What Are The Policy Options For Dealing With The Debt
Politicians and policy experts have put forward countless plans over the years to balance the federal budget and reduce the debt. Most include a combination of deep spending cuts and tax increases to bend the debt curve.
Cut spending. Most comprehensive proposals to rein in the debt include major spending cuts, especially for growing entitlement programs, which are the main drivers of future spending increases. For instance, the 2010 Simpson-Bowles plan, a major bipartisan deficit-reduction plan that failed to win support in Congress, would have put debt on a downward path and reduced overall spending, including military spending. It also would have reduced Medicare and Medicaid payments and put Social Security on a sustainable footing by reducing some benefits and raising the retirement age. However, Biden plans to address gaps in the U.S. social safety net, which could increase demand for more long-term funding.
Some optimists believe that the federal government could continue expanding the debt many years into the future with few consequences, thanks to the deep reservoirs of trust the U.S. economy has accumulated in the eyes of investors. But many economists say this is simply too risky. The debt doesnt matter until it does, says Maya MacGuineas, president of the bipartisan Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget. By taking advantage of our privileged position in the global economy, we may well lose it.
What Is The Debt Ceiling
The debt ceiling is the legal limit set by Congress on how much the Treasury Department can borrow, including to pay debts the United States already owes. Since it was established during World War I, the debt ceiling has been raised dozens of times. In recent years, this once routine act has become a game of political brinkmanship that has brought the United States near default on several occasions, CFRs Roger W. Ferguson Jr. writes. Ferguson and other experts argue that the debt ceiling should be scrapped entirely. The only other advanced economy to have one is Denmark, and it has never come close to reaching its ceiling.
Why Is The Us In Debt To China
The U.S. doesn’t restrict who may buy its securities. China invests in U.S. debt because of the positive effect these low-risk, stable investments can have on its economy. By investing in dollar-denominated securities, the value of the dollar increases relative to the value of China’s currency, the yuan. This, in turn, makes Chinese goods cheaper and more attractive than U.S. goods to buyers. That increases sales and strengthens the economy.
Also Check: Amazon Pallets For Sale Miami
How Does The Federal Debt Work
The government finances the operation of the different federal agencies by issuing treasuries. The Treasury Department is in charge of issuing enough savings bonds, Treasury bonds, and Treasury inflation-protected securities to finance the government’s current budget.
Revenues generated by taxes are used to pay the bonds that come to maturity. Investors, including banks, foreign governments and individuals, can cash in on these bonds when they reach maturity. The debt ceiling is the cap that is set on what the Treasury Department can issue.
Congress keeps raising the debt ceiling to finance government spending. A deficit occurs when spending increases faster than revenues.
Us Debt Hits Record: Should You Worry
Earlier this week, US gross national debt hit a new high, clocking $31 trillion. Gasp! Thats almost twice what it was a decade ago, and debt is now equal to well over 100% of GDP, hovering at the highest levels since World War II.
Is steadily rising US debt a problem, or is the risk of a financial meltdown overblown? Heres a quick guide to the debate over debt.
First, what is it? When the federal government spends more than it raises through tax revenue, it runs a deficit. Those deficits are financed by selling Treasury bonds to investors. The US government promises to buy back the bonds by a certain date and repays the interest in the meantime. The total amount of money that the US owes to its creditors is the gross national debt. It rises when the government spends more or has to pay higher interest rates, and falls when the government takes in more revenue either because of higher taxes or stronger economic growth .
