The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code Bill 2021
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Bill, 2021 was introduced in the Lok Sabha to amend the insolvency law and provide for a prepackaged resolution process for stressed Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises.
- The bill will replace the ordinance that was promulgated on April 4 this year. It proposed pre-packs as an insolvency resolution mechanism for MSMEs.
- under this mechanism, main stakeholders such as creditors and shareholders come together to identify a prospective buyer and negotiate instead of a public bidding process.
Shifting Existing Regime Debtor In Possession To A Creditor In Control
In India, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 is one matured step towards settling the legal position with respect to financial failures and insolvency. To provide easy exit with a painless mechanism in cases of insolvency of individuals as well as companies, the code has significant value for all stakeholders including various Government Regulators. Introduction of this Code has done away with overlapping provisions contained in various laws â
- Sick Industrial Companies Act, 1985
- The Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act, 1993
- The Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002
- The Companies Act, 2013.
Before the enactment of this Code, there were multiple agencies dealing with the matters relating to debt, defaults, and insolvency which generally leads to delays, complexities and higher costs in the process of Insolvency resolution. The âBoard for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction â, one of the Insolvency Regulators, has been a phantasm for sick industrial companies. It is expected that the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 will expedite the cases pending for a long time and resolve them within 180 days with a further period of 90 days.
The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code Ordinance 2018
- The Ordinance amends the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 to clarify that allottees under a real estate project should be treated as financial creditors.
- The voting threshold for routine decisions taken by the committee of creditors has been reduced from 75% to 51%. For certain key decisions, this threshold has been reduced to 66%.
- The Ordinance allows the withdrawal of a resolution application submitted to the NCLT under the Code. This decision can be taken with the approval of 90% of the committee of creditors.
Issues with IBC 2016
Parliament has recently passed the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Bill 2019 to resolve a few of the issues:
Indias Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code: An Overview
Abhishek Tripathi and Mani Gupta, Sarthak Advocates & Solicitors
This is an extract from the 2021 edition of GRR’s the Asia-Pacific Restructuring Review. The whole publication is available here.
In summary
This overview contains a summary of the most significant developments in Indian insolvency and bankruptcy law between July 2019 and August 2020, which have had an impact on the design of law and its implementation. Where possible, the legislative changes and the case law surrounding this have been discussed simultaneously to give the reader an understanding of the letter of the law and its interpretation. Some of the trend-setting judgments have been dealt with subsequently, and there is also a small overview of the changes brought about as a result of the covid-19 pandemic. The overview also provides a brief summary of legislative changes in the pipeline, such as group insolvency and cross-border insolvency.
Discussion points
- Amendments to the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code
- Changes related to covid-19
- Is the commercial wisdom of the committee of creditors unassailable in India?
- What steps have been taken to ensure that the corporate debtor has a clean slate?
- What other changes to Indian insolvency law can be expected in the coming year?
Referenced in this article
Introduction
Recent legislative amendments
The 2019 Amendment
These concerns were addressed by the 2019 Amendment as follows:
The First 2020 Amendment
Key regulatory changes
Changes related to covid-19
Reverse Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process

In Flat Buyers Association Winter Hills â 77, Gurgaonv. Umang Realtech Pvt. Ltd through IRP & Ors.,4the ‘Flat Buyers Association of Winter Hills -77, Gurgaon’and the original applicants wanted CorporateInsolvency Resolution Process for resolution but did not wantapproval of any plan of a third party . Insuch circumstances, Uppal Housing Pvt. Ltd. was directed to cooperate with the Interim Resolution Professionaland disburse amount fromoutside as Lender and not as promoter toensure that the project is completed with the time frame given byit. The disbursement of amount which had been made by Uppal HousingPvt. Ltd. and the amount as will be generated from dues of theAllottees during the CIRP was directed to bedeposited in the account of the company to keepthe company a going concern.
Overview Of Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code And Insolvency Process In India
Introduction
This blog meant to provide an overview of the Insolvency Process and some important provisions of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code. The highlight of the Code is the institutional framework it envisions. This framework consists of the regulator insolvency professionals, information utilities and adjudicatory mechanisms . These institutions and structures are aimed at promoting corporate governance and also enable a time bound and formal resolution of insolvency.
