Chapter 13 Tips And Tricks
Pro tips from Stiberman Law when filing Chapter 13 bankruptcy:
- Schedule your plan payment to be deducted electronically or via a wage deduction order to ensure that you always remain current. Failure to remain current will cause the dismissal of your bankruptcy case.
- Hire a competent bankruptcy attorney familiar with the local rules and your Chapter 13 Trustees procedures.
- Dont confuse reorganization with repayment. In most cases, you can discharge all of your debt by paying only a small percentage.
Voluntary Conversion To Chapter 13
The opportunity to change your case to a Chapter 13 one is one that is not often used but can be a valuable one for dealing with unexpected changes in circumstances. For example, you may sensibly decide to file a Chapter 7 case because you are just too far behind on your home mortgage payments, and your income is too low, even with the benefits of Chapter 13, to justify trying to save the home. However, if just a month or two afterward, you unexpectedly get a much better paying job, making a Chapter 13 payment plan feasible after all, there could be the possibility of converting your Chapter 7 case into 13 in order to keep the home.
Induced Conversion to Chapter 13
Although it happens quite rarely, you can be effectively required to convert from Chapter 7 to Chapter 13, although at least theoretically you cant be forced to do so. Section 706 specifically states that the bankruptcy court may not convert a case under this chapter to a case under chapter . . . 13 . . . unless the debtor requests or consents to such conversion.
Either under Sections 706 or 707, the court can dismiss, or throw out, your Chapter 7 case under certain circumstances, and in those situations, it is usually better to convert to Chapter 13 as a fall-back option instead of being without any protection from your creditors.
A Bankruptcy Lawyer In Cary North Carolina Will Handle All Of The Paperwork Required For A Bankruptcy Filing Which Includes Preparing:
- A statement of financial affairs
- Schedules of assets and liabilities
- A schedule of current income and expenditures
- A statement of monthly net income
- Evidence of income from employers received 60 days before filing
- Information about any interest you have in federal- or state qualified education or tuition accounts
- A schedule of executory contracts and unexpired leases
- Copies of tax returns or transcripts from the most recent year .
We will be able to determine what property should be considered protected from bankruptcy. North Carolina law provides a homestead exemption, a motor vehicle exemption, and several other personal property exemptions.
Our team can also move quickly to file a bankruptcy petition with the court, which will automatically stop creditors from contacting you while you are working your way through the bankruptcy process.
Your Sasser Law bankruptcy attorney will assist and advise you on the difference between Chapter 7 and 13. We will explain every step of the process ahead of time to make sure you are prepared for questions or decisions from the bankruptcy trustee or court.
Most bankruptcy cases proceed smoothly, but sometimes disputes arise and make litigation unavoidable. If this occurs, the seasoned bankruptcy litigation team at Sasser Law Firm has extensive trial experience and the understanding of bankruptcy code required to fight for your interests all the way through appeal, if necessary.
You May Like: Can You Pay A Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Off Early
Is Chapter 13 Worth It
Depending on your situation, filing for Chapter 13 bankruptcy may be worth it if you have a non-exempt property and dont want the Trustee to take it, if you are trying to save your property from foreclosure or are behind in your car payments or taxes, or if you make too much to qualify for chapter 7 bankruptcy.
Your bankruptcy attorney is key in advising you on which bankruptcy is best for your situation.
The Chapter 13 Discharge
![Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy [Infographic] Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy [Infographic]](https://www.bankruptcytalk.net/wp-content/uploads/chapter-7-vs-chapter-13-bankruptcy-infographic.jpeg)
The bankruptcy law regarding the scope of the chapter 13 discharge is complex and has recently undergone major changes. Therefore, debtors should consult competent legal counsel prior to filing regarding the scope of the chapter 13 discharge.
A chapter 13 debtor is entitled to a discharge upon completion of all payments under the chapter 13 plan so long as the debtor: certifies that all domestic support obligations that came due prior to making such certification have been paid has not received a discharge in a prior case filed within a certain time frame and has completed an approved course in financial management . 11 U.S.C. § 1328. The court will not enter the discharge, however, until it determines, after notice and a hearing, that there is no reason to believe there is any pending proceeding that might give rise to a limitation on the debtor’s homestead exemption. 11 U.S.C. § 1328.
The discharge releases the debtor from all debts provided for by the plan or disallowed , with limited exceptions. Creditors provided for in full or in part under the chapter 13 plan may no longer initiate or continue any legal or other action against the debtor to collect the discharged obligations.
Recommended Reading: Can You File Bankruptcy Without Tax Returns
You Must Repay Creditors
A Chapter 13 bankruptcy requires repayment to creditors using a three- or five-year repayment plan.
This means you must have enough income to pay creditors every month. You must:
- Repay priority debts and secured creditors in full
- Repay unsecured creditors an amount equal to what those creditors would have received if your trustee sold your nonexempt property in a Chapter 7 bankruptcy
Three Significant Differences Between Chapter 7 Bankruptcy And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy :
- Chapter 13 bankruptcy has no income limitations, but certain income limits are put in place for those seeking Chapter 7 bankruptcy protection.