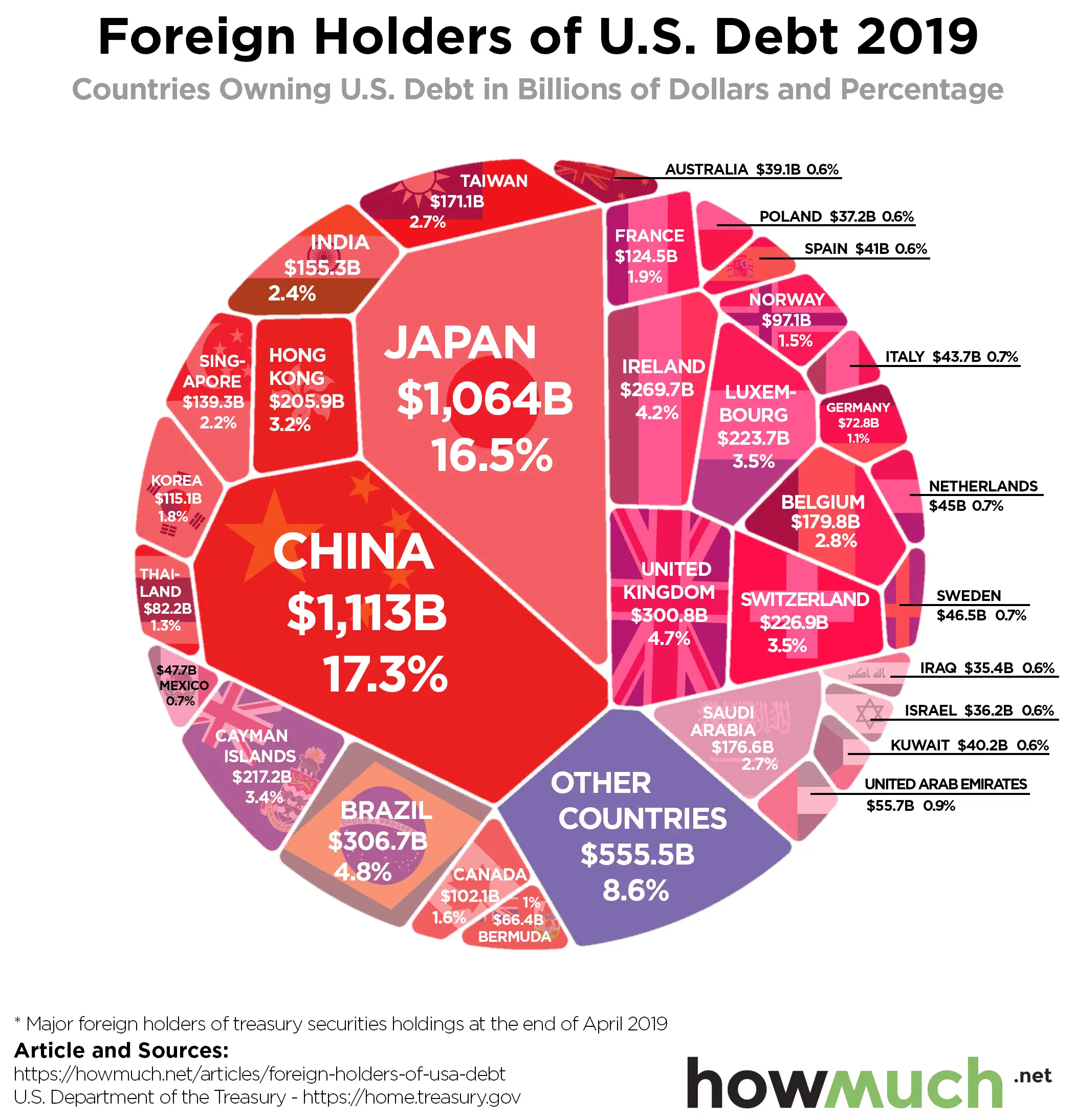
Who holds it? Government agencies hold some of it, but more than three quarters of US debt is held by the public, which includes private investors as well as foreign governments. Foreign governments currently hold about $7 trillion of it, with China , Japan , and the UK the top three creditors.
How can the US keep doing this? The strength of the US economy and the fact that the dollar is the worlds most widely used currency mean that people and governments around the world see US treasuries as safe investments.
Read Also: How To File Bankruptcy In Oklahoma
Us Debt By Presidential Term
The national debt between the Ronald Reagan era and Bill Clintons administration slowly increased, but it nearly doubled during the presidential term of George W. Bush to more than $9 trillion.
Here, then, is a brief timeline of how American debt has grown since John Hancock signed the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776.