The major features of the Code include a two step process -insolvency resolution for corporate debtors where the minimum amount of the default is 1,00,00,000/-.
Two processes are proposed by the Code:
a) Insolvency resolution process In this, the creditors play a crucial role in evaluating and ultimately determining whether the debtors business can be continued and if so, what are the choices for its revival; and
b) Liquidation If revival fails or is not a feasible option, then creditors can resolve to wind up the company. Upon winding up, assets of the debtor are to be distributed.
Important Steps of Insolvency Process:-
Who is Corporate Debtor-
Against whom debt has be unpaid which is more than 1 crore
There are three ways by which Insolvency proceedings can be started against the corporate debtor. The insolvency resolution process under Section 6 can be initiated by the financial creditor , operational creditor or Corporate Debtor himself.
Appellant Provision-
any remaining debts and dues;
What Is Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code 2016
One of the essential business supporting element is a mechanism to settle failed or bankrupt entities without causing damage to any players in the economy. Continuation of financially non-viable businesses leads to locking of funds and physical assets. Similarly, it may lead to stress for the lender who have provided loan to the distressed business entity. For this, a bankruptcy code in the form of set of laws for the resolution of failed entities/individuals is needed.
What is bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy is a financial condition where a firm/individual is unable to repay debts to creditors. Under Indias Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016, a bankrupt entity is a debtor who has been adjudged as bankrupt by an adjudicating authority through passing a bankruptcy order.
Need for Bankruptcy Code
In every economy, there should be a legal procedure accompanied by institutions that collectively can resolve or settle the problems of failed institutions. An early resolution with sound principles will help the related parties like banks not to suffer from the failure of the business entity to whom they have provided a loan. Similarly, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Procedures will help to ensure confidence of banks, foreign investors, associated companies in crisis mitigation mechanism related to business entities in the country.
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016
Features of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016
How insolvency procedures are conducted under the new law?
*********
Preferential Transactions: Interpretation Of Sections 43and 44 Of The Code
The Supreme Court in Anuj Jain, Interim ResolutionProfessional for Jaypee Infratech Limited v. Axis Bank LimitedEtc.,1 set aside the judgmentdated 1st August, 2019 of the Appellate Authority in relation toavoidance of transactions under Sections 43, 45 and 66 of the Code,whereby the corporate debtor had mortgaged its properties forthe financial assistance taken by its holding company . InAnuj Jain, the Supreme Court for thefirst time laid down certain principles in relation to avoidance oftransactions under the Code, which are discussed below:
Prelims Cum Mains Program 2022
Adopt ClearIAS ‘smart work’ approach. Learn fast and focused!
Learn online under expert guidance.
Save your time, effort, and money!
Achievements Of Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code
- Ease of doing business due to the faster insolvency resolution process.
- Deepening of bond markets to increase confidence among the creditors of getting the money back from the debtors.
- Stronger institutional framework such as Insolvency and Bankruptcy board of India , National Company Law Tribunal etc.
- Reduction in Non Performing Assets is one of the biggest achievements of insolvency and bankruptcy code,2016.
- The professionalisation of process with the help resolution professional.
- In 2 years of insolvency and bankruptcy code 2016, 1332 cases have been admitted before the NCLT and 4452 cases have been disposed of at pre-admission stage. This ultimately helped recover and settle around Rs. 2.2 lakh crore.
- 66 cases resolved after adjudication and realisation of creditors around Rs 80,000 crore in resolution cases.
- Helped to resolve and cure 12 big companies like Electrosteel Steels, Bhushan Steel, Monnet Ispat & Energy, Amtek Auto and few companies have been referred for liquidation because nobody came to buy them and a total 260 cases have been ordered for liquidation.
Explained: What Is Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code Bill How Is It Useful
New Delhi, Aug 03: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Bill, 2021 proposes a pre-packaged insolvency resolution mechanism for micro, small and medium enterprises. This Bill, was passed in the Lok Sabha in July.
It can be seen that the bill replaces the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Ordinance, 2021, which was promulgated on April 4, when Parliament was not in session, and amends the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
The proposed amendments will enable the government to notify the threshold of a default not exceeding Rs 1 crore for initiation of the pre-packaged resolution process.
The government has already prescribed the threshold of Rs 10 lakh for this purpose.
