Is Any Protection And/or Priority Afforded To The Providers Of New Money In The Context Of Restructuring Proceedings
The court may allow the court officer to lend new money required for the operation of the company.
The court may also allow for charges to be established over the company’s assets that may be ranked inferior, equal or even in priority to existing charges, in order to enable the receipt of new credit which is essential for the company’s operation.
The creation of such charges is subject to the court’s approval and to proper protection’ of the existing secured creditors. This proper protection’ means that the value of the debt secured by the charge must be preserved. The value of debt relates to the sum that would have been repaid from the sale of the charged asset independently from the recovery process that is, the reference point is not the original value, but the expected current realisation value.
The repayment of any such new credit shall be treated as recovery expenses and therefore as a priority claim, unless otherwise determined by the court.
Despite the favourable terms allowing the court officer to obtain this credit, we are not aware to any actual substantial use of this provision in practice.
How Can Those Security Interests Be Enforced
Self-foreclosure of collateral is permitted under Israeli law only in very limited circumstances by Israeli banks or financial institutions, and only with respect to certain tangible assets and traded securities deposited with such institutions.
Any other foreclosure of collateral will be reported and supervised by the court, execution office or court officer, depending on the type of proceedings.
Generally, where the value of the collateral is lower than the secured debt, the court will abstain from involvement and the creditor may foreclose the pledged asset. Where the value of the collateral exceeds the debt, the foreclosure process will be performed by a court officer in order to protect the residual value of the collateral for example, where the creditor holds a fire sale’ that may result in lower values.
In liquidation proceedings, a creditor is generally entitled to foreclose its pledge independently from the insolvency proceedings, subject to the provision of appropriate notice to the debtor trustee or the liquidation court, and subject to certain rights of redemption of the collateral granted to the debtor/trustee.
In recovery and reorganisation proceedings, a stay order prevents a secured creditor from foreclosing on its pledge instead, it must apply to the court in order to seek approval to foreclose on an asset charged in its favour. The court shall permit foreclosure if:
Alternatives To Chapter 7
Debtors should be aware that there are several alternatives to chapter 7 relief. For example, debtors who are engaged in business, including corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships, may prefer to remain in business and avoid liquidation. Such debtors should consider filing a petition under chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code. Under chapter 11, the debtor may seek an adjustment of debts, either by reducing the debt or by extending the time for repayment, or may seek a more comprehensive reorganization. Sole proprietorships may also be eligible for relief under chapter 13 of the Bankruptcy Code.
In addition, individual debtors who have regular income may seek an adjustment of debts under chapter 13 of the Bankruptcy Code. A particular advantage of chapter 13 is that it provides individual debtors with an opportunity to save their homes from foreclosure by allowing them to “catch up” past due payments through a payment plan. Moreover, the court may dismiss a chapter 7 case filed by an individual whose debts are primarily consumer rather than business debts if the court finds that the granting of relief would be an abuse of chapter 7. 11 U.S.C. § 707.
Debtors should also be aware that out-of-court agreements with creditors or debt counseling services may provide an alternative to a bankruptcy filing.
You May Like: Can Bankruptcy Clear A Judgement
Disposition Of Debtors Property
As a general rule, after the proceedings initiation, the procedure of disposition of the debtors property and moratorium on the satisfaction of creditors claims are introduced. This procedure may be called a transition because, on the one hand, the debtor continues to perform economic activity, on the other hand, a moratorium is valid and there are restrictions on the debtors property operations. The main goal is to examine the debtors property and determine the possibility of restoring the debtors solvency. Furthermore, the aim is to protect the creditors interests for which purpose this moratorium is introduced. During the disposition of debtors property procedure, the debtor shall be prohibited to satisfy the creditors claims, except for post-bankruptcy creditors and salary payments.
To determine the debtors amount outstanding, the announcement of the bankruptcy initiation shall be published on the website of the Ukrainian judiciary. Within 30 days after the publication, creditors should contact the competent commercial court, having initiated the proceedings with creditor claims against the debtor. Upon reviewing these applications, a registry of creditors of the debtor shall be drawn up, which is the basic document for determining due amounts and the number of votes of each creditor.
The procedure of disposition of the debtors property may not exceed 170 calendar days.
