Tracking The Federal Deficit: January 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $165 billion in January, the fourth month of fiscal year 2021. This months deficitthe difference between $552 billion of spending and $387 billion of revenuewas $132 billion greater than last Januarys. But federal finances deteriorated more than the raw numbers suggest. Adjusting for shifts in the timing of some payments, the deficit this January would have been $211 billion greater than last Januarys. The federal deficit has now reached $738 billion so far this fiscal year, an increase of 120% over the same point last year . Compared to the same point last fiscal year, cumulative revenues have ticked up 1%, but cumulative spending has surged 27%mostly due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the federal response to it.
Increased spending so far this fiscal year has likewise mostly resulted from pandemic relief. About 60% of the increase in cumulative year-to-date spending has come from refundable tax credits and unemployment insurance benefits . Outlays from the Public Health and Social Services Emergency Fund are also up $26 billion compared to the first four months of fiscal year 2020, and Medicaid spending is $29 billion greater.
Revenues rose 4% from last January, thanks to greater revenue from individual income, payroll, and corporate income tax revenue.
How Is The National Debt Measured
Measuring the national debt can bebroken into three parts: debt held by the public, gross federal debt, and debt subject to limit.
Debt held by the public is the amount of money that the U.S. treasury borrows from external lenders through financial markets. The money gathered funds the governments activities and programs. Many financial analysts and economists think of this portion of the debt as the most meaningful because it focuses on the money that is raised through financial markets. This portion of the debt is made up of two-thirds domestic creditors and one-third foreign creditors. By the end of fiscal year 2021, the debt held by the public was $22.3 trillion.
Gross federal debt includes the public debt and federal trust funds and other government accounts. This is the amount that the government owes other governments and itself. By the end of fiscal year 2021, the gross federal debt was $28.4 trillion .
Debt subject to limit is similar to gross federal debt but does not include debt issued by agencies other than the Treasury and Federal Financing Bank. At the end of fiscal year 2021, this number was $28.4 trillion.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: March 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $658 billion in March 2021, the sixth month of fiscal year 2021. This months deficitthe difference between $267 billion in revenue and $925 billion in spendingwas $487 billion greater than last Marchs . The federal deficit has now swelled to $1.7 trillion in fiscal year 2021, 129% higher than at this point last year. While revenues have grown 6% year-over-year, cumulative spending has surged 45% above last years pacelargely a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, its economic fallout, and the federal governments fiscal response.
Analysis of Notable Trends: Adjusted for timing shifts, outlays in March 2021 were $517 billion greater than last March, an increase of 127%. Unemployment insurance, refundable tax credits, and the Small Business Administrations Paycheck Protection Program accounted for most of the increaseboth from March to March and from last fiscal year to this one. Spending on refundable tax credits was $346 billion higher in March 2021 than March 2020, mostly due to the payment of pandemic recovery rebates authorized by the Consolidated Appropriations Act and American Rescue Plan Act..
Read Also: Can You Get A Bankruptcy Removed From Your Credit Report
Revolutionary War Kicks Off Us Debt
Wars were always a major debt factor for our nation. Congress could not finance the Revolutionary war with large tax raises, as the memory of unjust taxation from the British stood fresh in the minds of the American public. Instead, the Continental Congress borrowed money from other nations.
The founders led negotiations with Benjamin Franklin securing loans of over $2 million from the French Government and President John Adams securing a loan from Dutch bankers. We also borrowed from domestic creditors. While the war was still going on, in 1781, Congress established the U.S. Department of Finance.
Two years later, as the war ended in 1783, the Department of Finance reported U.S. debt to the American Public for the first time. Congress took initiative to raise taxes then, as the total debt reached $43 million.
The Federal Budget Deficit Is Projected To Reach A New Record
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past events that have had a lasting impact.
The U.S. federal budget deficit reached $2.8 trillion for the fiscal year 2021. It was the second-highest deficit since 1945 the 2020 deficit of $3.1 trillion as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic takes the top spot.
Learn more about the factors impacting the federal budget deficit, how it’s calculated, and whether you should be concerned.
You May Like: What Is Bankruptcy Code In India
What Are The Primary Drivers Of Future Debt
The main drivers are still mandatory spending programs, namely Social Securitythe largest U.S. government programMedicare, and Medicaid. Their costs, which currently account for nearly half of all federal spending, are expected to surge as a percentage of GDP because of the aging U.S. population and resultant rising health expenses. Yet, corresponding tax revenues are projected to remain stagnant.
Meanwhile, interest payments on the debt, which now account for nearly 10 percent of the budget, are expected to rise, while discretionary spending, including programs such as defense and transportation, is expected to shrink as a proportion of the budget.