The bill proposes a new chapter in the IB Code to facilitate the pre-packaged insolvency resolution process for corporate persons that are Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises .
Insolvency Professional And Agencies
The resolution process for resolving the insolvency is conducted by licensed insolvency professionals. The insolvency professionals are certified members of the agencies. The professionals will manage the entire insolvency process; they will have to manage the assets of the debtor and provide the information so that the creditors can make a decision on the matter.
The insolvency professionals are registered with the agencies which certify the professionals helping in the entire insolvency process after examination and enforcing a code of conduct upon the professionals.
Surendra Trading Company V Juggilal Kamlapat Jute Mills Company Limited & Ors

The Supreme Court took the view that there could be weighty, valid and justifiable reasons for not being able to remove the defects within seven days and the said stipulation was directory in nature, and that an insolvency application could be entertained even when the applicant had overshot the seven day period prescription, provided that the petitioner was able to show sufficient cause for the delay.
Explained: Aimed At Small Firms What Is Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code Bill 2021
New Delhi, July 28: Even as Opposition MPs continued to protest, the Lok Sabha passed the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Bill 2021 on Wednesday. Moving the bill in the House, the Minister of State for Corporate Affairs, Rao Inderjit Singh has said that the Bill replaces then Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Ordinance 2021 which was promulgated on 4th April this year.
He said that it amends the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016. The Minister said that amendment is necessary to ease the difficulties faced by the small scale industries. He said that during the last four years of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, the ease of business increased.
He said that the period for recovery has been reduced to 1.6 years now from earlier 4.3 years. As the opposition members were in the Well of the House, the Bill was passed without any discussion.
So what is Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Ordinance, 2021?
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Ordinance, 2021 was promulgated on April 4, 2021. It amends the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016. Insolvency is a situation where individuals or companies are unable to repay their outstanding debt.
Minimum default amount: Application for initiating PIRP may be filed in the event of a default of at least one lakh rupees. The central government may increase the threshold of minimum default up to one crore rupees through a notification.
The Ultimate Guide To Understanding The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code
MridusmitaEconomyria ExplainerIndian EconomyMay 3, 2020
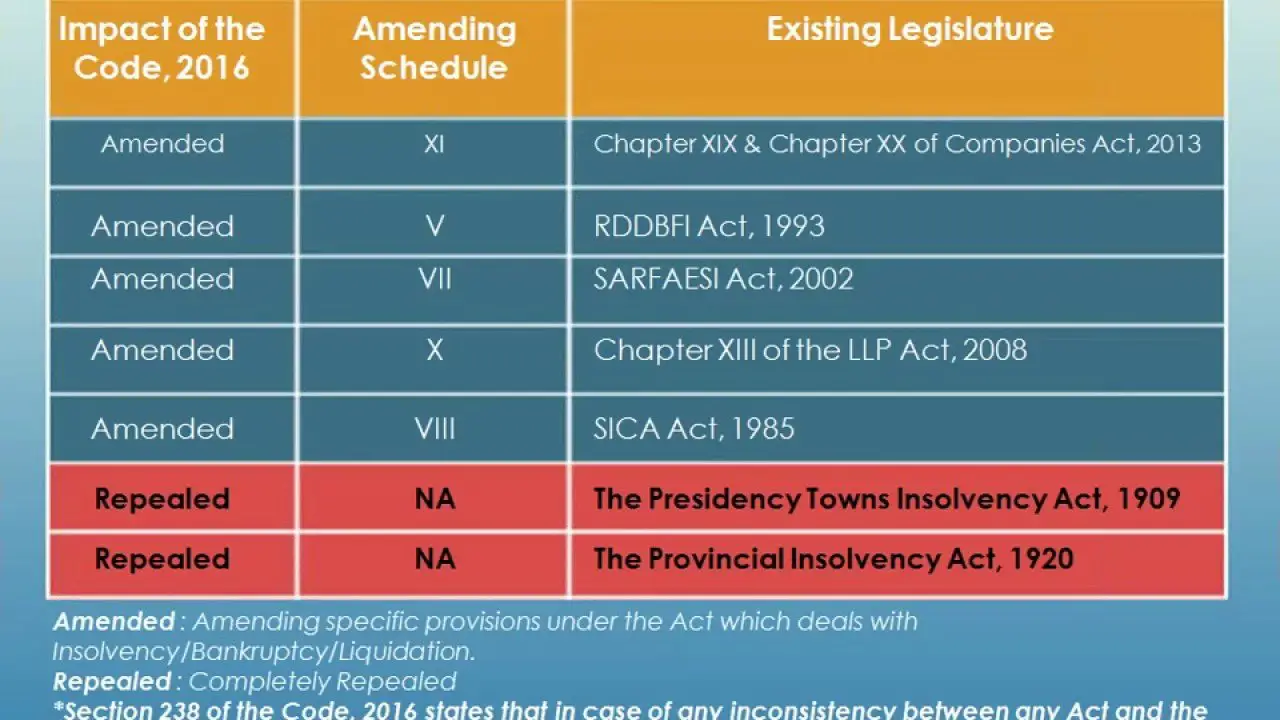
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code was passed on 11th May 2016. It was done to consolidate all the existing laws related to insolvency in India and to simplify the process of insolvency resolution.
