The Role Of Government
What role the government should play in managing the debt is contested. Some policymakers place a lower emphasis on this problem, while some see the debt as a dangerous symptom of out-of-control spending. Those who view the debt as a serious problem tend to fall into two lines of thought: seek spending restraint and new rules to enforce it, or expand the power of the federal government by raising taxes and imposing controls on the industries contributing most, such as healthcare.
What The National Debt Means To You
The national debt level has been a significant subject of controversy for U.S. domestic policy. Given the amount of fiscal stimulus pumped into the U.S. economy over the past couple of years, it is easy to understand why many people are starting to pay close attention to this issue. Unfortunately, the manner in which the debt level is conveyed to the general public is usually very obscure. Couple this problem with the fact that many people do not understand how the national debt level affects their daily lives, and you have a centerpiece for discussion.
Stock Market Crash & The Great Depression
On October 29, 1929, wild speculation and rapid expansion finally caught up with Wall Street. The Black Tuesday stock market crash resulted in billions of dollars lost. In its aftermath, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled into the Great Depression, which lasted until 1939. It was the deepest and longest-lasting economic downturn in the U.S. up to that time.
National Debt: $17 billion
Also Check: Can You Keep Your House If You File Bankruptcy
What Causes The National Debt To Increase
Sometimes the government needs to increase spending to stabilize the economy, and protect Americans and businesses from unexpected economic conditions.
During The Great Recession , for example, Congress passed legislation injecting $1.8 trillion into the economy. But that pales in comparison to the $4.5 trillion the Trump and Biden administrations have pumped into the economy since the Covid pandemic began in March 2020.
However, there are other reasons the national debt increases, even during years where spending is moderate and the economy is in good shape.
Us Debt Crisis Of 2008 Explained
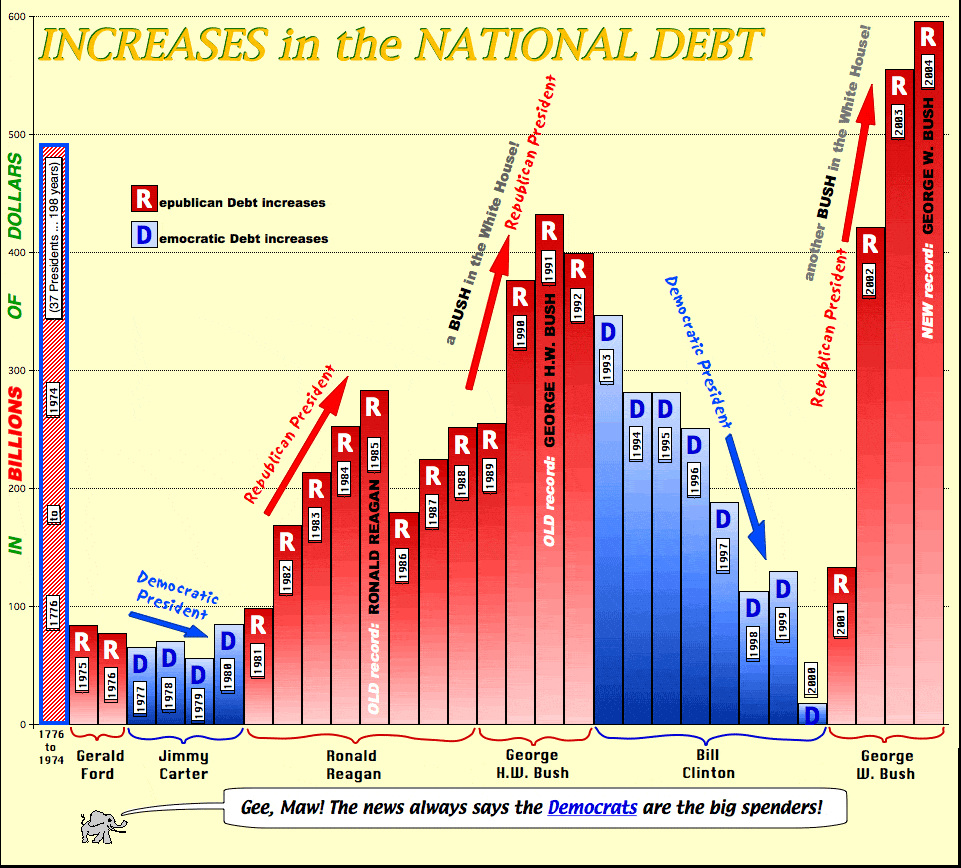
Democrats and Republicans in Congress created a recurring debt crisis by fighting over ways to curb the debt. Democrats blamed the Bush tax cuts and the 2008 financial crisis, both of which lowered tax revenues. They advocated increased stimulus spending or consumer tax cuts.
