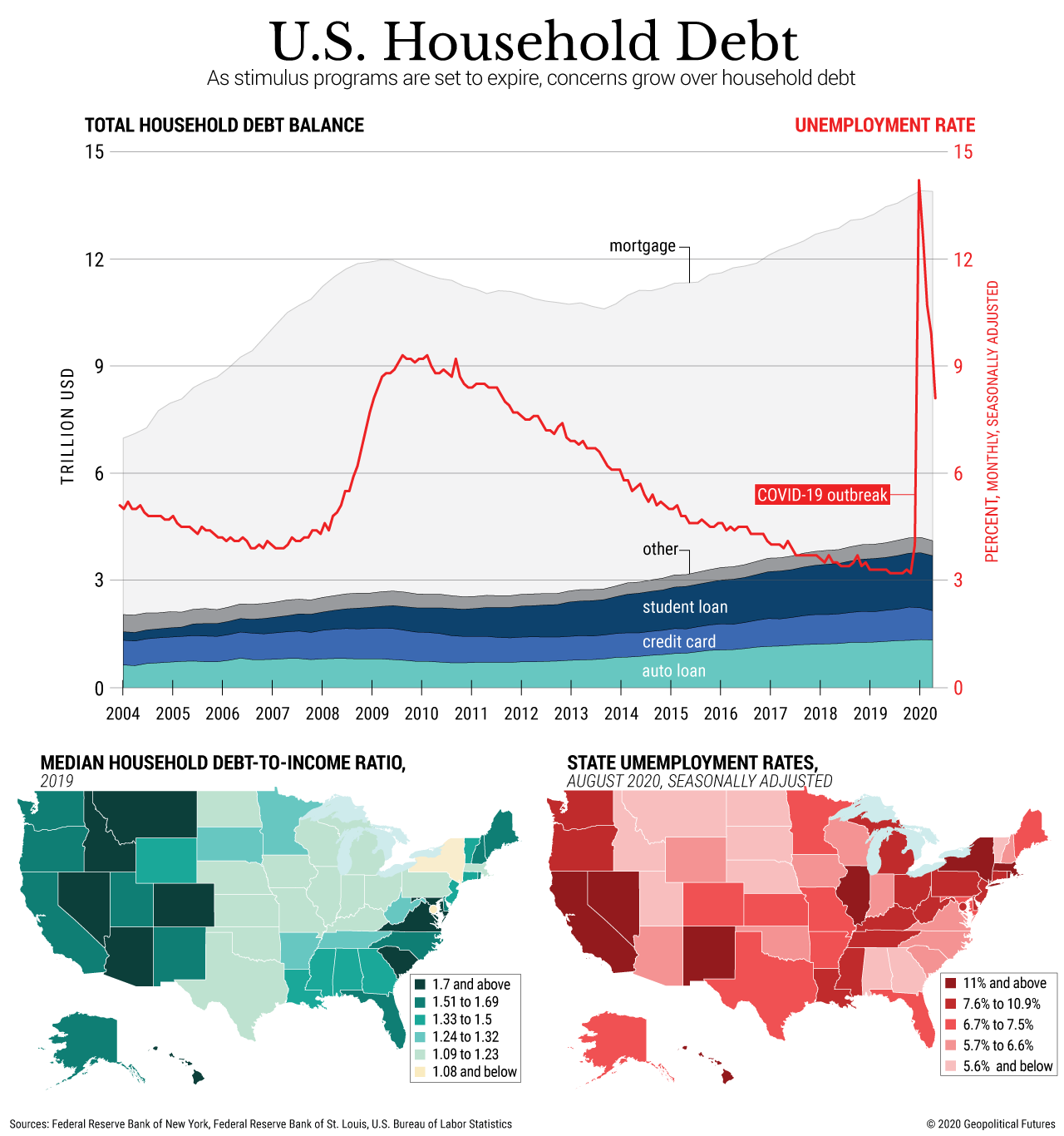
What Percentage Of Americans Are In Debt
Just how many Americans are in debt? According to financial experts, the percentage of Americans in debt is around 80%. 8 in 10 Americans have some form of consumer debt, and the average debt in America is $38,000 not including mortgage debt. Owing money just seems to be a way of life for Americans, as collectively we have $14 trillion in debt. That amount is climbing ever higher. Consumer debt can be broken up into 4 main categories: mortgage debt, auto loans, student loans, and credit card debt. Unpaid medical bills and expensive medical costs are quickly contributing to debt that Americans currently carry.