What is the need for Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code in India?
There was no single law dealing with insolvency and bankruptcy in India. The liquidation of companies and individuals were handled under various Acts . Some of them were:
- Presidency Towns Insolvency Act, 1909
- The Provincial Insolvency Act, 1920
- Sick Industrial Companies Act
- The Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002
- Companies Act 2013
- Recovery of debts due to banks and financial Institutions Act
It led to an overlapping jurisdiction of different authorities like High Court, Company Law Board, Board for industrial and financial reconstruction and Debt recovery tribunal.
This overlapping jurisdictions and multiplicity of laws made the process of insolvency resolution very cumbersome in India.
Nearly 60,000 bankruptcy cases are pending in Indias courts. As per the World Bank data, it takes an average 4.3 years to wind up a company in India. It is easier to start a business than to exit it.
The new Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code seeks to cut it to 1 year.
Also, the recovery of the debt under is just 25.7 cents on the dollar in India.
What are the salient features of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code?
Indian Parliament Passes The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code 2016
June 8, 2016
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 has been notified in the official gazette on May 28, 2016. The Code completely overhauls laws governing insolvency in India and is a major initiative of the government towards improving the ease of doing business in the country.
The Code applies to companies, partnerships, limited liability partnerships and individuals. The Code replaces the existing insolvency framework which was confusing and fraught with substantial delays. This note highlights the key provisions of the Code as applicable to corporate debtors,i.e., companies and limited liability partnerships .
Insolvency proceedings against a Debtor commence with a resolution process that seeks to resolve the insolvency of a Debtor as a going concern by formulating a resolution plan. In case this process fails to achieve a resolution, the Debtor is subjected to liquidation proceedings to settle pending claims against it. These aspects of the Code are discussed below:
What Is Insolvency Bankruptcy Code Bill 2021
Introduction
Recently, Insolvency Bankruptcy Code Bill, 2021 was passed by the Lok Sabha and currently it is pending in Rajya Sabha. The Bill introduced by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman will replace the ordinance that was promulgated on 4th April to provide relief for micro, small, medium enterprises adversely impacted by the pandemic.
The new Bill seeks to amend the Code of 2016. The Bill proposes a pre-packaged resolution process for stressed micro, small, medium enterprises .
Further, the Bill also provides a penalty for fraudulent or malicious initiation of the pre-packaged insolvency resolution process. It also provides punishment for the same.
Thus, this article tries to explain the new amendments put forth in the bill.
What are Insolvency and Bankruptcy?
Insolvency is a situation where an individual or a company can no longer meet their financial obligations i.e., unable to pay debts. It can be also called a state of financial distress where a person is not able to pay his debts or in a simpler way his liabilities are more than his assets.
Bankruptcy is the legal declaration of ones inability to pay debts. There are two types of bankruptcy-
- Reorganization: In this case, the debtors make a plan of payment structure to make paying off debts easier.
- Liquidation: It is a case where debtors have to sell certain assets to repay their debts.
What is the history of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code?
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016
- Minimum amount of default
The Right Measure To Evaluate The Ibc Is Not The Yardstick Of What Happened Under Sica Or Drt Laws But What Is Happening Now A 270
It is one of the tragedies of India that sooner than later, even the best of legislation is allowed to decay into irrelevance, thanks to endless litigation.