Dischargeability Of A Debt
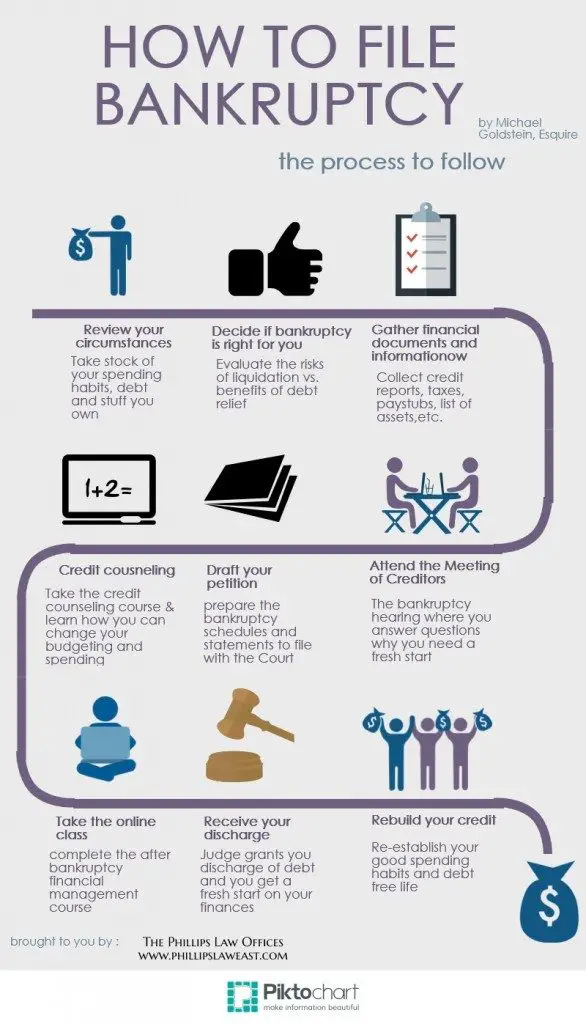
Discharging debts is one of the benefits of filing for bankruptcy. While many debts are dischargeable, some are not. In addition, the U.S. Bankruptcy Code provides that a creditor can challenge the dischargeability of a debt in specific circumstances.
Filing a non-dischargeability action constitutes an adversary proceeding within the bankruptcy case. Generally, a debt incurred through actual or constructive fraud of the debtor can be the subject of a non-dischargeability action. Additional information about non-dischargeability actions is available in our article, When Can a Creditor Challenge the Dischargeability of a Debt in Bankruptcy Litigation?
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Has Trump Declared Bankruptcy
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy 101
Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceedings are normally used by struggling businesses as a way to get their affairs in order and pay off their debts.
In addition, some individuals also file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy when they are not eligible for Chapter 13 bankruptcy or own large amounts of non-exempt property . However, Chapter 11 can be much more expensive and time-consuming when compared to Chapter 13.
Are Informal Workouts Available In Your Jurisdiction If So What Forms Do They Typically Take And What Are The Benefits And Drawbacks As Compared To Formal Restructuring Proceedings
Unfortunately, Luxembourg law has no express framework for informal out-of-court restructuring. That being said, there is nothing to prevent a company from seeking contractual arrangements with its creditors to the same effect. Most informal workouts involving Luxembourg entities or instruments are governed by foreign law.
Read Also: Bankruptcy Lawyer Software
What Is The Process For Filing Claims In The Insolvency Proceedings
Once bankruptcy proceedings have commenced, any individual legal actions against the debtor whether initiated by secured or unsecured creditors are suspended and the creditors must file proof of claim with the court. That said, bankruptcy proof’ secured creditors are not affected by the bankruptcy filing, and may act freely in relation to their security/mortgage and take any enforcement action irrespective of the bankruptcy proceedings.
Some Debtors Lose Little Property If Any
Chapter 7 liquidation bankruptcy is meant for low-income filers who don’t have sufficient income to repay creditors. By contrast, Chapter 13 reorganization bankruptcy provides income earners a way to repay creditors an affordable amount over time.
In many cases, Chapter 7 filers have little property to relinquish. They’ve often already converted any nonexempt property in an attempt to avoid bankruptcy. For instance, luxury items like boats or recreational vehicles are usually sold and the proceeds used for necessary living expenses before filing.
One exception is home equity, however. With home values on the rise, some filers find that the homestead exemption doesn’t cover all of the equity in their house. In that case, the trustee would sell the home, pay off any mortgages, return the exempt portion to the homeowner, and distribute any remaining funds to creditors.
Also Check: How Many Bankruptcies For Donald Trump
Are There Several Types Of Creditors And What Is The Effect Of A Difference
The Bankruptcy Code classifies creditors into categories depending on the type of claims and the existence of collateral. There are three types of creditors:
- secured creditors creditors whose claims are secured by the debtors property or any other security interest
- unsecured creditors creditors whose claims arose before the opening of insolvency proceedings, fulfilment of which is not secured by the debtors property or any other security interest
- current creditors creditors whose claims arose after the commencement of insolvency proceedings.