The resultant boost in demand would spur the economy out of recession and increase GDP and tax revenues. In other words, the United States would do as it did after World War II and grow its way out of the debt crisis. That strategy is called the Keynesian economic theory.
Republicans advocated further tax cuts for businesses, which would invest the saved tax money in expanding and subsequently create new jobs. That theory is called supply-side economics.
Both sides lost focus. They concentrated on the debt instead of continued economic growth. Whether Congress lowers taxes or increases spending is not worth arguing about until the economy is in the expansion phase of the business cycle. The most important thing is to take aggressive action to restore business and consumer confidence, to fuel the economic engine.
Both parties compounded the crisis by arguing over how much to cut spending. They fought over cutting from defense or entitlement programs such as Social Security and Medicare. To recover from a recession, government spending should remain consistent. Any cuts will remove liquidity and raise unemployment through government layoffs.
Read Also: How Filing Bankruptcy Affects Your Credit
How Is The Covid
In response to the pandemic, the federal government has spent trillions of dollars to boost the economy, including on stimulus checks for citizens and aid for businesses and state and local governments. According to the Congressional Budget Office , these measures swelled the federal deficit to $3.1 trillion in 2020, about 15 percent of GDP and the highest level since World War II. Even before the pandemic, the CBO projected that annual deficits would breach the $1 trillion mark in 2020 and remain above that level indefinitely.
More on:
Debt held by the publicthe measure of how much the government owes to outside investorswas $16.9 trillion in 2019. That was more than double the amount in 2007, an increase to almost 80 percent of GDP from 35 percent. Before accounting for spending to combat COVID-19, publicly held U.S. debt was set to nearly double to more than $29 trillion over the next decade. Now, it is about $22 trillion, and its projected to be double the size of the economy by 2051.
Major Events And The Impact On Us Debt
It helps to consider the national debt in context. During times of war, the U.S. increases military spending. When the economy is down, the federal government uses spending and tax cuts to spur growth. When these expansionary fiscal policies boost economic growth, higher tax revenues can be used to pay back the debt.
Heres a timeline of the national debt by year, and how it compares to national events.
Also Check: How To Claim Bankruptcies In Canada
Voluntary National Content Standards In Economics
CONTENT STANDARD 1
Students will understand that productive resources are limited. Therefore, people cannot have all the goods and services they want as a result, they must choose some things and give up others.
- Benchmark 1: Choices made by individuals, firms, or government officials often have long-run unintended consequences that can partially or entirely offset the initial effects of their decisions.
CONTENT STANDARD 16
Students will understand that there is an economic role for government to play in a market economy whenever the benefits of a government policy outweigh its costs. Governments often provide for national defense, address environmental concerns, define and protect property rights, and attempt to make markets more competitive. Most government policies also redistribute income.
- Benchmark 8: Governments provide an alternative method to markets for supplying goods and services when it appears that the benefits to society of doing so outweigh the costs to society. Not all individuals will bear the same costs or share the same benefits of those policies.
CONTENT STANDARD 20
Students will understand that federal government budgetary policy and the Federal Reserve Systems monetary policy influence the overall levels of employment, output, and prices.
What Is The National Debt
The national debt is the debt that the federal government holds – this includes public debt, federal trust funds, and various government accounts. In simpler terms, the national debt includes both what the government owes others and owes itself. This is the total amount of deficit that the government has accumulated over the years.
The national debt today stands at more than $30.2 trillion. Here are some facts to give you an idea of how big this number really is:
- With $23.8 trillion held by the public, the government could give $71,000 per U.S. citizen.
- From 2000 to 2019, the federal debt increased 297%.
- $23.8 trillion is about the size of the economies of China, Japan, and Germany combined – the three largest economies in the world after the united States.
- $23.8 trillion is enough to cover a four year college degree for every American high school graduate for the next 57 years.
You May Like: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Buying A House
What Causes The National Debt
The national debt is caused by government spending. This causes a budget deficit, but its necessary to help expand the economy. This is known as expansionary fiscal policy. The government expands the money supply in the economy and uses budgetary tools to either increase spending or cut taxes. This provides consumers and businesses with more money to spend, which, in turn, boosts economic growth over the short term.
The federal government pays for things like defense equipment, health care, and construction. It contracts with private firms that then hire new employees or the government hires employees directly. Those employees then spend their paychecks on gasoline, groceries, and new clothes. That consumer spending boosts the economy.
But in order to boost the economy, the government must spend money, which adds to the national debt.
