Liquidation Vs Debt Repayment
A trustee takes over a debtor’s assets in a Chapter 7 filing. These assets are liquidated sold by the trustee in exchange for cash which is then distributed among creditors.
Restructured debt, as found in Chapter 11 bankruptcy, must be repaid according to the new terms agreed upon during the filing process usually over a period of three to five years.
Ultimate Overview Of Bankruptcy
The word bankruptcy is inherently scary to people, as many of us associate the term with absolute financial ruin from which it can be very difficult if not impossible to recover from.
In reality, however, bankruptcy does not necessarily mean that your life is fully ruined financially. In fact, many people dont even know the details of what bankruptcy is and what it isnt, and many also dont know that there is more than just one kind of bankruptcy as well.
Educating yourself about the different kinds of bankruptcy and the details of each one is important in order to become more financially literate and informed, even if bankruptcy is not something on your horizon.
But if bankruptcy is something that is unfortunately looking like an increasing possibility for you, then receiving education on this subject will be even more important for you. Filing for bankruptcy is a very serious conversation just as much personally as it is financially, and its important to know the details of it just as to research your other options as well.
In this article, we are going to outline and discuss the details of the two basic bankruptcy options before you: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13.
Yes, theres also Chapter 11 bankruptcy as you may have heard, but that exists only for businesses. As an individual, Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 are your two primary options, although there is also a Chapter 12 for farmers and fishermen.
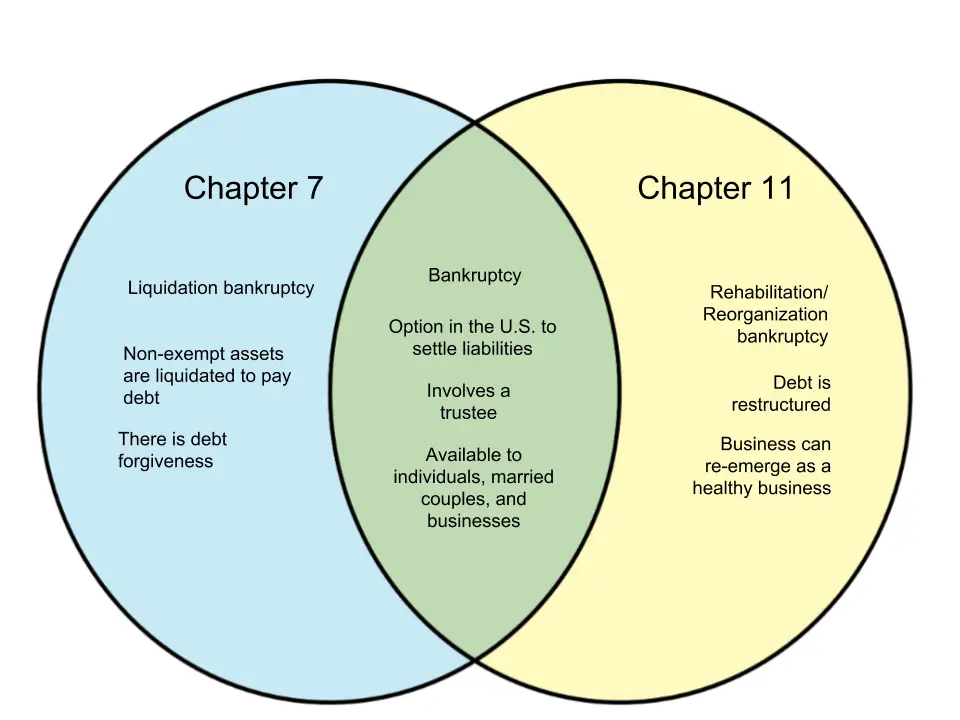
How Is The Individual Chapter 11 Liquidation Bankruptcy Different From Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Lets cut to the chase. The main difference between Chapter 11 liquidation and Chapter 7 is that you, as the debtor, remain debtor in possession. In other words, you have control over the sale process. You also control the distribution of assets through the bankruptcy court.
In a Chapter 7 case, by contrast, you are immediately taken out of possession. You no longer have right title or interest to any of your assets. In other words, except for special exceptions , you lose control over your real property and personal property.
Keep Control
Critically and additionally, when you file for Chapter 7, you also no longer control any litigation youre pursuing. In other words, the bankruptcy trustee can block you from having control or a say about litigation to be pursued.