- An approved Chapter 7 bankruptcy plan eliminates many forms of unsecured debt, while Chapter 13 bankruptcy sets up a repayment plan.
Many other differences exist, and the Columbus, Ohio-based Chapter 7 bankruptcy attorneys with the Calig Law Firm discuss several below. You can have all your questions answered, and get help with your bankruptcy case, by calling us as 252-2300. We also take appointments for consultations online through this contact form.
Also Check: Can You Rent An Apartment After Filing For Bankruptcy
Filing Bankruptcy: Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 13
- 3 Minute Read
Youre at the end of your financial rope. Youve tried everything selling off assets, credit counseling and debt consolidation. And youve finally decided that bankruptcy is your best option.
Now what?
One of your next steps is deciding which type of bankruptcy to file. There are two types of bankruptcies that individuals can file: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. The basic difference between the two is that one eliminates your debts and the other involves a payment plan to repay at least some of the debts you owe. Continue reading to learn more about the differences between Chapters 7 and 13 bankruptcy and which one is right for you.
Chapter 7 Or Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
When deciding what path you would like to take regarding bankruptcy, there are many factors that you need to take into account in order to reach the proper decision. This involves looking at your income, property, assets, if you are married, how many are living in your household and many more. Taking the wrong route has the potential to bring with it negative effects that will stay with you for years.
Most individuals and businesses in Ohio and Kentucky have only to consider two options for bankruptcy: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. Each has particular aspects that may work better for you depending on your personal situation. Figuring out which one will most effectively aid in fixing your legal financial issues is the single most important decision that you can make prior to filing.
Considering the long-term importance of this decision, it would be in your best interest to consult with a qualified bankruptcy attorney who has the legal understanding of bankruptcy to effectively advise you on what path to take, while also representing you during this stressful time.
Recommended Reading: Can A Creditor Sue After Bankruptcy
Impact On Credit History
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy stays on an individuals credit report for 10 years from the fate of filing
A record of Chapter 13 bankruptcy stays on an individuals for up to 7 years. You may apply for new credit cards after 12-24 months, a new FHA mortgage loan 24 months after discharge, and a new Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac loan after 36 months.
Chapter 13 Is Better If
-
you want to keep property thatâs not protected by an exemption,
-
youâre behind on your mortgage and want to catch up,
-
you have debts that canât be discharged,
-
you have a car loan with a high interest rate or negative equity from a trade-in
-
you have multiple mortgages
-
you owe money to your ex-spouse from a property settlement
Of course, life isnât always that clear cut, so itâs also important to consider the downsides when weighing your bankruptcy options.
Don’t Miss: How Much Do Lawyers Charge For Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
If You Have Sufficient Income You May Be Required To File Chapter 13
To qualify for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, youll have to prove you cant repay your debt. If, depending on your income and your states median income requirements, your current monthly income is more than your states median income for a family of your size, you may not be allowed to file Chapter 7. In this case, Chapter 13 could be the right option for you.
Chapter 13 Vs Chapter 7

A Chapter 13 differs from a Chapter 7 in that, instead of discharging your debts, it reorganizes them into a single monthly payment, with no interest or late fees. The only exceptions that would give a creditor interest are a secured creditors mortgage arrears, a vehicle paid through Chapter 13, or a secured tax claim.
Another difference is that, in a Chapter 13, you must file a repayment plan with a duration between 36 and 60 months. Your property, including your home, vehicle, and other personal property, are safe unless you voluntarily surrender it to your creditor. Mortgage or equity loans on homes are paid outside of the plan and must be on time and in full each month. In addition, during the Chapter 13, you are on a cash only basis and your trustee will require copies of your tax returns every year. For those below the median income level, the trustee will take 50% of your net tax refund and use them towards your debts. Those over the median income level can keep their full tax refund.
