discharge of otherwise dischargeable debts not listed in the petition due to an innocent mistake when there are no assets to distribute.
- certain taxes
- debts for spousal or child support or alimony
- debts owed to a former spouse or child if they arose out of a divorce or separation
- debts to government agencies for fines and penalties
- student loans
- debts for personal injury caused by the debtor’s operation of a motor vehicle while intoxicated
- debts owed to certain tax-advantaged retirement plans
- debts for certain condominium or cooperative housing fees
- attorney fees in child custody and support cases, and
- court fines and penalties, including criminal restitution.
While all of these debts are nondischargeable in Chapter 7, some of them can be eliminated in Chapter 13. Find out which debts are dischargeable in Chapter 13 but not Chapter 7.
If I Own A Home Will I Lose It If I File A Chapter 7 Or A Chapter 13 Case
The answer to that question depends on many factors, such as the equity in your home and whether you are seriously delinquent on your mortgage payments at the time you file bankruptcy. If you are concerned about what will happen to your home, you should consult an experienced bankruptcy attorney for guidance based on your circumstances. However, in most bankruptcy cases, individuals are able to keep their homes. In general, those who file for Chapter 13 bankruptcy have a greater ability to protect their assets than those who file under Chapter 7.
Don’t Miss: When Does Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Fall Off Credit Report
Can I Discharge A Court Judgment In A Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is an efficient and quick way for Florida residents to wipe out most unsecured debt, like credit card debt or medical debt. But what about court judgments? If you lose a lawsuit, the court will enter judgment against you, which tells you how much money you need to pay to the person who sued you. Generally, you can discharge a court judgment, but there are exceptions.
No Discharge of Unpaid Child or Spousal Support
You might owe thousands of dollars in unpaid child support or alimony, and a judge can enter a judgment against you for your unpaid amounts . Unfortunately, these debts are not dischargeable, so any court judgment based on these debts is likewise not dischargeable. Instead, work on finding ways to save money or, if you have recently lost your job, contact a family law attorney for help modifying your child support or spousal support orders.
No Discharge for Fraud
The government does not want to reward dishonest behavior, so it prohibits you from discharging a court judgment based on fraud. For example, you cannot discharge a court judgment for a lawsuit based on the following:
- You lied to obtain credit, goods or services
- You stole money while serving in a position of trust, such as while serving as a court-appointed guardian
No Discharge for Debts Owed to the Government
The government wants its money, so you cannot use bankruptcy to eliminate certain debts to the government such as:
No Discharge for Judgments for Willful or Malicious Acts
Resource:
Which Debts Are Not Discharged In Bankruptcy
Debts discharged in bankruptcy vary from case to case and chapter to chapter of the bankruptcy code. According to chapter 11 of the bankruptcy code, where a business hopes to become profitable after a reorganization plan, the approved debts to be paid by the debtor in the reorganization plan become non-dischargeable debts. Meanwhile, unapproved debts become dischargeable debts.
According to chapter 13 bankruptcy, an individual debtor or a;small business owner, like a proprietorship business, needs to repay all debts in monthly installments within a period of three to five years. However, some debts like court fees and homeowners association fees can be discharged.
Chapter 7 of the bankruptcy code states common dischargeable debts. These are debts from credit cards, unpaid taxes, bad checks, utility bills, court judgments, lease, and others. Debts that cannot be discharged are debts to government agencies, recent taxes, federal tax liens, and debts that debtors successfully challenge.
Don’t Miss: How Many Bankruptcies Has Donald Trump
Discharge Exceptions To Discharge And Objections To Discharge
Consumer bankruptcy principally is designed to permit debtor rehabilitation through the discharge of debts. The Bankruptcy Code authorizes a broad discharge, which provides a fresh start to “honest but unfortunate debtors,” to fulfill one of its most fundamental purposes.
Notwithstanding the general availability of the discharge, section 523 of theBankruptcy Code specifically enumerates certain debts that are not discharged. A debtor may discharge all other debts in bankruptcy, but those exceptions remain postbankruptcy charges against the debtor. The exceptions are to be construed narrowly, and a creditor bears the burden to prove each element of an exception to discharge by a preponderance of the evidence.
Debts excepted from the bankruptcy discharge obtain distinctive treatment forpublic policy reasons. Many nondischargeable debts involve “moral turpitude” orintentional wrongdoing. Other debts are excepted from discharge because of the inherent nature of the obligation, without regard to any culpability of the debtor. Regardless of the debtor’s good faith, for example, support obligations and many taxclaims remain nondischargeable. Society’s interest in excepting those debts fromdischarge outweighs the debtor’s need for a fresh economic start.
1.4.1;;;
However, with increasing frequency, section 523 is used to challengethe dischargeability of debt arising from the routine use of credit cards even in theabsence of actual fraud.