For instance, lets say that your husband, Peter, got hit from behind on the New Jersey Turnpike six months ago. The truck driver at fault had been speeding while driving way in excess of allowable hours. The accident left Peter in traction. He had to step down from his lucrative position as Vice President of a bank in Manhattan. Peters sudden lack of income created a cash flow emergency for the family, prompting the need for debt relief. He initiated a lawsuit against the trucking company to recover damages. However, this might take months or longer to sort out.
If you and Peter file for Chapter 7, you cant determine a settlement on that lawsuit. The trustee gets to control the outcome.
Recommended Reading: What Is Epiq Bankruptcy Solutions Llc
How Is Property Handled In A Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Case
A Chapter 7 case is a liquidation bankruptcy. Debtors who have non-exempt equity in property may lose that property in a Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 case.
Most Chapter 7 cases filed by individuals are no-asset cases. No-asset cases mean the debtors keep all assets, but get rid of substantial debts.
A business that files Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 closes its doors. The trustee sells the business assets to pay unsecured creditors in a Chapter 7 case. Secured creditors repossess or foreclose on the collateral, including real estate. Unsecured claims are paid in order of the priorities set by the U.S. Bankruptcy Code.
In a Chapter 11 case, the debtor chooses whether to keep or surrender property to the secured creditor holding the lien. A lien is a security interest that gives the creditor the ability to take property back if the debt is getting paid, either through a repossession or foreclosure. The property with the lien on it is called the collateral. If the property does not have a lien and it does not serve as collateral for a secured debt, the debtor is generally able to keep all property.
Can I Lose Property in a Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 Case?
Each bankruptcy case is different. However, most people who file a Chapter 7 case don’t lose any property because everything they own is protected by an exemption. As a result, debtors in Chapter 7 bankruptcy don’t pay back any unsecured creditors as part of their bankruptcy case.
Debt Forgiveness Vs Debt Reorganization

Debt forgiveness is the common term for what is legally known as a bankruptcy discharge, a core component of a Chapter 7 filing that is also used to a lesser degree in Chapter 11 filings. Unless a creditor disputes a particular discharge request, most discharges are automatically approved. A bankruptcy court then mails a copy of discharge orders to all applicable creditors. Under a discharge order, the creditor must “forgive” the debts listed by no longer seeking repayment. In the eyes of the law, discharged debt is no longer owed.
This is a different process from debt reorganization, which is used in a Chapter 11 filing. Under debt reorganization, debts are not discharged or forgiven. Instead, loan terms are altered in a way that a debtor will hopefully be able to repay his debt more successfully. For example, debt APR or interest rates may be lowered, or the length of time a debtor has to repay a loan may be extended.
Unsecured debt, such as credit card debt, is more likely to be forgiven than secured debt, such as a home or auto loan. And student loan debt is never discharged in bankruptcy.
Exempt Property
Mortgages are very rarely exempt from the bankruptcy process. This means that someone filing for Chapter 7 must continue to make payments on his mortgage. If he cannot make these payments, he may also eventually end up going through a judicial or non-judicial foreclosure process on top of his bankruptcy.
You May Like: How Soon After Filing Bankruptcy Can I Buy A House
What Eligibility Requirementsmust Be Met
Individualsmust pass a Means Test that demonstrates they will be able to pay down debts,and they must be current on tax filings. Chapter 13 also has debt limits thatdebtors cant exceed. Unsecured debt, e.g. credit card bills and personalloans, may be no more than $394,725 and secured debt, e.g. mortgages andvehicle loans, may be no more than $1,184,200. Corporations and partnershipsare not eligible under Chapter 13.
Would I Be Required To Repay All My Debts In Chapter 7 Or Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
It varies depending on what type of debt is involved.;For example, you wont be required to pay unsecured debts that are not secured by collateral .
These debts will be discharged with Chapter 7. This can take up to a few months.;Chapter 13 requires that you continue to pay those amounts during your court-ordered repayment program. Unsecured debts can then be discharged.
However, certain debts cannot be discharged under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
- Mortgages
- Alimony or child support
- Students can get financial aid in the form of student loans.
You may be able to reduce some of your secured loans through Chapter 13 bankruptcy. This is a way to make it easier to pay the debt.;You may be eligible for a lower amount of auto loans depending on how much the vehicle has appreciated.;
You may be eligible to discharge secured debts such as auto loans if you sell the property in Chapter 7 bankruptcy. In this instance, the car.