Interest And Debt Service Costs
Despite rising debt levels, interest costs have remained at approximately 2008 levels because of lower than long-term interest rates paid on government debt in recent years. The federal debt at the end of the 2018/19 fiscal year was $22.7 trillion. The portion that is held by the public was $16.8 trillion. Neither figure includes approximately $2.5 trillion owed to the government. Interest on the debt was $404 billion.
The cost of servicing the U.S. national debt can be measured in various ways. The CBO analyzes net interest as a percentage of GDP, with a higher percentage indicating a higher interest payment burden. During 2015, this was 1.3% GDP, close to the record low 1.2% of the 19661968 era. The average from 1966 to 2015 was 2.0% of GDP. However, the CBO estimated in 2016 that the interest amounts and % GDP will increase significantly over the following decade as both interest rates and debt levels rise: “Interest payments on that debt represent a large and rapidly growing expense of the federal government. CBO’s baseline shows net interest payments more than tripling under current law, climbing from $231 billion in 2014, or 1.3% of GDP, to $799 billion in 2024, or 3.0% of GDPthe highest ratio since 1996.”
According to a study by the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget , the U.S. government will spend more on servicing their debts than they do for their national defense budget by 2024.
Coronavirus And The National Debt
The U.S. government has taken efforts to offset the effects of worldwide health pandemic by borrowing money to invest in individuals, businesses, and state and local governments. Of these responses, the CARES Act has been the largest stimulus package in U.S. history. This stimulus package included $2.3 trillion towards relief for large corporations, small businesses, individuals, state and local governments, public health, and education. In order to pay for the relief fund, the government needed to expand its debt to do so, the government borrowed money from investors through the sales of U.S. government bonds.
Also Check: What Do You Lose When You File For Bankruptcy
How Did The Debt Get Where It Is Today
More on:
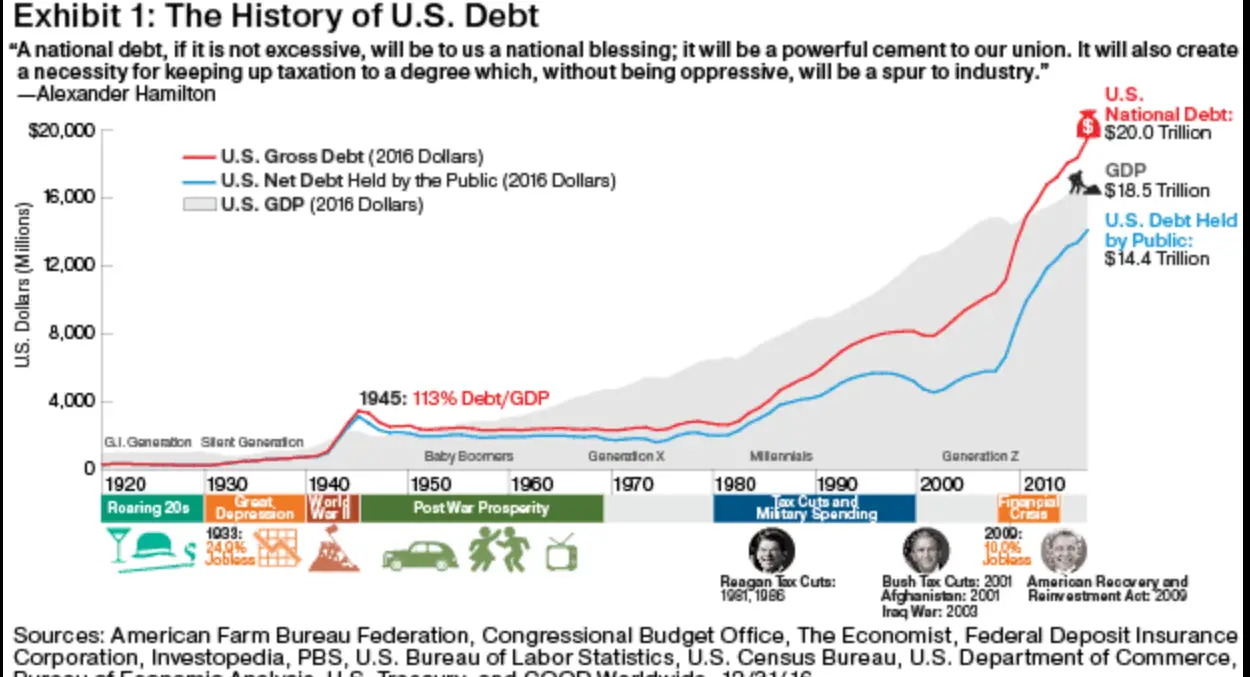
The United States has run annual deficitsspending more than the Treasury collectsalmost every year since the nations founding. The period since World War II, during which the United States emerged as a global superpower, is a good starting point from which to examine modern debt levels. Defense spending during the war led to unprecedented borrowing, with the debt skyrocketing to more than 100 percent of gross domestic product in 1946.
