United States Census Bureau
2015
The table below presents the total state debt as well as debt per capita for each state in 2015. Click on the arrow in the upper righthand corner of the table to view debt figures for more states.
2014
The table below presents the total state debt as well as debt per capita for each state in 2014. Click on the arrow in the upper righthand corner of the table to view debt figures for more states.
Use These Pay Off Debt Tools
Now that you have our debt numbers, youve prepared for the change, increased your knowledge on the topic, and have a motivating reason to move forward, lets dig into the tools to pay off debt.
Negotiate
When you are trying to pay off debt, let your creditors know. Some will be willing to work with you. You can call credit card companies and ask for a reduced interest rate. If you have a lump sum bill like a medical bill, you can call and try to work out a realistic payment plan.
The worst you can receive is a no, and you can call back at another time and speak with someone else or escalate to a supervisor or manager.
Debt Pay Off Techniques
Debt Snowball
The debt snowball is an accelerated debt payoff strategy. Its called the snowball because like a small snowball or anything for that rolling downhill it begins to pick up momentum. You attack the smallest debt first and once paid off move on to the next.
Debt Avalanche
The debt avalanche is another accelerated debt payoff strategy. Its called the avalanche because its likelier to pay off debts in a shorter time and save you the most money on interest.
To best understand which if the snowball or avalanche payoff method might be right for you, test out some what if scenarios to conclude what works best for you.
How To Look At The National Debt By Year
It’s best to look at a country’s national debt in context. During a recession, expansionary fiscal policy, such as spending and tax cuts, is often used to spur the economy back to health. If it boosts growth enough, it can reduce the debt. A growing economy produces more tax revenues to pay back the debt.
The theory of supply-side economics says the growth from tax cuts is enough to replace the tax revenue lost if the tax rate is above 50% of income. When tax rates are lower, the cuts worsen the national debt without boosting growth enough to replace lost revenue.
Major events, like wars and pandemics, can increase the national debt.
During national threats, the U.S. increases military spending. For example, the U.S. debt grew after the September 11, 2001, attacks as the country increased military spending to launch the War on Terror. Between fiscal years 2001 and 2020, those efforts cost $6.4 trillion, including increases to the Department of Defense and the Veterans Administration.
The national debt by year should be compared to the size of the economy as measured by the gross domestic product. That gives you the debt-to-GDP ratio. That ratio is important because investors worry about default when the debt-to-GDP ratio is greater than 77%that’s the tipping point.
You can also use the debt-to-GDP ratio to compare the national debt to other countries. It gives you an idea of how likely the country is to pay back its debt.
You May Like: What Happens If You Declare Bankruptcy Uk
Average American Debt By Age
Youve probably heard the saying You have to spend money to make money. Economists debate that, but theres little doubt that people spend more when theyre making more.
The average American has $90,460 in debt, according to a 2021 CNBC report. That included all types of consumer debt products, from credit cards to personal loans, mortgages and student debt.
The average amount of debt by generation in 2020:
- Gen Z : $16,043
- Millennials : $87,448
- Gen X : $140,643
- Baby boomers : $97,290
- Silent generation : $41,281
List Of Countries By External Debt

This is a list of countries by external debt, it is the total public and private debt owed to nonresidents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods or services, where the public debt is the money or credit owed by any level of government, from central to local, and the private debt the money or credit owed by private households or private corporations based on the country under consideration.
For informational purposes, several non-sovereign entities are also included in this list.
Note that while a country may have a relatively large external debt it could actually be a “net international creditor” if its external debt is less than the total of external debt of other countries held by it.