Recommended Reading: Bankruptcy Document Preparer
Chapter 11 Reorganization Bankruptcy
Chapter 11 bankruptcy is designed to allow businesses to continue to operate while repaying necessary debts and restructuring the company for long-term success. Specifically, Chapter 11 reorganization bankruptcy is most commonly implemented when big businesses require time to restructure and repay their debts. Either a commercial bankruptcy attorney or the business itself may voluntarily file a bankruptcy petition, or creditors may file an involuntary petition with the bankruptcy court.;
Once a petition is filed, the debtor must submit all relevant financial documents to the court. Additionally, most debtors include a reorganization plan that specifies how the business will pay each claim back. This reorganization strategy is then voted on for approval by the creditors. If approved, the debtor becomes the debtor in possession, which allows the company to keep business assets and continue operating while the plan goes into effect. Throughout this process, the creditors oversee the reorganization plan and ensure the debtor adheres to the agreed-upon regulations outlined in the restructuring strategy.;
What Are The Disadvantages
Chapter7 filing means liquidating property that you may value unless you can afford toschedule payments to keep said property.
Notall debts are eligible for discharge under Chapter 7. Most taxes, domesticsupport obligations, and school loans are exempt from discharge, and bankruptcydoes not eliminate a lien on a property.
Recommended Reading: How Many Donald Trump Bankruptcies
What Is The Bankruptcy Process
Bankruptcy is an option to eliminate or reduce debt if you are unable to pay your creditors.;However, this should only be considered a last resort and used only after exhausted all other options.
Most people who file bankruptcy are filing under Chapter 7 and Chapter 13.;What happens to your property is the most important distinction.
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is also known as liquidation bankruptcy. This means that you must sell a portion or all of your assets to meet your obligations.;This is often the best option if you dont have a house or have a limited budget.
Chapter 13, also known as a Reorganization Bankruptcy, allows you to keep your property as long as you follow a three to five-year court-mandated repayment program.
Depending on your marital status and where you live, you may be able to exclude some of your property from being auctioned.;The exemption amounts are taken from your home equity, retirement funds or personal items, and the rest of the profits can be used to pay debts.;This graphic will provide a quick overview of both the types and details about exemptions.
Chapter 7
Who is authorized;to file?
- Both individuals and businesses can be included in this category.
Eligibility restrictions
- Chapter 7 means the test requires that disposable income be sufficiently low to pass.
What is the time it takes for a discharge?
- It is common for three to five months.
What happens to a persons property if they file for bankruptcy?
- No
- No
Drawbacks
The Different Types Of Bankruptcy
Depending on your situation, there are different types, officially known as chapters of bankruptcy, that you can file for. These different chapters of bankruptcy provide different results for different cases, and its important to have some knowledge on these chapters before filing for bankruptcy.
Also Check: Can I File Bankruptcy Without My Spouse Knowing
Differences Between Chapter 7 & Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
To recap, then: Chapter 7 is the least complicated of the various bankruptcy programs. Its designed for low-income individuals or people with severely upside-down finances to quickly eliminate qualified unsecured debt like credit cards or medical bills.
Chapter 11 is for businesses and individuals who need breathing room to reorganize their finances. They have high, reliable income and valuable assets. They can get back on their feet if theyre able to renegotiate the terms of their debts.
How Resolve Can Help
If youre dealing with debt and not sure what to do, were here to help. Become a Resolve member and well contact your creditors to get you the best offers for your financial situation. Our debt experts will answer your questions and guide you along the way. And our platform offers powerful budgeting tools, credit score insights and more.Join today.
Also Check: How To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
How Does Bankruptcy Work
Bankruptcy is a method to eliminate or at least reduce your debt when bills pile up beyond your ability to repay them. It should be viewed as a last resort to be considered only when all other potential courses of action to get back on track have been exhausted.
Individuals filing for bankruptcy mostly use either Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. The biggest difference between the two is what happens to your property:
- Chapter 7, which is known as liquidation bankruptcy, involves selling some or all of your property to pay off your debts. This is often the choice if you don’t own a home and have a limited income.
- Chapter 13, also known as a reorganization bankruptcy, gives you the chance to keep your property if you successfully complete a court-mandated repayment plan that lasts between three and five years.