The Federal Debt Ceiling
The federal debt ceiling is the legal amount of federal debt that the government can accumulate or borrow to fund its programs and pay for fees such as the national debt interest. Since its creation through the Second Liberty Bond Act in 1917, the debt ceiling has grown about 100 times. These instances have included permanent raises, temporary extensions, and revisions to what the debt limit can be defined as. When the debt ceiling isnt raised, the federal government is unable to issue Treasury bills and must rely solely on tax revenues to pay for its programs this has occurred 7 times since 2013.
Recommended Reading: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Credit
What Will Happen To Our National Debt
U.S. spending is currently at an all-time high to combat the effects of COVID-19. The current level of debt-to-GDP is comparable to the period immediately after World War II. Despite the effort to reduce the national debt, it is apparent and crucial for the government to take on the debt during times of crisis. Being able to adequately and successfully respond to emergencies is one of the many reasons why the national debt should be reduced governments should respond to events in an appropriate and timely manner with its citizens in thought.
Who Are The Holders Of Public Debt
Other holders of the public debt include insurance companies, U.S. savings bonds, private pension funds, and other holders, including individuals, government-sponsored enterprises, brokers and dealers, banks, bank personal trusts and estates, corporate and non-corporate businesses, and other investors. 3
Also Check: How To Get Out Of Credit Card Debt Without Bankruptcy
What Is The Current National Debt
As of June 23, 2022, the total U.S. national debt was $30.4 trillion, after crossing the $30 trillion mark for the first time in February. At the end of 2019, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the national debt was $23 trillion. One year later, it had risen to $27.7 trillion. Since then, it has increased by more than $2 trillion.
A Brief History Of Us Debt
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
Nearly all national governments borrow money. The U.S. has carried national debt throughout its history, dating back to the borrowing that financed the Revolutionary War. Since then the debt has grown alongside the economy, as a result of increased government responsibilities, and in response to economic developments.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Bankruptcy Stay On Credit Report In Australia
Another Hot Topic For El Salvador: Bitcoin
In September 2021, El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt bitcoin as legal tender. This means that Bitcoin is recognized by law as a means to settle debts and other obligations.
The International Monetary Fund criticized this decision in early 2022, urging the country to revoke legal tender status. In hindsight, these warnings were wise, as Bitcoins value has fallen by 56% year-to-date.
While this isnt directly related to El Salvadors default risk, it does open potential avenues for relief. For instance, large players in the crypto space may be willing to assist the government to keep the concept of nation-state bitcoin adoption alive.
States With The Most Debt
1. New York
New York has the highest debt of any state, with total debt of over $203.77 billion. New York’s total assets are around $106.61 billion, giving the state a debt ratio of 273.8%. The main culprit for New York’s towering debt is overspending on Medicaid. New York has attempted to fill budget gaps by cutting school aid and health care costs in recent years.
2. New Jersey
New Jersey has the second-highest amount of debt in the country. The state’s total liabilities total $222.27 billion, surpassing its assets by $198.67 billion. New Jersey’s debt ratio is 441.7%. The largest source of debt is the state’s unfunded pension and benefits system for public employees. New Jersey legislators are looking toward tax increases because of the state’s debt and the growing pressure to fund other priorities such as infrastructure and education.