Based on the category of creditors, the sequence of fulfilment of their claims in the course of insolvency proceedings differs.
Secured creditors
Secured creditors claims should be satisfied outside the priority sequence from the proceeds of the property used to secure those debts.
Unsecured creditors
Unsecured creditors claims should be fulfilled only after inter alia the discharge of different social payments, compensation for death or injury caused to individuals and tax payments.
Current creditors
Assets Subject To Liquidation Proceedings
One of the most important aspects of bankruptcy legislation is the determination of the assets to be seized and sold for the purpose of distributing the proceeds among the creditors. Various legal systems have vastly different approaches. The disparities relate mainly to the status of assets acquired by the bankrupt subsequent to his adjudication or conveyed away by him prior to that date.
In the majority of civil-law countries that follow the traditional French model, the bankrupt estate likewise includes all nonexempt property owned by the debtor at the date of the adjudication and all property acquired during the course of the proceedings until the close of the case or the rehabilitation of the debtor. Subject to variations in details, laws of that type operate in, for example, Argentina, Austria, Brazil, Italy, Portugal, Spain, and Switzerland. Some of these laws make special exceptions for future earnings to the extent that they are necessary for the debtors maintenance. The 1985 French law on economic rehabilitation and liquidation also includes in the bankrupt estate all property acquired on whatever grounds until the close of the proceedings. With the exception of Austria, Italy, and Switzerland, the countries listed above retract the effective date of adjudication to the date of the cessation of payments.
Don’t Miss: How To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
Ies To The Bankruptcy
The following persons may become a debtor in bankruptcy proceedings:
- a legal entity,
- an individual entrepreneur or an individual.
Moreover, the procedures for legal entities and individuals significantly differ from each other.
The parties to the bankruptcy cases proceedings are the following: parties, an insolvency officer, the state body for bankruptcy, the State Property Fund of Ukraine, local authorities representatives, representatives of debtors employees, an authorized person of debtors founders , and in some cases, other parties to the bankruptcy proceedings whose rights and obligations are the dispute subject matter.
The parties to the bankruptcy proceedings are the bankruptcy creditors , secured creditors and the debtor .
Common Types Of Adversary Proceedings In Bankruptcy Cases

In some bankruptcy cases, issues arise that require a bankruptcy court proceeding separate from the bankruptcy itself. These actions, called adversary proceedings, are a type of bankruptcy litigation. They take place as an independent legal action within the bankruptcy case. While there are a number of different kinds of bankruptcy litigation, there are some common types of adversary proceedings in bankruptcy cases.
Also Check: Epiq Bankruptcy Solutions Beaverton Oregon
What Are The Insolvency Proceedings In Luxembourg
Insolvency proceedings in Luxembourg include controlled management , suspension of payments , composition with creditors , and procedures intended to realise the assets of the debtor and to discharge the liabilities: bankruptcy and compulsory liquidation.
Bankruptcy is the most common type of insolvency proceeding in Luxembourg. A commercial company is considered bankrupt if it can no longer pay its debts as they fall due and if it may no longer raise credit. These two conditions must be met cumulatively.
The Single Asset Real Estate Debtor
Single asset real estate debtors are subject to special provisions of the Bankruptcy Code. The term “single asset real estate” is defined as “a single property or project, other than residential real property with fewer than four residential units, which generates substantially all of the gross income of a debtor who is not a family farmer and on which no substantial business is being conducted by a debtor other than the business of operating the real property and activities incidental.” 11 U.S.C. § 101. The Bankruptcy Code provides circumstances under which creditors of a single asset real estate debtor may obtain relief from the automatic stay which are not available to creditors in ordinary bankruptcy cases. 11 U.S.C. § 362. On request of a creditor with a claim secured by the single asset real estate and after notice and a hearing, the court will grant relief from the automatic stay to the creditor unless the debtor files a feasible plan of reorganization or begins making interest payments to the creditor within 90 days from the date of the filing of the case, or within 30 days of the court’s determination that the case is a single asset real estate case. The interest payments must be equal to the non-default contract interest rate on the value of the creditor’s interest in the real estate. 11 U.S.C. § 362.
Single asset real estate cases are ineligible for the small business or subchapter V election. 11 U.S.C. § 101, 1182.