What Is The Current National Debt
As of June 23, 2022, the total U.S. national debt was $30.4 trillion, after crossing the $30 trillion mark for the first time in February. At the end of 2019, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the national debt was $23 trillion. One year later, it had risen to $27.7 trillion. Since then, it has increased by more than $2 trillion.
Read Also: How To Declare Bankruptcy In Western Australia
Who Decides How Much Interest The Us Pays On Its Debt
Supply and demand. In other words, the marketplace. When the government needs to raise debt financing, it sells debt securities in an auction. Bidders offer to buy the debt for a specific rate, yield, or discount margin, and all successful bidders receive the highest yield or discount the Treasury accepts. Government debt buyers may include central banks, though their goal is typically to foster sustainable economic growth rather than to finance deficit spending.
Negative Real Interest Rates
Since 2010, the U.S. Treasury has been obtaining negative real interest rates on government debt, meaning the inflation rate is greater than the interest rate paid on the debt. Such low rates, outpaced by the inflation rate, occur when the market believes that there are no alternatives with sufficiently low risk, or when popular institutional investments such as insurance companies, pensions, or bond, money market, and balanced mutual funds are required or choose to invest sufficiently large sums in Treasury securities to hedge against risk. Economist Lawrence Summers states that at such low interest rates, government borrowing actually saves taxpayer money and improves creditworthiness.
In the late 1940s through the early 1970s, the U.S. and UK both reduced their debt burden by about 30% to 40% of GDP per decade by taking advantage of negative real interest rates, but there is no guarantee that government debt rates will continue to stay this low. Between 1946 and 1974, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio fell from 121% to 32% even though there were surpluses in only eight of those years which were much smaller than the deficits.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Bankruptcy Lower Your Credit Score
Revolutionary War Kicks Off Us Debt
Wars were always a major debt factor for our nation. Congress could not finance the Revolutionary war with large tax raises, as the memory of unjust taxation from the British stood fresh in the minds of the American public. Instead, the Continental Congress borrowed money from other nations.
The founders led negotiations with Benjamin Franklin securing loans of over $2 million from the French Government and President John Adams securing a loan from Dutch bankers. We also borrowed from domestic creditors. While the war was still going on, in 1781, Congress established the U.S. Department of Finance.
Two years later, as the war ended in 1783, the Department of Finance reported U.S. debt to the American Public for the first time. Congress took initiative to raise taxes then, as the total debt reached $43 million.
Cori Bush Condemns Gops Ongoing Attacks On Student Debt Relief
As a federal court in her home state of Missouri heard arguments Wednesday in a case that could determine the fate of federal student debt cancellation, Democratic Rep. Cori Bush condemned GOP attorneys general for attempting to tank much-needed economic relief for tens of millions of borrowers.
Efforts to undermine the Biden administrations student loan cancellation program are the latest example of Republicans and student loan servicers prioritizing profits over people and corporations over constituencies, Bush said in a statement as a group of GOP attorneys general including Missouri AG Eric Schmitt made their case for an injunction against student debt forgiveness.
The Republican plaintiffs claim in their lawsuit that the Biden administrations student debt cancellation plan would harm the Missouri Higher Education Loan Authority by depriving it of the ongoing revenue it earns from servicing privately held Federal Family Education Loan Program loans.
In an effort to undercut such legal claims of harm, the Biden administration decided last month to scale back its debt forgiveness program to exclude many student borrowers with FFELP loans, denying relief to hundreds of thousands of people.
At least one of the lawsuits against the debt relief program has already been struck down.
Recommended Reading: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Credit Rating
Top 10 Countries The Us Owes Money To
In 1989, New York real estate investor Seymour Durst spent $120,000 to erect a “National Debt Clock” in Times Square to track the exact amount of money that the U.S. federal government was borrowing to pay its bills. At the time, the country had run up a $2.7 trillion tab, but that figure seems almost quaint today. In 2008, the clock briefly ran out of available digits when the debt topped $10 trillion. By June 2021, the upgraded clock which can now display up to a quadrillion dollars registered more than $28 trillion .