President Trump signed off on several pieces of legislation with implications for the debt. The most significant of these is the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Signed into law in December 2017, it is the most comprehensive tax reform legislation in three decades. Trump and some Republican lawmakers said the bills tax cuts would boost economic growth enough to increase government revenues and balance the budget, but many economists were skeptical of this claim.
The CBO says the law will boost annual GDP by close to 1 percent over the next ten years, but also increase annual budget shortfalls and add another roughly $1.8 trillion to the debt over the same period. In addition, many of the provisions are set to expire by 2025, but if they are renewed, the debt would increase further.
Great Depression And Stock Market Crash
People started investing heavily in the stock market in 1920 unaware that Black Tuesday would dawn with an $8 billion loss in market value when the stock market crashed on October 29, 1929. The United States relied on the gold standard and raised inflation, rather than lowering rates to ease the burden of inflation.
During the following era, income inequality between classes grew. More than 25 percent of the workforce was unemployed, people made purchases on credit and were forced into foreclosures and repossessions.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt developed programs for unemployment pay and social security pensions, along with providing assistance to labor unions. Although Roosevelt addressed many problems in the U.S. economy, the funding for his programs grew the national debt to $33 billion.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Bankruptcy Affect Credit Score
Calculating The Annual Change In Debt
Conceptually, an annual deficit should represent the change in the national debt, with a deficit adding to the national debt and a surplus reducing it. However, there is complexity in the budgetary computations that can make the deficit figure commonly reported in the media considerably different from the annual increase in the debt. The major categories of differences are the treatment of the Social Security program, Treasury borrowing, and supplemental appropriations outside the budget process.
Social Security payroll taxes and benefit payments, along with the net balance of the U.S. Postal Service, are considered “off-budget”, while most other expenditure and receipt categories are considered “on-budget”. The total federal deficit is the sum of the on-budget deficit and the off-budget deficit . Since FY1960, the federal government has run on-budget deficits except for FY1999 and FY2000, and total federal deficits except in FY1969 and FY1998FY2001.
How Much Do Other Countries Owe The Us
Public debt makes up three-quarters of the national debt, and foreign governments and investors make up one-third of public debt. As of , the countries with the most debt owed to the U.S. are Japan, China, the United Kingdom, Luxembourg, and Ireland.
Though China had been the long-standing top placeholder for the country with the most debt owed to the United States, Japan currently holds $1.3 trillion worth of U.S. debt. The second place holder, China, currently holds $1.1 trillion in Treasury holdings. Together, they hold 31% of all foreign-owned U.S. debt.
Also Check: How Many Years Does Bankruptcy Stay On Your Credit Report
Why The Federal Reserve Owns Treasurys
As the nation’s central bank, the Federal Reserve is in charge of the country’s credit. It doesn’t have a financial reason to own Treasury notes. So why does it?
The Federal Reserve actually tripled its holdings between 2007 and 2014. The Fed had to fight the 2008 financial crisis, so it ramped up open market operations by purchasing bank-owned mortgage-backed securities. The Fed began adding U.S. Treasurys in 2009. It owned $1.6 trillion, by 2011, maxing out at $2.5 trillion in 2014.
This quantitative easing stimulated the economy by keeping interest rates low and infusing liquidity into the capital markets. It gave businesses continued access to low-cost borrowing for operations and expansion.
The Fed purchased Treasurys from its member banks, using credit that it created out of thin air. It had the same effect as printing money. By keeping interest rates low, the Fed helped the government avoid the high-interest-rate penalty it would incur for excessive debt.
The Fed ended quantitative easing in October 2014. Interest rates on the benchmark 10-year Treasury note rose from a 200-year low of 1.43% in July 2012 to around 2.17% by the end of 2014 as a result.
The Federal Open Market Committee said the Fed would begin reducing its Treasury holdings in 2017. But it purchased Treasurys again just a few years later.
Government Spending Gdp And The Budget Deficit
A budget deficit occurs when government spending exceeds revenue. The federal government’s revenue is the income it collects from taxes, fees, and investments. When spending is less than revenue, it creates a budget surplus.
The president and Congress overspend on purpose. They realize that the more the government spends, the more it stimulates the economy. Government spending is itself a component of GDP. It is the country’s total economic output for a year.
Read Also: How To Declare Bankruptcy In Maryland
Tracking The Federal Deficit: June 2019
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated an $8 billiondeficit inJune, theninth monthof Fiscal Year 2019, for a total deficit of$746 billionso far this fiscal year. If not for timing shifts of certain payments, Junes deficit would have been $57 billion, which is $28 billion larger than the adjusted deficit forJune 2018. Total revenues so far inFiscal Year 2019increased by3 percent , while spending increased by7 percent , compared to the same period last year.