Don’t Miss: What Does Declaring Bankruptcy Do For Me
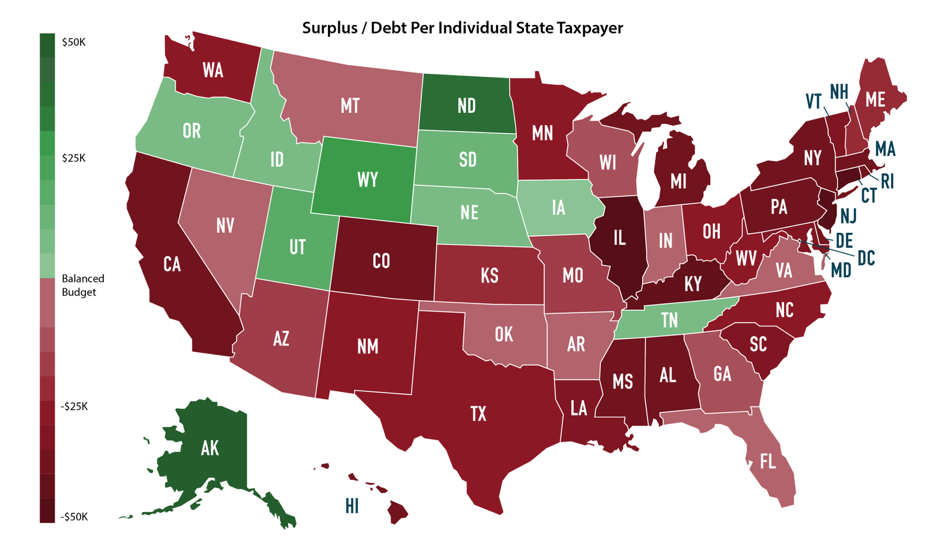
States With The Least Debt
1. Texas
Texas has the lowest debt of any state in the U.S. Alaska‘s total liabilities add up to $222.64 billion, and its total assets add up to $356.01 billion, giving Texas the highest net position in the country of $115.08 billion. Texas’s debt ratio is 62.5%
2. Florida
Florida’s debt is the second-lowest in the country. With total liabilities coming out to $66.78 billion and total assets coming out to $163.24 billion, Florida’s net position is $97.6 billion. This means that Florida’s debt ratio is 40.9%. While Floridas debt has decreased in recent years, it is expected to increase over the next two years.
3. Alaska
Alaska has the third-lowest debt and the third-highest net position of $76.74 billion. Alaska’s total liabilities add up to $12.65 billion, and its total assets add up to $89.17 billion. Although Alaska does not have a state income tax, its revenue is well-supplied by taxes on oil and gas production.
Impact Of Debt And Income On Credit Scores
How a borrower’s debt compares with their income has no direct impact on credit scores. However, lenders can consider debt-to-income ratios in tandem with credit score when determining whether to approve a loan. To see your own credit factors the way lenders see them, here’s how to calculate your debt-to-income ratio and how to get your FICO® Score for free.
Don’t Miss: Does Bankruptcy Cover Private Student Loans
Individuals Debt By State
A recent gives a clear picture of debt by State. Here are some of the key finding of that report:
- Residents of Washington, D.C. have the highest debt-to-income ratio at 1.09, meaning that overall people in D.C. have 9% more debt than their income can cover. This area also has the highest total debt per capita at $84,380, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
- West Virginia has the lowest debt-to-income ratio, at 0.65, meaning that overall West Virginians make about 35% more money than they owe. This State also has the least total debt per capita at $28,790, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
- In states with the highest debt-to-income ratios, mortgage debt makes up a much higher percentage of residents total debt compared to other forms of debt.
- In states with the lowest debt-to-income ratios, residents have a higher percentage of credit card debt compared to residents in states with the highest DTI.
- Overall, Washington, D.C. has more than 3x more total debt per capita than West Virginia.
Here are the ten states with the highest debt-to-income ratios:
Here are the ten states with the lowest debt-to-income ratios:
Interest And Debt Service Costs
Despite rising debt levels, interest costs have remained at approximately 2008 levels because of lower than long-term interest rates paid on government debt in recent years. The federal debt at the end of the 2018/19 fiscal year was $22.7 trillion. The portion that is held by the public was $16.8 trillion. Neither figure includes approximately $2.5 trillion owed to the government. Interest on the debt was $404 billion.
