Not Sure Whether To File Chapter 7 Or Chapter 13
The decision to file for bankruptcy is complicated enough in itself. Choosing the appropriate form of bankruptcy and preparing to file will involve many considerations that you might not be aware of until it’s too late.
Learn how an experienced bankruptcy lawyer can help guide you through the process and ensure that your bankruptcy solves your financial problems.
Dealing With Secured Creditors
With Chapter 7, you are generally allowed to either keep or surrender any collateral. So you can decide that you can no longer afford your mortgage or vehicle payment and give up the house or car and discharge the remaining debt. Or you can arrange to continue making the payments and keep the collateral. If you are behind on those payments, you will have limited time to catch up, depending on the discretion of the creditor.
Contrast that with Chapter 13, under which you can usually stretch out payment of your mortgage or vehicle arrears over the entire three-to-five year repayment plan. Also, you may be able to save a tremendous amount by cramming down the balance on an older vehicle loan to the value of the vehicle.
Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Upsolve is a nonprofit tool that helps you file bankruptcy for free.Think TurboTax for bankruptcy. Get free education, customer support, and community. Featured in Forbes 4x and funded by institutions like Harvard University so we’ll never ask you for a credit card.Explore our free tool
In a Nutshell
Chapter 7 bankruptcy vs. Chapter 13 bankruptcy: Learn the differences, which type of bankruptcy is better depending on the situation, and the downsides of each.
Written byAttorney Andrea Wimmer.
Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy are the two most commonly filed types of bankruptcy. Each is a legal tool to get debt relief if youâre no longer able to keep up with your minimum payments. Which one of these bankruptcy options is right for you depends on your financial situation and goals for the future. Even though there are many differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy, each one grants the filer a fresh financial start in the form of a bankruptcy discharge. The discharge is a court order that permanently bans creditors from trying to collect money from you.
After a brief overview, this article will explore the differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13, which type of bankruptcy is better depending on the situation, and the downsides of each.
Don’t Miss: How Does Bankruptcy Work With Student Loans
The Impact On Your Credit May Not Be As Severe
Like Chapter 7, Chapter 13 bankruptcy may have a very negative impact on your credit. A completed Chapter 13 bankruptcy can stay on your for up to seven years from the date you file. But some creditors could view a Chapter 13 bankruptcy more favorably than a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. It could be an indication that you repaid more of your debt.
Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Are Two Very Different Legal Options With Different Potential Consequences But Both Can Help Borrowers Who Are Over Their Heads In Debt
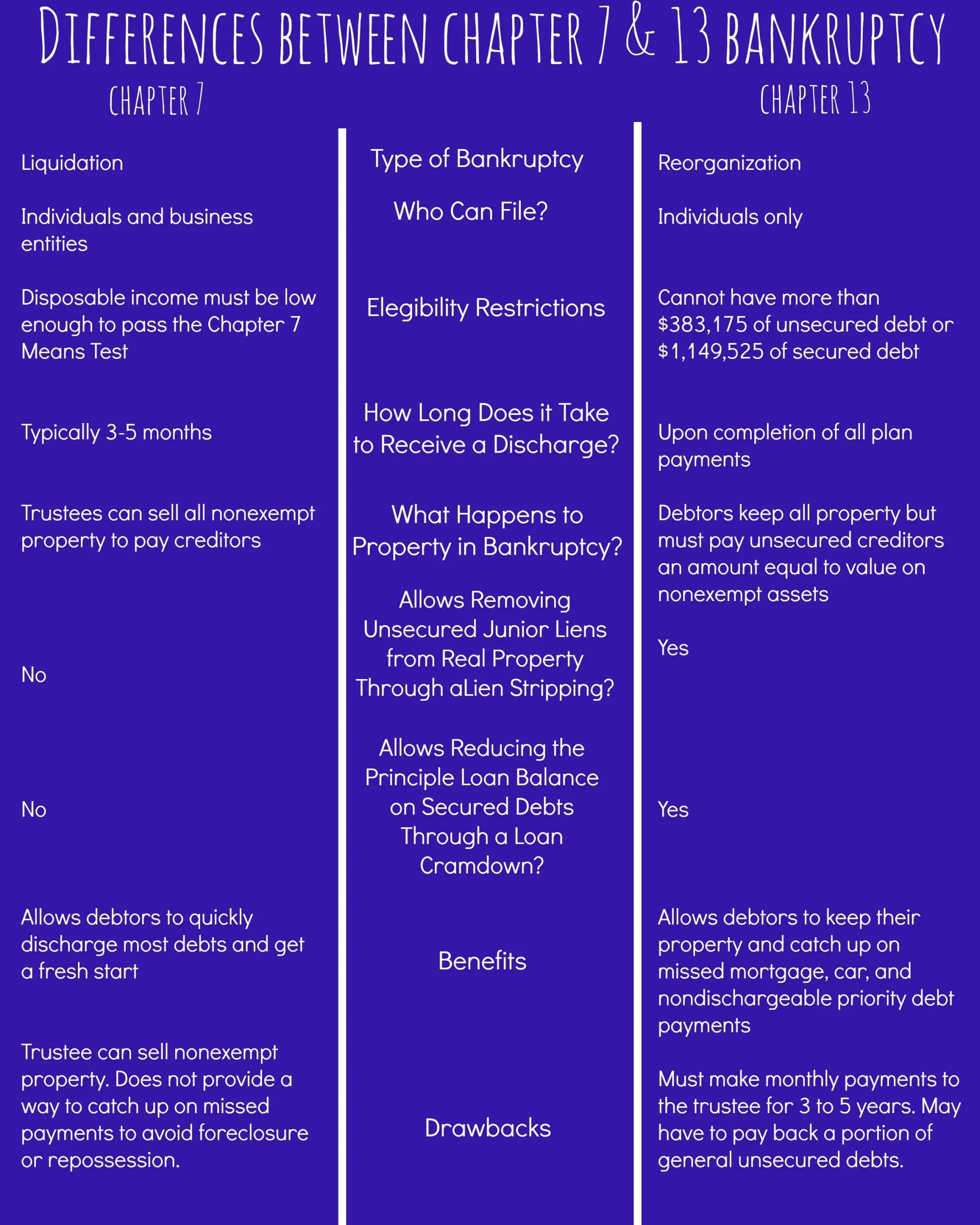
Chapter 7 bankruptcy, also known as a liquidation, is a legal option that can help you clear some or all of your debt. But it will also mean having to surrender assets, like property or cash, to do so. Chapter 13 bankruptcy is also a legal option that can help you get some debt discharged, but allows you to keep your property and repay your debt by completing a three- to five-year repayment plan.
But before filing either type of bankruptcy, consider the type of debt you owe. Neither option lets you discharge the following:
If your debts are outside of those categories and youve exhausted all your other options to repay them such as asking for help or Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy might give you the help you need. Each has pros and cons, so its important to carefully consider which one, if either, is right for you.
Read Also: Why Did Boy Scouts File Bankruptcy
Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 13
When deciding between Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 13 bankruptcy, itâs important to consider:
-
the types of debt you have ,
-
if any of your personal property would be considered a nonexempt asset,
-
if your regular monthly income is enough to cover your living expenses, and
-
the difference between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 on your credit report
Bankruptcy can be a powerful poverty fighting tool and help thousands of families get back on their feet every month. If youâre facing wage garnishment, know the Bankruptcy Codeâs âautomatic stayâ protects you from any future garnishment as soon as your case is filed. If youâre not sure whether bankruptcy is right for you, keep doing what youâre doing and research. You may even consider signing up for a free credit counseling session to learn more.
Donât be discouraged – or embarrassed – by the idea of filing bankruptcy. If COVID-19 and its impact on everyone in the United States and around the world has shown us anything, it’s that life happens. Bankruptcy laws exist to give you a fresh start. Thereâs no shame in using this legal tool, just like Walt Disney, Abraham Lincoln, and Henry Ford did when they needed help.
Filing Chapter 7? Upsolve may be able to help…
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy The Quick And Easy Option
Chapter 7 is generally the quicker and easier option, as its usually over within a few months and entirely discharges any qualifying debt. Its a liquidation bankruptcy, meaning the trustee might sell your assets to pay down your debts. If you only have unsecured, nonpriority debts and dont have a lot of assets, Chapter 7 is usually the better option.
During Chapter 7, the bankruptcy trustee, an individual the court assigns to represent your estate in bankruptcy, can sell your belongings, whether theyre high-value items like a boat or motorcycle or lower-value items like furniture or designer clothing.
Chapter 7 does have income limits, so you might not qualify if you earn too much or if your debt-to-income ratio, the amount of debt you owe versus how much you make expressed as a percentage of how much of your income goes toward debts, isnt high enough. That in addition to your family size is what the government calls a means test.
Debts you can discharge in Chapter 7 bankruptcy include:
- Past-due attorneys fees
- Civil court judgments
Secured debts, which are backed by property, such as a car or house, get treated differently in Chapter 7. You can discharge any back debt on them, provided you give up the collateral. If you want to keep the property connected to secured debts, you must reaffirm the debt and continue making payments. You need to be up-to-date on payments to do so.
There are several advantages to Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
Also Check: How Long Does Bankruptcy Stay On Credit
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Debt Reorganization And Payment Plan
If you dont qualify for Chapter 7, Chapter 13 is the way to go. Unlike Chapter 7, Chapter 13 requires you to pay off your debts through a payment plan created by the bankruptcy trustee. Chapter 13 is a reorganization bankruptcy since the payment plan rearranges your debts.