Analysis of Notable Trends this Fiscal Year to Date: Individual and payroll taxes together rose by 3 percent , reflecting an expanding economy and a low unemployment rate. Furthermore, customs duties increased by 77 percent versus last year, primarily due to the imposition of new tariffs. On the spending side, Social Security expenditures increased by 6 percent compared to last year due to increases in the number of beneficiaries and the average benefit payment. Finally, net interest payments on the federal debt continued to rise, increasing by 16 percent versus last year due to higher interest rates and a larger federal debt burden.
What Is The Current National Debt
![US National Debt (And Related Information) [OC] US National Debt (And Related Information) [OC]](https://www.bankruptcytalk.net/wp-content/uploads/us-national-debt-and-related-information-oc-national-debt.png)
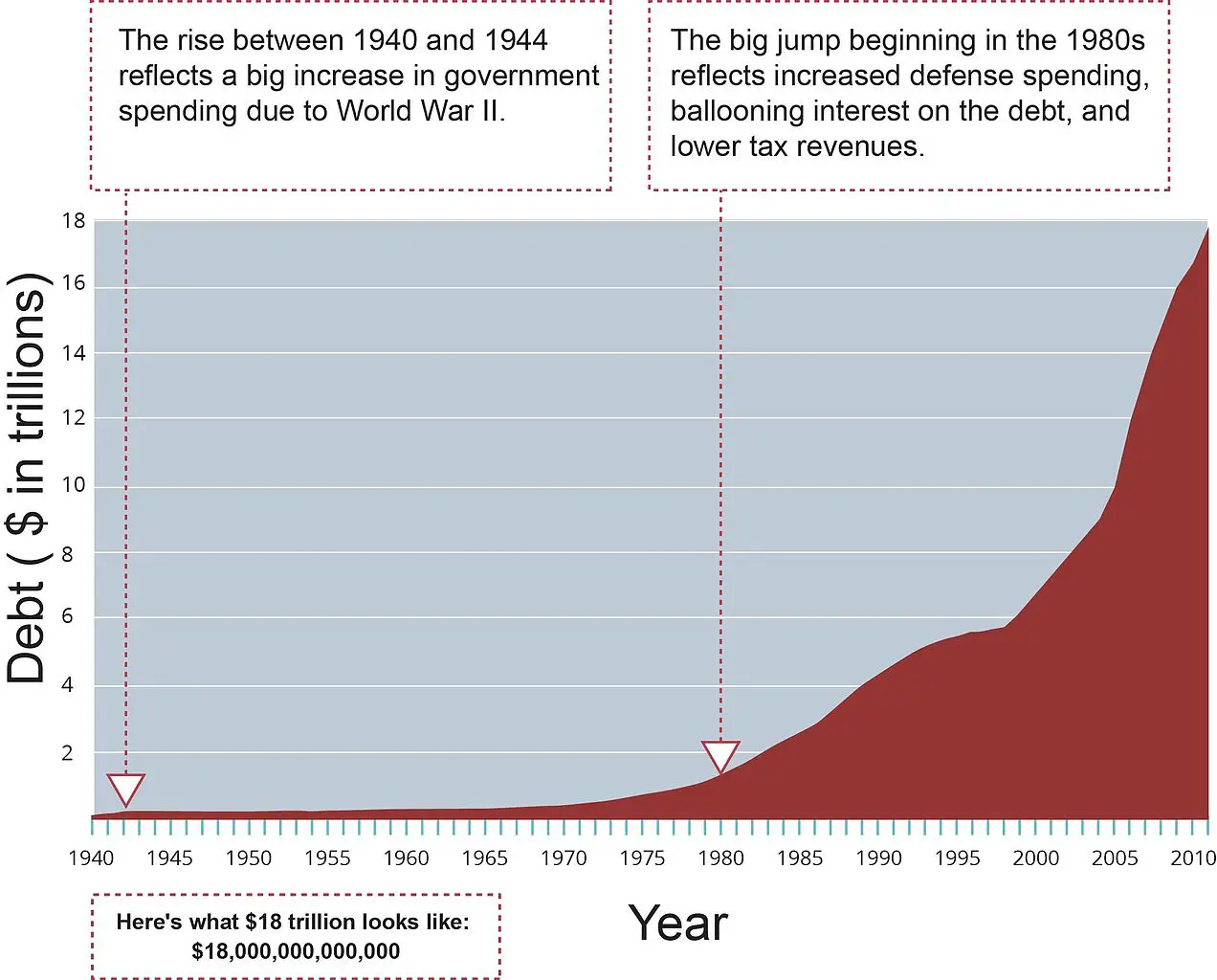
Despite the nations economic recovery, and the end of the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio has remained above 100 percent since 2013. During fiscal year 2017, the total national debt passed $20 trillion for the first time in the nations history. Debt levels continue to rise.