Forms Of Government Borrowing
In addition to selling Treasury bills, notes, and bonds, the U.S. government borrows by issuing Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities and Floating Rate Notes . Its borrowing instruments also include savings bonds as well as the government account securities representing intergovernmental debt.
Other nations have borrowed from international organizations like the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank as well as private financial institutions.
Recommended Reading: File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Online
How The National Debt Affects You
When the national debt is below the tipping point, government spending continues and contributes to a growing economy, which means more funding for programs that you can take advantage of.
But when the debt exceeds the tipping point, your standard of living could be impacted. Interest rates may increase and that could slow the economy. The stock market could react to a lack of investor confidence, which could mean lower returns on your investments. And a recession may even be possible.
This also puts downward pressure on a countrys currency because its value is tied to the value of the countrys bonds. As the currencys value declines, foreign bond holders’ repayments are worth less. That further decreases demand and drives up interest rates. As the currencys value declines, goods and services may become more expensive and that contributes to inflation.
How Does Us Debt Compare To That Of Other Countries
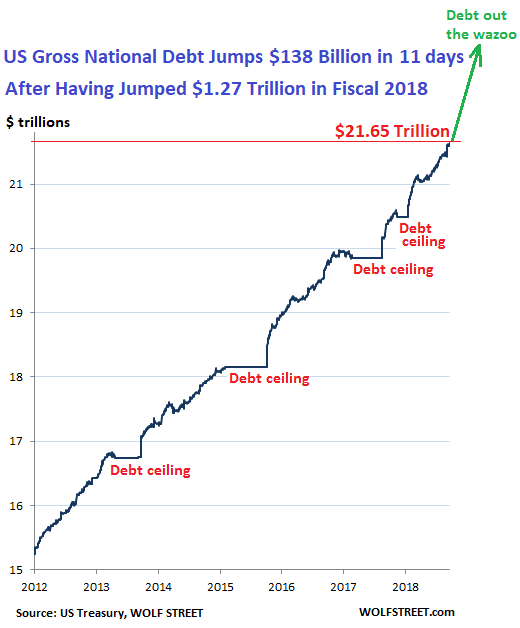
The United States debt-to-GDP ratio is among the highest in the developed world. Among other major industrialized countries, the United States is behind only Japan.
The pandemic has sharply increased borrowing around the world, according to the International Monetary Fund. Among advanced economies, debt as a percentage of GDP has increased from around 75 percent to nearly 95 percent, driven by double-digit increases in the debt of the United States, Canada, France, Italy, Japan, Spain, and the United Kingdom .
The United States has long been the worlds largest economy, with no record of defaulting on its debt. Moreover, since the 1940s it has been the worlds reserve-currency country. As a result, the U.S. dollar is considered the most desirable currency in the world.
High demand for the dollar has helped the United States finance its debt, as many investors put a premium on holding low-risk, dollar-denominated assets such as U.S. Treasury bills, notes, and bonds. Steady demand from foreign creditorslargely central banks adding to their dollar reserves, rather than market investorsis one factor that has helped the United States to borrow money at relatively low interest rates. This puts the United States in a more secure position for a fiscal fight against COVID-19 compared to other countries.
Recommended Reading: What Is Your Credit Score After A Bankruptcy
What School Was Like In The 13 Colonies
During the Civil War, the national debt ballooned to some $2.76 billion by 1866. Economic growth in the late 19th century, accompanied by inflation, helped make debt a smaller percentage of economic output. But after World War I, the debt-to-GDP ratio hit a record high 33 percent, with a debt of more than $25 billion .
World War I also saw a major shift in control over the national debt, as Congress agreed to give the Treasury Department more flexibility in raising money through sales of its bonds. Though it ceded its right to approve or disapprove of each individual sale, Congress would set an overall limit to that borrowing, known as the debt ceiling.
Congress has since raised or lowered the debt ceiling, or the maximum amount of outstanding debt that the federal government can legally incur, numerous times.
Looking To The Future
Now that we have seen what the historical picture of the debt, deficits, mandatory spending, discretionary spending, and revenues look like, lets look at projected spending levels and deficits for 20202030. Figure 16 shows that:
- Federal spending as a percentage of GDP is projected to increase from 21% to about 23.5% during the 2020s.
- The projected increase in spending will culminate in a projected deficit increase of about 1% of GDP per year, from just under 5% to just under 6%.
- The growth will be driven by increases in mandatory spending, which is projected to increase from just under 13% to just over 15% of GDP per year.
- Net interest on the debt is also projected to increase during the 2020s from under 2% to over 2.5% of GDP per year.