Note that there is a limit to how much debt you can have to qualify for Chapter 13. You need to have less than $465,275 in unsecured debts and less than $1,395,875 in secured debts.
The trustee will rank your debts under the payment plan to ensure priority debts get paid in full by the time the plan is complete . The plan will also account for secured debts you have and, if you can afford to pay them, unsecured debts. The amount you pay under the payment plan is based on your monthly income.
Chapter 13 takes longer than Chapter 7, in some cases up to five years. How long depends on the repayment plan. If your income is below the states median monthly income, your plan lasts three years. If you earn more than the state median income, it lasts five years.
Chapter 13 bankruptcy lets you discharge a few more debts than Chapter 7. The additional debt types you can discharge in Chapter 13 include:
You must continue making payments on secured debts if you want to keep the property associated with them. The benefit of Chapter 13 is that it allows you to reschedule the debt and potentially reduce the value of some property types, such as a car.
But there are still some significant disadvantages.
What Are The Benefits
One of the primary benefits of Chapter 13 bankruptcy is that it may allow you to avoid foreclosure on your home or repossession of your car. As long as you make payments on time, you can keep your property.
Another advantage is that you have more time to pay off your debts. Bill collectors will stop hounding you and you can start the process of rebuilding your credit.
For help with a Chapter 13 bankruptcy case, trust Bueker Law Firm in Stuttgart, AR. Attorney Jeremy Bueker has more than 19 years of experience providing reliable legal counsel and representation to clients across central and southeast Arkansas. The firm specializes in bankruptcy, repossession, and foreclosure. You can count on them to assess your situation and determine a plan to get you back on a healthy financial track. Call 673-1313 for a consultation or visit their website for more information.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Automatic Stay In Bankruptcy
Nonsupport Debts Owed In A Divorce Property Settlement Or Agreement
If a creditor objects, then these debts will not be discharged unless you demonstrate that:
Any remaining balance at the end of Chapter 13 bankruptcy will be erased.
How Do I Apply For Bankruptcy
The unfortunate reality of bankruptcy is that it will cost some moneymore if you hire legal help, which you probably should . All filings have to go through U.S. bankruptcy courts, where the cost to file is $335 for Chapter 7 and $310 for Chapter 13. However, you can ask the court to either waive your fee or let you pay with monthly installments. You’ll also have to take debtor education courses if you file on your own.
And that’s just the beginning. There’s a list of documents you’ll need to take care of, as well as the specific repayment proposal you need to submit for Chapter 13. That proposal gets reviewed by a court-appointed trustee, who contacts your creditors before approving your submission. Overall, neither filing is an easy process to handle on your own, and even minor mistakes on your end could be a setback for your case.
So, whether you file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy, it’s typically a good idea to hire a lawyer to help you petition. A bankruptcy attorney’s price depends on the nature and complexity of your filing, with Chapter 13 filings on the pricier end, but the price tag doesn’t necessarily mean a lawyer is out of the question for you. Discuss payment plans with potential attorneys, check out local pro-bono lawyers and legal aid offices, or use an online tool like Upsolve to cover your bases when it comes to bankruptcy.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You File Bankruptcy On Student Loans
A Note On Foreclosure
While both bankruptcies will temporarily stop foreclosure, Chapter 13 may be a better option for stopping it more permanently.
Once a Chapter 13 repayment plan is confirmed, you will pay back the missed payments over the life of the plan. The terms and conditions of the original agreement will govern the debtor and the lender’s relationship.
Chapter 13, however, will not prevent foreclosure if you filed for bankruptcy within the past two years, and the bankruptcy court lifted the automatic stay to allow the creditor to proceed with foreclosure.
In Chapter 7, it is less likely that you can keep your home if you are behind on mortgage payments. The court can, and often will, grant a lender’s request to lift an automatic stay to continue foreclosure proceedings on the home.
Which Chapter Is Right For You

Much depends on individual circumstances, butfor some broad classes of debtsone chapter is more likely to be better than another:
- Chapter 7. This is usually best for filers with limited income and only unsecured debts, such as credit cards and personal loans. Chapter 7 is also a better choice for a filer who wants to get the process over with fast, and who may not have the money to hire an attorney.
- Chapter 13. This is likely to be the smartest type of bankruptcy for a filer who has regular, reliable income, wishes to keep some of their assets and can pay debts over time. Chapter 13 filers have to be ready to fulfill the repayment plan, which may take three to five years, and will generally need the money to pay an attorney.