3. Illinois
Illinois has the third-highest debt in the U.S., with total liabilities equaling $248.67. With total assets of $53.05 billion, Illinois has $187.7 billion in unfunded liability. This creates a debt ratio of 468.7%, the largest in the U.S. To pay that off, every person in Illinois’s 12.7 million population would need to pay $14,780. Like New Jersey, the biggest problem in Illinois contributing to the debt is billions of dollars for retired government workers’ pensions and health insurance benefits.
4. Massachusetts
5. California
Don’t Miss: How Does Bankruptcy Affect The Economy
Debt By Year Compared To Nominal Gdp And Events
In the table below, the national debt is compared to GDP and influential events since 1929. The debt and GDP are given as of the end of the fourth quarter in each year to coincide with the end of the fiscal year. That’s the best way to accurately determine how spending in each fiscal year contributes to the debt and compare it to economic growth.
From 1947-1976, debt and GDP are given at the end of the second quarter since, during that time, the fiscal year ended on June 30. For years 1929 through 1946, debt is reported at the end of the second quarter, while GDP is reported annually, since quarterly figures are not available.
At the end of the fourth quarter in 2021, the national debt was about $29.6 trillion. Based on the fourth-quarter GDP of $23.9 trillion, the debt-to-GDP ratio was about 124%.
| End of Fiscal Year |
|---|
| COVID-19 and American Rescue Plan Act |
United States Total Debt: % Of Gdp

Key information about United States Total Debt: % of GDP
- United States Total Debt accounted for 810.2 % of the country’s GDP in 2022, compared with the ratio of 820.1 % in the previous quarter.
- US Total Debt: % of GDP data is updated quarterly, available from Dec 1951 to Mar 2022.
- The data reached an all-time high of 856.1 % in Mar 2021 and a record low of 291.9 % in Mar 1952.
View United States’s Total Debt: % of GDP from Dec 1951 to Mar 2022 in the chart:
Also Check: What Happens When You Declare Bankruptcy In Quebec
How The National Debt Has Changed Under Trump
The national debt over the nationâs history has grown from a modest $83.7 million under George Washington to a whopping $23.3 trillion today.
But the debt has had some significant spikes for some very important reasons, and there was a brief period of time, one year to be exact, where the debt was entirely paid off.
In 1835, Andrew Jackson paid off the national debt through severe cost-cutting and land sell-offs. Jacksonâs distrust of banks led him to redistribute funds to the states, which in turn caused an economic bubble, which led to recession. Restarting the national debt to reinvigorate the economy was inevitable.
World War I led to the debt increasing by more than $21 billion to a total of $24 billion. Two decades later, Franklin Delano Roosevelt would see the national debt rise from $22 billion to over $205 billion dollars, largely due to World War II. The Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan added $2.1 trillion to the debt just in George W. Bushâs administration alone. US Debt by President: By Dollar and Percentage Both Bush and Obama had massive stimulus packages to fight the 2008 recession that each added hundreds of billions to the national debt.
Coronavirus Lockdown & Unemployment
But by far, one of the most significant impacts on the national debt occurred very recently during Donald Trumpâs administration. President Trump inherited a rising economy which continued to rise through the last two and a half years. The Dow reached 20,000, more than 140,000 jobs were added to the economy, and low unemployment persisted.
Then in February 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic, which had already caused economic havoc in China and Europe, reached the United States.
A highly contagious disease, COVID-19 could not only kill the very old, very young, and very sick, it could also be spread by carriers not displaying any symptoms who were completely unaware that they had it. And, it could live for hours in the air and up to days on surfaces. Faced with what was deemed an âinvisible enemy,â governors across the US ordered schools and non-essential businesses closed, and citizens to self-isolate, telling them to leave their homes only for essential supplies and only when absolutely necessary.
Needless to say, the economic impacts of these decisions were staggering. The eight largest drops in the Dow Jones Industrial Average were recorded during this period. 26 million people had filed for unemployment benefits by late March . And, Congress passed multiple large stimulus bills to assist individuals, families, and businesses.
Also Check: When Can Bankruptcy Be Removed From Credit Report
Less To Spend On Other Government Initiatives
The more money the U.S. has to spend on meeting its debt obligations as interest rates increase, the less financial capacity it could have to fund programs focused on education, veterans benefits and transportation.
This breakdown of the 2019 Federal Budget from the Council on Foreign Relations shows how the budget pie is only so big, so when one area increases , another must decrease.