Depending on where you live and your marital status, some of your property may be exempt from being sold when you file Chapter 7 because of state-specific and federal exemptions. With exemptions, whether they be your home equity, retirement accounts or even personal possessions such as jewelry, you receive the allowed exemption amounts, and the rest of the proceeds will be used to pay off debts. You can read more about potential exemptions, and check out this chart for a quick rundown on the two types:
| Chapter 7 |
|---|
- Child support or alimony
- Student loans
Debt Discharge Through Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
The most valuable part of filing Chapter 7 is that it discharges the qualifying debt of the filer. However, you should note that not all debts will be discharged. Upon filing the bankruptcy, you will receive the debt discharge within three or four months, even if the trustee is not yet finished selling the assets.
You May Like: How To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
No Creditor Committee Disclosure Statement Or Creditor Consensus Required
Some of the requirements that typically generate litigation in a traditional Chapter 11 aren’t required in Chapter 11, Sub V, such as:
- the appointment of a creditor committee
- the filing of a disclosure statement, and
- plan confirmation by creditor consensus.
As long as the plan pays creditors according to bankruptcy rules and is objectively fair, the bankruptcy judge can confirm it over creditor objections.
How To Prevent Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is generally a last resort, for businesses and individuals alike. Chapter 7 will, in effect, put a business out of business, while Chapter 11 may make lenders wary of dealing with the company after it emerges from bankruptcy. A Chapter 7 bankruptcy will remain on an individuals credit report for 10 years, a Chapter 13 for seven.
While bankruptcy may be unavoidable in many instances , one key to preventing it is borrowing judiciously. For a business, that could mean not using debt to expand too rapidly. For an individual, it might mean paying off their credit card balances every month and not buying a larger home or costlier car than they can safely afford.
Before filing for bankruptcy, and depending on their own internal legal resources, businesses may want to consult with an outside attorney who specializes in bankruptcy law and discuss any alternatives that are available to them.
Individuals are required by law to take an approved credit-counseling course before they file. Individuals also have other resources available to them, such as a reputable debt relief company, which can help them negotiate with their creditors. Investopedia publishes an annual list of the best debt relief companies.
Read Also: How Many Times Has Donald Trump Filed For Bankruptsy
Personal Bankruptcy Options Chapter 7
As far as personal bankruptcy options go, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common type. This is a liquidation bankruptcy where a Chapter 7 trustee is assigned to your personal bankruptcy case. This trustee has the power to sell any of your assets that are not protected by bankruptcy exemptions. In most Chapter 7 bankruptcy cases, people are able to discharge the majority of their general unsecured debts such as credit cards, loans, medical bills, and other debts which are not secured against property, and are not certain types of priority unsecured debts.;
Individual and joint debtors may qualify for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy case if they pass the means test. This is a calculation to determine if your income is more than the average income of a household of your same size in your county. If you do pass the means test, then you may choose Chapter 7 over other kinds of bankruptcy. However, if you have exposed equity in your assets, or are concerned that the Chapter 7 trustee assigned to your case will believe that you have exposed equity in your assets, then you may want to consider a reorganization bankruptcy under Chapter 13 or Chapter 11.
Which Debts Cannot Be Eliminated Through Bankruptcy
Some types of debt generally cannot be discharged through bankruptcy. There are rare exceptions, depending on the facts in an individual case. Debts that typically cannot be discharged include:
- Child support
- Unpaid taxes
- Student loans
- Debts for personal injury or death you caused while driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs
- Debts you failed to list in your bankruptcy filing.
Also Check: How To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
Essential Information About Chapter 13
Chapter 13 does not provide debt relief as quickly as Chapter 7 can, but it does allow the filing party to retain ownership over most of their property and assets. Chapter 13 bankruptcy revolves around restructuring the filing partys debts into a manageable repayment plan, and this filing option is only available to individuals, not businesses.
If you believe that Chapter 13 is more suitable for you, you must ensure that you can file for Chapter 13 before starting the process. As of 2020, any unsecured debts an individual has must be less than $394,725, and they must have no more than $1,184,200 in secured debts to be eligible for Chapter 13.
You and your attorney must fill out a financial disclosure package that includes complete and accurate records of all your assets, debts, and property in order to start Chapter 13 proceedings. You will be allowed to keep your property as long as the bankruptcy court approves your proposed debt repayment plan. An experienced Chapter 13 bankruptcy attorney is your best resource if you need help developing your plan. Once you complete all of your repayments under the terms of an approved plan, your debts are discharged.