Don’t Miss: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Tax Return
Reasons To File For Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Instead Of Chapter 13
By FindLaw Staff | Reviewed by Bridget Molitor, J.D. | Last updated May 17, 2021
When given a choice, many people prefer filing Chapter 7 bankruptcy instead of Chapter 13 because it discharges most medical bills and credit card debt. In this article, we discuss the advantages of Chapter 7 and the disadvantages of Chapter 13.
You Should File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy If
Overall, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is best for lower-income Americans who are in way over their heads. Chapter 7 bankruptcy is a better fit if:
- Your Income Is Below the Median in Your State. You need to pass a means test to be eligible for Chapter 7. You automatically pass the test if you earn less than the median monthly income in your state.
- You Dont Have a Lot of Assets. Your bankruptcy trustee can sell your stuff to pay off creditors during Chapter 7. While there are exemptions, its usually better for a debtor not to have a lot of assets or possessions when they file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
- You Mainly Have Unsecured Debts. If you owe back taxes, alimony, child support, or student loans, bankruptcy wont help. Youre still on the hook if you have secured debts and want to keep the collateral. Chapter 7 isnt a magical get-out-of-debt-free pass. But if you have credit card debt, medical bills, or unsecured personal loans, Chapter 7 can give you a fresh start.
- You Dont Have Enough Disposable Income to Repay Your Debts. You can pass the means test even if your income is above the state median, provided your disposable income isnt enough to cover your monthly debt payments.
Don’t Miss: When Will My Bankruptcy Be Discharged
Differences Between Chapters 7 11 12 & 13
What is the difference between filing bankruptcy under Chapter 7, under Chapter 13, and under Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code?
Chapter 7:
This is a liquidation bankruptcy, sometimes calledstraight bankruptcy. The principle advantage is that the debtor comes out without any future obligations on his discharged debts. However, bankruptcy does not wipe out most mortgages or liens. If a debtor wants to keep an item which is security for a loan, he/she must continue these payments. If the debtor wants to discharge that car loan, then he/she must surrender the car to the creditor that holds the lien.
The fact that the term liquidation is used in describing a chapter 7 can be misleading. A chapter 7 bankruptcy trustee can only liquidate nonexempt assets owned by the debtor. In Mississippi, most consumer chapter 7 filings are what we call no asset cases because the debtor owns no nonexempt assets or such a small amount of nonexempt assets that liquidating those assets would not provide a meaningful distribution to creditors. For an understanding of what is exempt and not exempt, see Exemptions in Mississippi.
Another type of debt that is not discharged is debt that is reaffirmed by the person filing the bankruptcy. Reaffirm and reaffirmation agreement are terms that are described in the Bankruptcy Glossary.
Chapter 13:
Chapter 11:
Chapter 12:
Pennsylvania Bankruptcy Lawyers Handling Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Cases
Every person who files for bankruptcy has a unique set of goals and challenges. Our Bucks County bankruptcy lawyers will take the time to learn why you are thinking of bankruptcy, what your financial background is, and what you hope to achieve by filing. We can help you make an informed decision about when to file, which chapter is optimal, and whether there are suitable alternatives.
Young, Marr, Mallis & Associates handles Chapter 13 and Chapter 7 cases throughout southeastern Pennsylvania, including Bucks County, Berks County, Montgomery County, and Philadelphia. For a free consultation with our experienced Philadelphia bankruptcy attorneys, contact us online or call 701-6519 today.
You May Like: Did Loot Crate File For Bankruptcy
Summarizing Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Generally, Chapter 7 is more appropriate for simple cases while Chapter 13 for more complicated bankruptcies. Or somewhat more accurately, Chapter 13 can give you more power over and flexibility with certain kinds of creditors, and if you have non-exempt assets. However, if you do not have those kinds of debt or assets, or not much in terms of tangible assets, then Chapter 7 would likely be the faster and easier option.
Next, well get into a few scenarios where knowing the difference could pivotal.
Essential Information About Chapter 13
Chapter 13 does not provide debt relief as quickly as Chapter 7 can, but it does allow the filing party to retain ownership over most of their property and assets. Chapter 13 bankruptcy revolves around restructuring the filing partys debts into a manageable repayment plan, and this filing option is only available to individuals, not businesses.
If you believe that Chapter 13 is more suitable for you, you must ensure that you can file for Chapter 13 before starting the process. As of 2020, any unsecured debts an individual has must be less than $394,725, and they must have no more than $1,184,200 in secured debts to be eligible for Chapter 13.
You and your attorney must fill out a financial disclosure package that includes complete and accurate records of all your assets, debts, and property in order to start Chapter 13 proceedings. You will be allowed to keep your property as long as the bankruptcy court approves your proposed debt repayment plan. An experienced Chapter 13 bankruptcy attorney is your best resource if you need help developing your plan. Once you complete all of your repayments under the terms of an approved plan, your debts are discharged.
Don’t Miss: How To File For Bankruptcy In Nyc