The cost of servicing the U.S. national debt can be measured in various ways. The CBO analyzes net interest as a percentage of GDP, with a higher percentage indicating a higher interest payment burden. During 2015, this was 1.3% GDP, close to the record low 1.2% of the 19661968 era. The average from 1966 to 2015 was 2.0% of GDP. However, the CBO estimated in 2016 that the interest amounts and % GDP will increase significantly over the following decade as both interest rates and debt levels rise: “Interest payments on that debt represent a large and rapidly growing expense of the federal government. CBO’s baseline shows net interest payments more than tripling under current law, climbing from $231 billion in 2014, or 1.3% of GDP, to $799 billion in 2024, or 3.0% of GDPthe highest ratio since 1996.”
According to a study by the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget , the U.S. government will spend more on servicing their debts than they do for their national defense budget by 2024.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Companies File For Bankruptcy
How Bad Is National Debt
Americans living with high levels of government and private debt tend to see saving in a positive light, while treating borrowing as a problem. In fact, they go hand in hand since borrowings come from savings and provide savers with the interest they earn from deferring consumption.
U.S. national debt provides corresponding low-risk assets for pension funds and families, and enables consumption in excess of production for the country as a whole.
At the same time, nothing more than simple arithmetic is required to see the pace of the recent growth of government debt as unsustainable. That’s the term the U.S. Treasury used in the Financial Report of the U.S. Government for Fiscal Year 2021, after calculating that under prevailing trends the federal debt-to-GDP ratio would increase from 100% in 2021 to 701% by 2096.Economists and policy analysts on the left often differ from those on the right in evaluating the tradeoffs between the everyday utility of government debt and its growing risks amid rapid accumulation.
Critics of public debt often contend it can crowd out private investment, a theory not supported by U.S. credit markets developments in recent decades. In contrast, economists using Modern Monetary Theory argue government borrowing can improve economic outcomes if it fosters public investment that expands the economy’s productive potential.
Current Foreign Ownership Of Us Debt
Japan owned $1.32 trillion in U.S. Treasurys in July 2021, making it the largest foreign holder of the national debt. The second-largest holder is China, which owns $1.07 trillion of U.S. debt. Both Japan and China want to keep the value of the dollar higher than the value of their own currencies. This helps to keep their exports to the U.S. affordable, which helps their economies grow.
China replaced the U.K. as the second-largest foreign holder in 2006 when it increased its holdings to $699 billion.
The U.K. is the third-largest holder with $579.8 billion. Its holdings have increased in rank as Brexit continues to weaken its economy. Ireland is next, holding $324.3 billion. Luxembourg, Switzerland, Cayman Islands, Brazil, Taiwan, and France round out the top 10.
Don’t Miss: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Tax Filing
States With The Most And Least Debt In 2020
Illinois, home to Chicago, has five times as much debt as it does assets for the fiscal year … 2018-2019. States like New Jersey, Massachusetts and New York aren’t much better off.
getty
The year 2020 has not been a kind one for budgets. Whether its spending more than ever to stay alive or cutting costs to stay afloat, everyones been feeling the pressure, especially state governments. Fortunately, most states are in the black in terms of their finances, at least according to their latest comprehensive annual financial reports , covering the fiscal year July 1, 2018 to June 30, 2019. There are, however, several states whose budgets went into this years pandemic crisis already in poor shape.
We analyzed every U.S. states most recent CAFR to determine how much debt it was carrying, based total assets, total liabilities, deferred outflows of resources and deferred inflows of resources. Deferrals are not assets or liabilities. They also are not revenues or expenses. While revenues are inflows of resources and expenses outflows of resources, they are related to the period in which they occur. Deferred inflows of resources and deferred outflows of resources are related to some period in the future. A states net position is calculated by total assets and deferred outflows minus total liabilities and deferred inflows.
Read on to find out which states have the most debt and which states have the least in 2020.
Who Decides How Much Interest The Us Pays On Its Debt
Supply and demand. In other words, the marketplace. When the government needs to raise debt financing, it sells debt securities in an auction. Bidders offer to buy the debt for a specific rate, yield, or discount margin, and all successful bidders receive the highest yield or discount the Treasury accepts. Government debt buyers may include central banks, though their goal is typically to foster sustainable economic growth rather than to finance deficit spending.
Read Also: How To Tell If Someone Filed Bankruptcy
The Pandemic Impact On Debt
The less your income, the easier it is to pile up debt. That obvious lesson hit home in 2020.