Don’t Miss: Fizzics Net Worth
Is There Any Obligation To Initiate Restructuring / Insolvency Proceedings For Whom Does This Obligation Exist And Under What Conditions What Are The Consequences If This Obligation Is Violated
Under the Bankruptcy Code, within a 1 month period, the debtor is obliged to apply to the commercial court with a request to open insolvency proceedings in case the fulfilment of claims of one or more creditors leads to failure to fulfil the debtors obligations in full to all other creditors . The Bankruptcy Code specifically provides for joint and several liability of the management of the company for non-compliance with the above obligation.
Where insolvency is the result of the representative bodies mismanagement or destructive interference, managers will bear the subsidiary liability in case of lack of debtors property to satisfy all creditors claims. Note that fault of the representative bodies in mismanagement and/or destructive intervention should be proven by the court
What Is Liquidation
Choosing a Chapter 7 liquidation bankruptcy could potentially give you a fresh start within four months from filing if all goes smoothly. However, with this type of bankruptcy, your assigned trustee would sell non-exempt assets, if any, and use the proceeds to pay back your creditors. Under Arizona exemption laws, much of your property is protected as exempt, so in many cases your liquidation will result in a no-asset bankruptcy and you will lose nothing other than your debt.
After the bankruptcy, you will receive a discharge of your debt. When this happens, the remainder of your debt is cancelled, even if some creditors go unpaid. Certain debts, such as taxes, child support or student loans, are considered priority debts these cannot be discharged.
You May Like: How Many Bankruptcies Has Donald Trump Filed
Who Can File A Plan
The debtor has a 120-day period during which it has an exclusive right to file a plan. 11 U.S.C. § 1121. This exclusivity period may be extended or reduced by the court. But in no event may the exclusivity period, including all extensions, be longer than 18 months. 11 U.S.C. § 1121. After the exclusivity period has expired, a creditor or the case trustee may file a competing plan. The U.S. trustee may not file a plan. 11 U.S.C. § 307.
A chapter 11 case may continue for many years unless the court, the U.S. trustee, the committee, or another party in interest acts to ensure the case’s timely resolution. The creditors’ right to file a competing plan provides incentive for the debtor to file a plan within the exclusivity period and acts as a check on excessive delay in the case.
Only the debtor may file a plan in a subchapter V case. 11 U.S.C. § 1189.
Can Transactions Entered Into By The Debtor Prior To Be Insolvency Be Challenged And Set Aside What Are The Relevant Grounds / Look
A debtor’s pre-insolvency transactions can be affected by bankruptcy proceedings if they were concluded during the claw-back period. The court will determine the date on which it deems the cessation of payments to have occurred and then determine the length of the claw-back period, which cannot be longer than six months from the bankruptcy declaration.
Certain payments made, as well as other transactions concluded or performed, during the claw-back period can then be subject to cancellation by the court . The following transactions may be set aside or declared null and void upon request by the receiver:
- contracts entered into by the debtor, if its own obligations are significantly more onerous than the obligations of the other party
- the payment of debts that have not fallen due
- any payment made in kind by the debtor in respect of debts that are due
- the granting of a security interest for antecedent debts and
- the payment of certain debts that have fallen due, but that arose during the claw-back period .
Additionally, certain payments made for matured debts, as well as other transactions concluded for consideration, during the claw-back period are subject to cancellation by the court if they were concluded with the counterparty’s knowledge that the debtor was insolvent at the time.
Finally, the receiver may, without any limitation in time, challenge any transaction or payment made in fraud of the creditors’ rights.
Don’t Miss: Fizzics Net Worth 2021
Federal Bankruptcy Jurisdiction And Procedure
Regardless of the type of bankruptcy and the parties involved, basic key jurisdictional and procedural issues affect every bankruptcy case. Procedural uniformity makes bankruptcies more consistent, predictable, efficient, and fair.
Judges and Trustees Pursuant to federal statute, appoint bankruptcy judges to preside over bankruptcy cases . Bankruptcy judges make up a unit of the federal district courts called bankruptcy court. Actual jurisdiction over bankruptcy matters lies with the district court judges, who then refer the matters to the bankruptcy court unit and to the bankruptcy judges.
A trustee is appointed to conduct an impartial administration of the bankrupt’s nonexempt assets, known as the bankruptcy estate. The trustee represents the bankruptcy estate, which upon the filing of bankruptcy becomes a legal entity separate from the debtor. The trustee may sue or be sued on behalf of the estate. Other trustee powers vary depending on the type of bankruptcy, and can include challenging transfers of estate assets, selling or liquidating assets, objecting to the claims of creditors, and objecting to the discharge of debts. All bankruptcy cases except chapter 11 cases require trustees, who are most commonly private citizens elected by creditors or appointed by the U.S. trustee.