In early 2018, an analysis by the nonpartisan Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget concluded that recent tax and spending legislation passed by Congress under President Donald Trump was on track to push the countrys debt-to-GDP ratio to highs not seen since immediately after World War II.The report stated that if the temporary spending increases and tax cuts are made permanent, the national debt would reach $33 trillion, or 113 percent of GDP, by 2028, and could be twice the size of the U.S. economy in about 25 years.
The COVID-19 epidemic is impacting national debts across the globe. The Congressional Budget Office projects a federal deficit of $1 trillion in 2020. An economic stimulus package from congress could prompt the U.S. national debt to surpass $25 trillion or higher.
Read Also: Can You Keep Your Home If You File Bankruptcy
National Debt By President
The National Debt has always been an area of interest for the United States President George Washington appointed future President Alexander Hamilton to understand and solve the $80 million debtthat had accrued due to the Revolutionary War. Hamilton came up with the plan to pay off the debt through taxes and the creation of the national bank. Since then the United States has steadily increased its budget deficit, and the national debt has continued to rise.The first time that the national debt hit the $1 billion mark was in 1863 while the Civil War was occurring it hit the $2 billion was two years later when the civil war ended in 1865. As the country went to battle during World War I and World War II, the national debt hit the $10 billion mark and $100 billion marks respectively. By 1982 after the Vietnam War and the Cold War, the national debt hit the $1 trillion mark for the first time in history. By the 21st Century, the national debt got to $20 trillion after major events such as the War on Terror and the Great Recession. Today , the national debt stands at $30.2 trillion and public debt is roughly 100% of the country’s GDP.
How Is The Covid
In response to the pandemic, the federal government has spent trillions of dollars to boost the economy, including on stimulus checks for citizens and aid for businesses and state and local governments. According to the Congressional Budget Office , these measures swelled the federal deficit to $3.1 trillion in 2020, about 15 percent of GDP and the highest level since World War II. Even before the pandemic, the CBO projected that annual deficits would breach the $1 trillion mark in 2020 and remain above that level indefinitely.
More on:
Debt held by the publicthe measure of how much the government owes to outside investorswas $16.9 trillion in 2019. That was more than double the amount in 2007, an increase to almost 80 percent of GDP from 35 percent. Before accounting for spending to combat COVID-19, publicly held U.S. debt was set to nearly double to more than $29 trillion over the next decade. Now, it is about $22 trillion, and its projected to be double the size of the economy by 2051.
Don’t Miss: How To File Bankruptcy In Florida For Free
Tracking The Federal Deficit: March 2022
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $191 billion in March 2022, the sixth month of fiscal year 2022. This shortfall was the difference between $315 billion in receipts and $506 billion in spending. The March 2022 deficit was $469 billion smaller than the March 2021 deficit, largely a result of the winding down of most pandemic relief spending that was in place during March 2021.
Analysis of notable trends: Halfway through fiscal year 2022, the cumulative deficit has fallen relative to last year and is now comparable to pre-COVID deficits. Through the first six months of FY2022, the federal government ran a deficit of $667 billion, 61% less than at the same point in FY2021 and in the ballpark of the FY2019 and FY2020 deficits, which stood at $691 billion and $743 billion, respectively.
Revenues remained strong, rising $418 billion from the same period in FY2021 to a total of $2.1 trillion during this fiscal year to date. Increases in individual income and payroll tax receipts rose by $357 billion and drove much of the overall surge in receipts. Higher total wages and salaries, especially among upper-income workers who are subject to higher tax rates, contributed to the increase in those tax revenues, as did the receipt of some payroll taxes that pandemic relief legislation authorized companies to defer from 2020 into 2021. Corporate income tax revenues rose by $22 billion year-over-year.
Payment Of Us National Debt
On January 8, 1835, president Andrew Jackson paid off the entire national debt, the only time in U.S. history that has been accomplished. However, this and other factors, such as the government giving surplus money to state banks, soon led to the Panic of 1837, in which the government had to resume borrowing money.
Also Check: Do You Lose Your Home If You File Bankruptcy
How Did The Debt Get Where It Is Today
More on:
The United States has run annual deficitsspending more than the Treasury collectsalmost every year since the nations founding. The period since World War II, during which the United States emerged as a global superpower, is a good starting point from which to examine modern debt levels. Defense spending during the war led to unprecedented borrowing, with the debt skyrocketing to more than 100 percent of gross domestic product in 1946.