The unemployment rate went from 3.5% pre-COVID to a peak of 14.8% in April 2020the highest level since 1948.
The total U.S. consumer debt balance grew $800 billion, according to Experian. That was an increase of 6% over 2019, the highest annual growth jump in over a decade.
Student loan debt increased the most , followed by mortgage debt and personal loan debt .
But dropped $73 billion, a 9% decrease from 2019 and the first annual drop in eight years.
A November 2020 Experian survey showed that 66% of consumers were spending the same or less during the pandemic than they had in 2019. About 33% of those surveyed said they put more in savings in 2020 than they did in the last year.
Income Security And Covid
Income security spending of $1.6 trillion was boosted by $569.5 billion in pandemic relief payments and $79 billion in child tax credit payments. It also included $397.9 billion for unemployment compensation, $168.1 billion on food and nutrition assistance, $89.8 billion in housing assistance, and $156.1 billion in federal employee retirement and disability costs.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have A Bankruptcy Removed From Your Credit Report
States With The Highest Debt Amount
California is the most indebted state with an outstanding debt of $152.80 billion during the 2019 fiscal year. New York comes second with an outstanding debt of $139.20 billion. Although the two states have a high Gross State Product of $3091.2 billion and $ 1738.4 billion respectively, making them the richest states, their burden of debts is enormous. The two states require huge amounts to reimburse the debts each year, a factor that has dwarfed development.
Massachusetts is ranked third with a debt of $77.0 billion followed closely by New Jersey with an outstanding debt of $65.90 billion. Illinois is ranked fifth with an outstanding debt of $61.80 billion. Texas, Pennsylvania, and Connecticut follow each other with a debt of $51.0 billion, $47.5 billion and $38.8 billion respectively. The States of Michigan, Ohio, and Washington have debts of $33.5 billion each.
However, it is worth noting that there are states with relatively very little outstanding debts. The bottom on the list is Wyoming with owing only $ 0.8 billion. Nebraska, Montana and North Dakota have a debt of $2.0 billion, $2.80 billion and $2.90 billion. The other states ranked low in terms of the debt are Nevada, Idaho, Vermont, and South Dakota. These states are also among the least populated states in the country.
Consumer Debt Trends Across The Us
Consumer personal debt can vary significantly depending on where you live. To illustrate the differences between states, particularly those with the highest and lowest levels of personal debt compared to income levels, we’ve listed the national debt averages for mortgages, student loans, auto loans and credit cards for individuals with each debt type. For Americans who carry mortgages, their home financing debt is more than 10 times the amount of the average auto loan. That mortgage number can climb drastically if the state has a competitive housing market and strong economytwo major factors that can determine how much individuals need to borrow to afford a home. Therefore, the more expensive the state, the more debt load they may have.
| Average Personal Income and Debt Among U.S. Consumers | |
|---|---|
| Average ratio of personal debt compared with income | 1.50 |
You May Like: When Does Bankruptcy Clear From Credit Report
Why The Federal Reserve Owns Treasurys
As the nation’s central bank, the Federal Reserve is in charge of the country’s credit. It doesn’t have a financial reason to own Treasury notes. So why does it?
The Federal Reserve actually tripled its holdings between 2007 and 2014. The Fed had to fight the 2008 financial crisis, so it ramped up open market operations by purchasing bank-owned mortgage-backed securities. The Fed began adding U.S. Treasurys in 2009. It owned $1.6 trillion, by 2011, maxing out at $2.5 trillion in 2014.
This quantitative easing stimulated the economy by keeping interest rates low and infusing liquidity into the capital markets. It gave businesses continued access to low-cost borrowing for operations and expansion.
The Fed purchased Treasurys from its member banks, using credit that it created out of thin air. It had the same effect as printing money. By keeping interest rates low, the Fed helped the government avoid the high-interest-rate penalty it would incur for excessive debt.
The Fed ended quantitative easing in October 2014. Interest rates on the benchmark 10-year Treasury note rose from a 200-year low of 1.43% in July 2012 to around 2.17% by the end of 2014 as a result.
The Federal Open Market Committee said the Fed would begin reducing its Treasury holdings in 2017. But it purchased Treasurys again just a few years later.