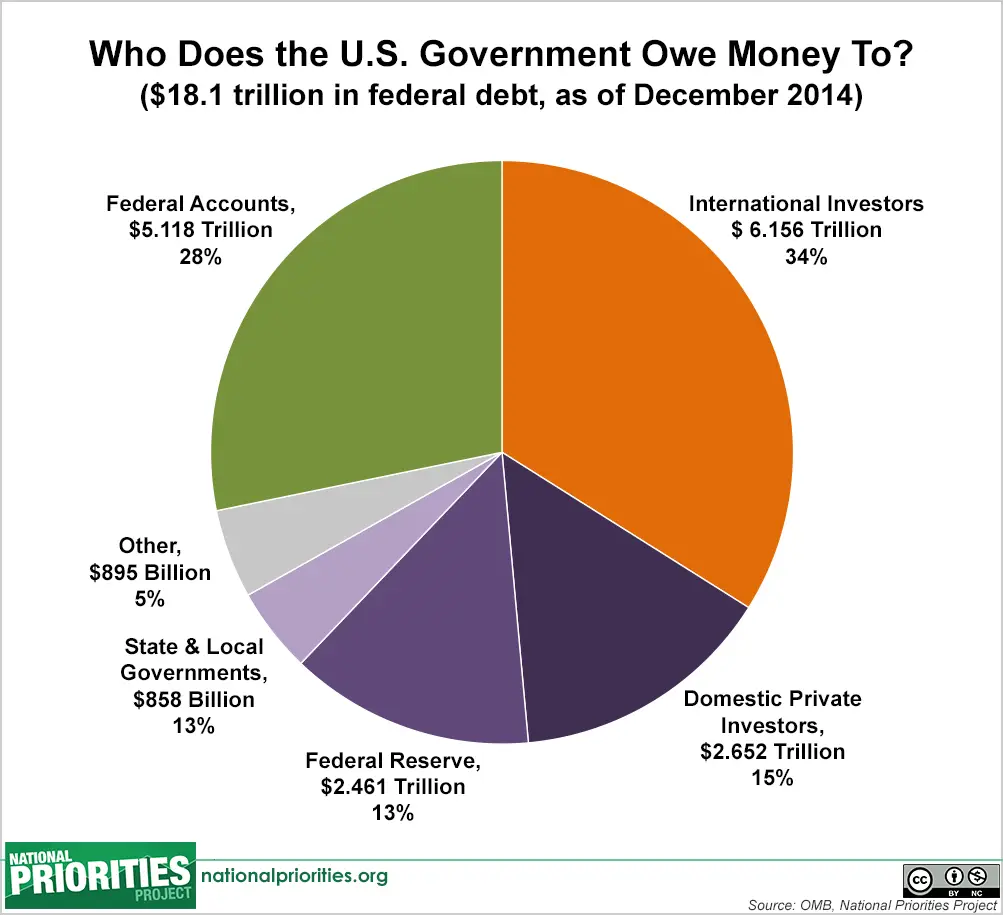
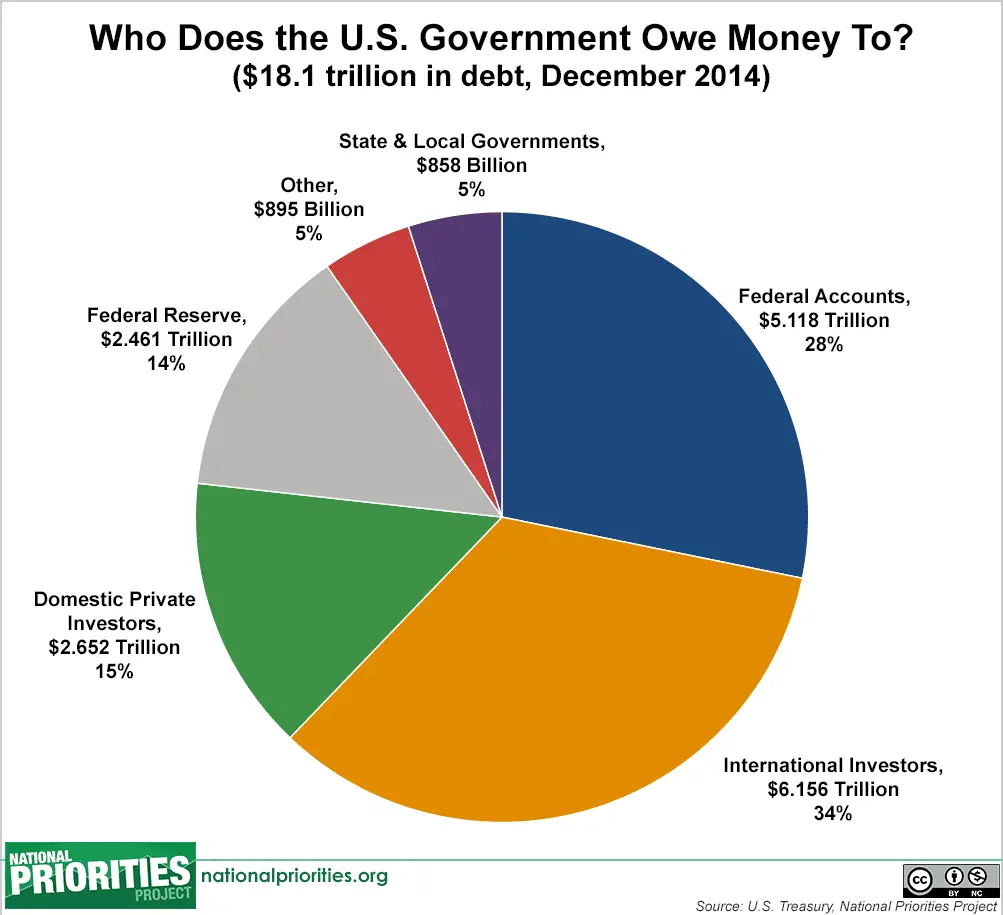
Now, it’s important to understand that U.S. doesn’t owe that entire $28 trillion to its creditors, which include individuals, businesses and foreign governments who purchased U.S. Treasury bonds and securities. More than 20 percent of the national debt, or $6.2 trillion, is incurred for intragovernmental holdings, which are funds the U.S. government owes itself, mainly for the Social Security and Medicare trust funds . In June 2021, these two trust funds alone accounted for some $2.4 trillion of the national debt.
But the question we want to answer today is, who owns the bulk of that $28 trillion in public debt? You can find out by perusing our global parade of America’s biggest sugar daddies, according to the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
Contents
Whats The Difference Between Deficit And Debt
Every year, Congress passes a budget outlining the expenses the government is liable for costs of the countrys federal programs and services. And each year, mostly around April 15, the government collects revenue from taxes.
If expenses outweigh revenues in any given year, a deficit is created. For 2012, the deficit was about $1.2 trillion.
That means the country is in the red for that amount. We are obligated to spend more money for last years costs than we have in the treasury. So to pay our bills and prevent going into default, the government must borrow enough to make up for the shortfall.
The national debt is the sum total of all our yearly national deficits.
For all those who decry such national accounting after all, were hardly permitted to carry on this way with our personal finances, are we? fear not. America has carried a national debt for almost its entire existence. Even when there is no deficit for a particular year in years when the economy is booming, we often have budget surpluses there is still an accumulated debt on the books.
Today the national debt is $16.4 trillion. We owe that amount to all those from whom we have borrowed over the years, allowing us to pay our bills and obligations in a timely manner.
Read Also: How To Find Foreclosure Auctions
How Is The Covid
In response to the pandemic, the federal government has spent trillions of dollars to boost the economy, including on stimulus checks for citizens and aid for businesses and state and local governments. According to the Congressional Budget Office , these measures swelled the federal deficit to $3.1 trillion in 2020, about 15 percent of GDP and the highest level since World War II. Even before the pandemic, the CBO projected that annual deficits would breach the $1 trillion mark in 2020 and remain above that level indefinitely.