1.4.3;;;Criminal Restitution Orders
Notes:
Can A Creditor Still Collect After A Discharge
No, generally a creditor may not collect after there has been a discharge order recorded by the bankruptcy court. If a creditor still collects after a discharge, the debtor can file a motion with the court to address this matter. It is important to ensure that the discharge order is not violated. The bankruptcy courts discharge order constitutes a permanent statutory injunction prohibiting creditors from taking any action on the case.;
This includes the filing of a lawsuit and it is designed to collect discharged debt. If a creditor does not abide by the order they can be sanctioned by the court for violating the discharge injunction. Generally, the penalty for violating the discharge injunction is civil contempt, which is often punishable by a fine.
Also Check: Who Is Epiq Corporate Restructuring Llc
Do The Courts Ever Deny A Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
It can happen. Most individual debtors receive a discharge under Chapter 7.
However, if the courts find that an individual concealed money or other assets, fraudulently transferred assets that should have been used to pay off debts, or otherwise broke the law, the entire bankruptcy case may be denied.
How We Make Money

The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to stricteditorial integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Heres an explanation forhow we make money.
You May Like: Epiq Corporate Restructuring Llc
What Can You File Bankruptcy On
There are several kinds of debt in which bankruptcy can be filed, though some might be treated differently under Chapter 7 versus Chapter 13. Some types of debt that are typically eligible for both include:
- Personal loans
- Medical bills
- Unpaid utility bills
Although these types of debt can be erased, you might lose your assets if you have secured debt, which requires you to offer collateral, such as a car or house.
Almost all unsecured debt is dischargeable, explained attorney Arnold Hernandez. Secured debt is dischargeable, but there is almost always a lien on the property, so even if the debt is discharged, the property can be recovered by the creditor.
Under Chapter 7 bankruptcy, creditors could seize both your home and car. Under Chapter 13, you have a greater chance of holding on to these assets if you can keep up with your new repayment plan.
Keeping Your Discharge Certificate
The paperwork that you receive once your discharge is complete is important to keep in a safe place.
You can use it to prove that you are no longer going through bankruptcy, and you may need it if you are applying for credit or need proof of your discharge for other reasons.
It can be helpful to have if the bankruptcy is later not removed from your credit report when it should be, for example.
You should keep it in the years after your discharge, preferably at least until your bankruptcy no longer shows on your credit report.
Read Also: How To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
What Are The Dischargeable Debts In Bankruptcy
People often misunderstand that filing for bankruptcy discharges or absolves them from paying all debts. This is not true. There are two types of debts: dischargeable debts and debts that cannot be discharged.
This;narrative-driven blog will help you explore and understand more about dischargeable debts.
Can Bankruptcy Discharge Be Denied
A court can deny a discharge in Chapter 7 for a number of reasons, including, among others, the debtor’s failure to provide tax documents that have been requested, destruction or concealment of books or records, violation of a court order, or an earlier discharge in an earlier case that began within eight years before the date the second petition was filed, and failure to complete a course on personal financial management. In addition, a creditor, trustee in the case, or U.S. trustee may file an objection to the debtor’s discharge.
A discharge may also be denied in Chapter 13 if the debtor doesn’t complete a course on personal financial management or if they’ve gotten a prior discharge in another Chapter 13 case within two years before the filing of the second case, with a few exceptions. A court may even revoke a discharge under certain circumstances, such as allegations that the debtor obtained the discharge fraudulently or fails to provide documents or information requested in an audit of the case.
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Has Donald Trump Filed For Bankruptsy
How Can The Debtor Obtain Another Copy Of The Discharge Order
If the debtor loses or misplaces the discharge order, another copy can be obtained by contacting the clerk of the bankruptcy court that entered the order. The clerk will charge a fee for searching the court records and there will be additional fees for making and certifying copies. If the case has been closed and archived there will also be a retrieval fee, and obtaining the copy will take longer.
The discharge order may be available electronically. The PACER system provides the public with electronic access to selected case information through a personal computer located in many clerk’s offices. The debtor can also access PACER. Users must set up an account to acquire access to PACER, and must pay a per-page fee to download and copy documents filed electronically.
Student Loans Are Non
Most people know that student loan debt can’t be discharged in bankruptcy. This is true in Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 cases. However, there are some cases where a filer is able to get a bankruptcy discharge for all or part of their student loans. Requirements for such a discharge are very hard to meet. You must prove that paying the student loans will create an undue hardship that prevents you from meeting your basic needs. You must also prove that your current financial situation is expected to continue indefinitely. If you can prove these two requirements, you must also prove you made a good faith effort to repay the non-dischargeable debts. Since many people are behind on their monthly payments when they file for Chapter 7 relief, they are often unable to prove all required elements to get rid of student loans in a bankruptcy case.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Bankruptcy Petition Preparer
Grounds For Denial Of A Debt Discharge
The grounds for denying an individual debtor a discharge in a Chapter 7 case are narrow. They are construed against the moving party .
Among other reasons, the court may deny the debtor a discharge if it finds that the debtor:
- Failed to keep or produce adequate books or financial records
- Failed to explain any loss of assets
- Committed a bankruptcy crime such as perjury
- Failed to obey a lawful order of the bankruptcy court
- Fraudulently transferred, concealed, or destroyed property that would have become the property of the estate
- Failed to complete an approved instructional course concerning financial management