President Andrew Jackson Cuts Debt To Zero
The War of 1812 more than doubled the nations debt. It increased from $45.2 million to $119.2 million by September 1815. The Treasury Department issued bonds to pay a portion of the debt, but it was not until Andrew Jackson became president and determined to master the debt that this national curse, as he deemed it, was addressed.
The time of prosperity was short-lived, as state banks began printing money and offering easy credit, and land value dropped.
Recommended Reading: How To File Bankruptcy In Oklahoma
How Much Of The Us Debt Is Owned By The Public
As of August 31, 2020, federal debt held by the public was $20.83 trillion and intragovernmental holdings were $5.88 trillion, for a total national debt of $26.70 trillion. At the end of 2020, debt held by the public was approximately 99.3% of GDP, and approximately 37% of this public debt was owned by foreigners.
Debt held by the public such as Treasury securities held by investors outside the federal government, including those held by individuals, corporations, the Federal Reserve, and foreign, state and local governments.
Content
Solutions To Reduce The National Debt
76% of voters believe that the President and Congress should allocate more time and energy towards addressing the national debt. Americans care about the national debt, and some work has been done in order to address this issue. Solutions include raising revenue , cutting spending, and growing the countrys GDP.
Policy options such as the Simpson-Bowles plan and the Domenici-Rivlin Task Force have made efforts to create plans to reduce the national debt. Centers and institutes such as the American Enterprise Institute, Bipartisan Policy Center, Center for American Progress, and Economic Policy Institute all proposed things ranging from slow growth to reduction in benefits for high-income individuals.
Young people across America are getting educated about fiscal policy and making changes at their colleges and universities with Up to Us. Sign the pledge to let local representatives know that you are concerned about the nations fiscal future, or get involved by learning about how you can make a difference in your own community.
You May Like: Foreclosed House For Sale
Domestic Social Programs And The Military
In order to make an impact on a huge and ever-increasing amount of money like the national debt, you have to cut into the largest spending programs. The largest of these programs are mandatory obligations made by previous acts of Congress.
One of the biggest, Social Security, is on that list.
For fiscal year 2021, Social Security benefits cost $1 trillion a year, Medicare, $722 billion, and Medicaid costs $448 billion. The interest alone on the national debt is $378 billion. These together total $3.3 trillion. Eliminating that entire sum will only have the tiniest of impacts on the national debt.
Outside of domestic social programs, the spending on the military makes the spending on any individual social program look tiny by comparison. If you want to have any impact on the debt, military spending must also be cut.
Trump increased military spending in fiscal year 2021 to $934 billion. US Military Budget, Its Components, Challenges, and Growth This figure includes the $636 billion base budget for the Department of Defense, $69 billion in overseas contingency operations for the fight against the Islamic State, and $228 billion to fund the other agencies that protect the U.S. and service the military.
This includes some expenditures you probably had no idea were part of the Defense Department budget.
They include:
Key Dates In Trumps Trade War With China The Trouble With Tariffs Is Unintended Consequences Https: //wwwbarronscom/articles/trump
Trumpâs trade war with China produced several new trade agreements both with China and other nations, but at what cost?
In August of 2019, the Congressional Budget Office reported their estimates of the U.S. economic impact of tariffs . Congressional Budget Office: The Effects of Tariffs and Trade Barriers in CBOâs Projections
In this estimate, the CBO projected that by 2020, tariffs would:
- Reduce the U.S. GDP by 0.3 percent
- Reduce real consumption by 0.3 percent
- Reduce real private investment by 1.3 percent
- Reduce real income by $580 per household.
- U.S. exports would be 1.7 percent lower and imports would be 2.6 percent lower
This is economistsâ arguments against tariffs coming to fruition. Tariffs affect economic activity in three ways:
- Consumer goods become more expensive
- Business uncertainty increases, which slows investment
- Other countries follow by imposing retaliatory tariffs, which makes US exports more expensive.
Also Check: Where Do You File For Bankruptcy
Debt Grows Into The Trillions During 1980s And 1990s
At the start of the 1980s, an increase in defense spending and substantial tax cuts continued to balloon the federal debt. The national debt at the end of the Ronald Reagan era was $2.7 trillion.
The era under President Bill Clinton was marked with tax increases, reductions in defense spending and an economic boom that reduced the growth of debt, but it still reached a staggering $5.6 trillion by 2000.