In the 1980s, we had the Board for Financial and Industrial Reconstruction and the Sick Industrial Companies Act . Repeated resorts to courts ensured that both were rendered useless in either reviving sick companies or closing them down to recover value from assets.
Then we had the Debt Recovery Tribunals of the early 1990s. They too failed to solve the problem of hastening the recovery of assets from moribund or failing companies. In fact, the courts, through various judgements, introduced more complications in the earlier resolution laws by giving some categories of creditors precedence over banks with valid collateral. In another judgement the same year , the Supreme Court decided on the overlaps between the SICA and DRT laws by giving the former precedence, which meant reviving units had to take priority over loan recoveries.
Also read:
Now, we have the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code , which is less than three years old, but increasingly shows signs of wear and tear. The last two years of IBC-related litigation have shown that we are capable of ruining the best of legislation by allowing court processes to drag on endlessly when the whole purpose of the IBC was quick resolution of bad debts.
Also read:
Also read:
This article first appeared on Swarajya Magazine.
Key Objectives Of The Code
The sole intention of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 is to provide a justified balance between-
- an interest of all the stakeholders of the company, so that they enjoy the availability of credit
- the loss that a creditor might have to bear on account of default
The objective behind Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 are listed below-
Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code Explained : What Is Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code
What is the insolvency and bankruptcy code? This law passed in the parliament in 2016 that deals with insolvency resolution. This means that it gives companies and people to resolve their insolvency and clearing off any debts.
What does it do? It protects one from creditors taking control over their assets. When an issue in repayment arises, the creditor can take control over the debtors assets and resolve the insolvency by selling the assets or using them as theirs. This code gives them immunity against any action taken by creditors and also creates a common legally bound forum for both parties to deal with the issues at hand.
Breaking the Code Down
The code sets down methods to solve insolvency and how to go about it.
1). For Corporate debtors
For corporate debtors to resolve insolvency the default amount has to at least be INR 1,00,000 and the code suggests two stages to deal with this.
First stage Insolvency Resolution Process, in which financial creditors evaluate the debtors business whether it can be saved or not.
The second stage is Liquidation in which the creditors start to convert all assets into cash. This will happen if the first stage fails.
For Individuals or Unlimited Partnerships
The code is applicable when the default amount is at least INR 1000 and above. The government suggests two methods for them too.
Nclt Has Jurisdiction To Enquire Into Allegations Of Fraudbut It Is Not Vested With The Power Of Judicial Review Overadministrative Action
In M/s Embassy Property Developments Pvt. Ltd v. State ofKarnataka & Ors.,6 the Apex Court mainly dealtwith two issues:
While answering the second issue, the Supreme Court whilstreferring to Section 65 of the Code observed thatif, as contended by the Government of Karnataka, the CIRP had beeninitiated by one and the same person taking different avatars, notfor the genuine purpose of resolution of insolvency or liquidation,but for the collateral purpose of cornering the mine and the mininglease, the same would fall squarely within the mischief addressedby Section 65. It was thus held that the NCLT has jurisdictionto enquire into allegations of fraud. As a corollary, NCLAT willalso have jurisdiction. Hence, fraudulent initiation of CIRP cannotbe a ground to bypass the alternative remedy of appeal provided inSection 61.
Provisions Of The Bill:
- It specifies a minimum threshold of not more than Rs 1 crore for initiating the pre-packaged insolvency resolution process
- It provides for disposal of simultaneous applications for initiation of the insolvency resolution process and pre-packaged insolvency resolution process, pending against the same corporate debtor.
- Penalty for fraudulent or malicious initiation of pre-packaged insolvency resolution process or with intent to defraud persons, and for fraudulent management of the corporate debtor during the process.
- Punishment for offences related to the pre-packaged insolvency resolution process.
What Are Insolvency And Bankruptcy
Insolvency is the situation where the debtor is not in a position to pay back the creditor. For a corporate firm, the signs of this could be a slow-down in sales, missing of payment deadlines etc. Bankruptcy is the legal declaration of Insolvency. So the former is a financial condition and latter is a legal position. All insolvencies need not lead to bankruptcy. The new code has a sequential procedure of Insolvency resolution, failing which, it leads to Bankruptcy .