More on:
Debt held by the publicthe measure of how much the government owes to outside investorswas $16.9 trillion in 2019. That was more than double the amount in 2007, an increase to almost 80 percent of GDP from 35 percent. Before accounting for spending to combat COVID-19, publicly held U.S. debt was set to nearly double to more than $29 trillion over the next decade. Now, it is about $22 trillion, and its projected to be double the size of the economy by 2051.
Taking National Debt Personally
While voters are not fans of national debt on principle, the debt-to-GDP ratio makes for a lackluster rallying point in practice, since even economists can’t agree on what percentage is too high.
Hence efforts to frame the national debt burden in easily understood terms. One popular tactic is to divide national debt by the population to determine debt per capita. Dividing the U.S. national debt of $30.5 trillion as of July 2022 by an estimated U.S. population of 332.4 million as of Jan. 1, 2022 yields national debt per capita of nearly $92,000, which sounds like a lot.
Fortunately, the per capita apportionment of government debt ignores the fact that no individual, not even a child, can hope to repay debt in a currency they create, the way the U.S. government and many other sovereign borrowers do. The improbability of default by a sovereign borrowing in its own currency is what marks out such debt as a “safe asset” relative to credit issued to private borrowers. In this sense, national debt can be thought of as an interest-bearing currency supplementing the interest-free banknotes. Like currency, national debt is a government obligation serving as an asset and store of value for its owners.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Way To Reestablish Credit After Bankruptcy
What Makes The Debt Bigger
The leading federal spending categories currentlySocial Security, Medicare/Medicaid and defenseare the same as in the 1990’s, when national debt was much lower relative to GDP. The U.S. remains the world’s largest economy and one of the richest countries. How, then, did the debt situation deteriorate? Numerous factors are in play.
Wars In Iraq And Afghanistan
Overseas wars and military operations launched after the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks in the U.S., in combination with increased domestic security spending, interest costs, and long-term veterans funding obligations, has added about $8 trillion to the national debt since 2001, by one estimate.
Meanwhile, annual U.S. military spending exceeds that of the next nine highest spenders combined.
Don’t Miss: Do Medical Bills Go Away With Bankruptcy
What To Read Next
-
Mitt Romney says a billionaire tax will trigger demand for these two physical assets get in now before the super-rich swarm
-
House Democrats have officially drafted a bill that bans politicians, judges, their spouses and children from trading stocks but here’s what they’re still allowed to own and do
-
Biggest crash in world history’: Robert Kiyosaki issues another dire warning and now avoids anything that can be printed here are 3 hard assets he likes instead
This article provides information only and should not be construed as advice. It is provided without warranty of any kind.
Public Debt And Intragovernmental Holdings
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past events that have had a lasting impact.
The Social Security Trust Fund owns a significant portion of U.S. national debt, but how does that work and what does it mean? Below, we’ll dive into who actually owns the U.S. national debt and how that impacts you.
Also Check: How Long Does A Bankruptcy Stay On Your File
Is The National Debt A Problem
Economists and lawmakers frequently debate how much national debt is appropriate. Most agree that some level of debt is necessary to stimulate economic growth and that there is a point at which the debt can become a problem, but they disagree about where that point is. If the debt does get too big, it can result in cuts to government programs, tax hikes, and economic turmoil.
States With The Least Debt
1. Texas
Texas has the lowest debt of any state in the U.S. Texas’s total liabilities add up to $222.64 billion, and its total assets add up to $356.01 billion, giving Texas the highest net position in the country of $115.08 billion. Texas’s debt ratio is 62.5%
2. Florida
Florida’s debt is the second-lowest in the country. With total liabilities coming out to $66.78 billion and total assets coming out to $163.24 billion, Florida’s net position is $97.6 billion. This means that Florida’s debt ratio is 40.9%. While Floridas debt has decreased in recent years, it is expected to increase over the next two years.
3. Alaska
Alaska has the third-lowest debt and the third-highest net position of $76.74 billion. Alaska’s total liabilities add up to $12.65 billion, and its total assets add up to $89.17 billion. Although Alaska does not have a state income tax, its revenue is well-supplied by taxes on oil and gas production.
Also Check: How Many Times Can I File Bankruptcy