- Discretionary spending is projected to continue its decline from 6.25% to 5.6% per year.
- Increases in the deficit are likely to be driven primarily by the increases in mandatory spending.
There are several reasons to have concerns about the current and projected path of government spending and revenues and the corresponding additional debt with these deficits.
The amount the government borrows each year may impact credit markets, which may slow economic growth.
You May Like: J And J Bankruptcy
Us Starts Fiscal Year With Record $31 Trillion In Debt
WASHINGTON The nations gross national debt has surpassed $31 trillion, according to a U.S. Treasury report released Tuesday that logs Americas daily finances.
Edging closer to the statutory ceiling of roughly $31.4 trillion an artificial cap Congress placed on the U.S. governments ability to borrow the debt numbers hit an already tenuous economy facing high inflation, rising interest rates and a strong U.S. dollar.
And while President Joe Biden has touted his administrations deficit reduction efforts this year and recently signed the so-called Inflation Reduction Act, which attempts to tame 40-year high price increases caused by a variety of economic factors, economists say the latest debt numbers are a cause for concern.
Owen Zidar, a Princeton economist, said rising interest rates will exacerbate the nations growing debt issues and make the debt itself more costly. The Federal Reserve has raised rates several times this year in an effort to combat inflation.
Zidar said the debt should encourage us to consider some tax policies that almost passed through the legislative process but didnt get enough support, like imposing higher taxes on the wealthy and closing the carried interest loophole, which allows money managers to treat their income as capital gains.
Dont Miss: Banks That Do Debt Consolidation Loans
The Impact Of Covid 19
In response to the coronavirus pandemic, the federal government passed several bills to try to address the health-related issues associated with the pandemic as well as the pandemics effect on the economy. The passage of bills to address the pandemic began on March 6th and continues as of the writing of this unit. Today these measures have totaled over $2 Trillion.
- The response by the federal government increased the projected deficit to GDP ratio from nearly 5% of GDP to almost 20 percent of GDP in 2020.
- It is also anticipated that the deficit will be nearly 10% of GDP in 2021.
- The increase has pushed the debt held by public-to-GDP ratio from an expected 80 percent of GDP to over 100 percent of GDP.
- The pandemic has also increased total projected deficits for 20202030 from 16.9 trillion dollars to 23.9 trillion dollars .
Figure 10 and Figure 11 are taken directly from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget and show how big of an impact COVID-19 has had on federal deficits and the debt based on their models .
Figure 10: Projected Impact of COVID-19 on Federal Deficits
Figure 11: Projected Impact of COVID-19 on the Federal Debt
Also Check: Will Filing Bankruptcy Affect Me Buying A House
The Types Of Presidential Decisions That Impact National Debt
Presidents can have a tremendous impact on the national debt. They can also have an impact on the debt in another presidentâs term. When President Trump took office in January of 2017, for the first nine months of his presidency, he operated under President Obamaâs budget which didnât end until September, 2017. So for most of a new presidentâs first year in office, he isnât accountable for the spending that takes place. As strange as this may seem, itâs actually by design to allow time for the new president to put a budget together when in office.
A Brief History Of Us Debt
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
Nearly all national governments borrow money. The U.S. has carried national debt throughout its history, dating back to the borrowing that financed the Revolutionary War. Since then the debt has grown alongside the economy, as a result of increased government responsibilities, and in response to economic developments.
You May Like: How Old Does Debt Have To Be To File Bankruptcy
National Debt And Budget Deficit
The federal government creates an annual budget that allocates funding towards services and programs for the country. This is made up of mandatory spending on government-funded programs, discretionary spending on areas such as defense and education, and interest on the debt. The budget deficit can be thought of as the annual difference between government spending and revenue. When the government spends more money on programs than it makes, the budget is in deficit.
Solutions To Reduce The National Debt
76% of voters believe that the President and Congress should allocate more time and energy towards addressing the national debt. Americans care about the national debt, and some work has been done in order to address this issue. Solutions include raising revenue , cutting spending, and growing the countrys GDP.
Policy options such as the Simpson-Bowles plan and the Domenici-Rivlin Task Force have made efforts to create plans to reduce the national debt. Centers and institutes such as the American Enterprise Institute, Bipartisan Policy Center, Center for American Progress, and Economic Policy Institute all proposed things ranging from slow growth to reduction in benefits for high-income individuals.
Young people across America are getting educated about fiscal policy and making changes at their colleges and universities with Up to Us. Sign the pledge to let local representatives know that you are concerned about the nations fiscal future, or get involved by learning about how you can make a difference in your own community.
Don’t Miss: What Happens After Bankruptcy Is Dismissed