Read Also: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Future In Canada
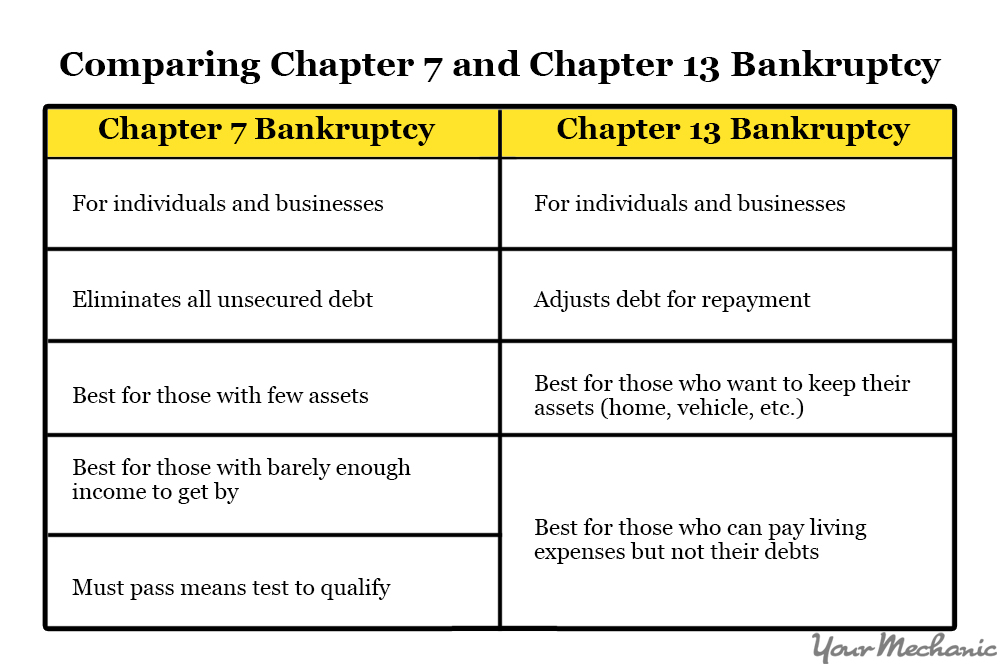
Chapter 13 Vs Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
In the Bankruptcy Quick Chart below we have answered your questions in an easy format making your filing process easier. Find out which bankruptcy is right for you in our Chapter 13 vs Chapter 7 table. Learn the subtle, but important, distinctions between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy. If you feel this chart does not answer your specific questions regarding filing bankruptcy, please complete our Free Confidential Evaluation Form for a no obligation chat with a local attorney.
Other Ways Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Differs From Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- You must submit a detailed financial reorganization plan that explains how you will pay all the debts creditors did not forgive.
- You have the choice to surrender property that you financed or to negotiate with lenders to reset the terms on the loans.
- While you are under Chapter 13 protection, you make a monthly payment to a trustee who uses the money to make payments to creditors according to the plan you put together with the help of your Columbus Chapter 13 lawyer.
Also Check: Can Private Student Loans Be Discharged In Bankruptcy
Other Ways Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Differs From Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
- You can only file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy protection once every eight years. On the other hand, you can file a new Chapter 13 bankruptcy petition as often as you need to do so.
- A Chapter 7 bankruptcy petition discharges credit card debt, medical bills, and unsecured personal loans. A Chapter 13 bankruptcy requires a portion of those obligations to be paid back.
- If your mortgage is current, you will be able to keep your home in a Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. However, if the mortgage is behind, the court will only allow you to keep the home in a Chapter 13.
How Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Works
Chapter 13 is a reorganization bankruptcy designed for debtors with regular income who have enough left each month to pay back at least a portion of their debts. The amount you’ll repay will depend on how much you earn, your debt, and how much property you own.
Typically, Chapter 13 bankruptcy is for debtors who:
- don’t qualify for Chapter 7 but need debt relief to lower credit card payments, stop litigation, prevent a wage garnishment
- have nondischargeable debts such as alimony or child support arrears that they’d like to pay off over three to five years, or
- have fallen behind on a house or car payment and want to catch up on missed payments and keep the property.
Other benefits exist, too, such as the ability to “cram down” the amount owed on a vehicle or investment property to the property’s value. Some filers can also strip wholly unsecured junior liens from your residence.
In Chapter 13 bankruptcy, the trustee doesn’t sell your property. However, you must pay creditors an amount equal to the nonexempt property value. But that’s not all you’ll pay. The total amount of your repayment plan will depend on your income, expenses, and debt type.
Read Also: What Does It Mean When You File For Bankruptcy
Where Can I Get More Information
To learn more about bankruptcy in America, go to Bankruptcy America. If you are suffering in Canada from debts which could lead to bankruptcy, contact a Canadian Licensed Insolvency Trustee in your area. We have trustees everywhere, ranging from Montreal to Calgary and more. Get your questions answered for free today!
When To Consider Filing Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
When is Chapter 13 right for you?
- You have too much money to qualify for Chapter 7.
- You have property you dont want to lose.
- You want to catch up on your mortgage so you can stay in your house.
- You have debts that cant be discharged.
- You have more than one mortgage.
- You owe money to your ex-spouse from a property settlement.
Also Check: Which Statement Regarding Bankruptcy Is Not True
What Is Chapter 7
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is generally a fast bankruptcy the cases usually last about three to four months, and you can discharge credit card debt, medical bills, personal loans, utilities and some income tax debts without having to repay them. You can keep your house and your car in Chapter 7 if you can afford the payments and if you are current on your payments, but you must repay these loans if you want to keep the property. If you have debt that is nondischargeable, such as child support, alimony and most student loans and some taxes, you will still be responsible for them after a Chapter 7.
You Want To Save Your Home From Foreclosure
Filing for Chapter 13 may permanently stop a foreclosure. An automatic stay will temporarily prevent a foreclosure until the court confirms the debtor’s repayment plan. Once confirmed, the debtor will pay back the missed payments over the life of the plan and the terms and conditions of the original agreement will govern the debtor and the lender’s relationship.
Chapter 13, however, will not prevent foreclosure if the debtor filed for bankruptcy within the past two years and the bankruptcy court lifted the automatic stay to allow the creditor to proceed with foreclosure.
In Chapter 7, it is less likely that a debtor can keep their home if they are behind on their mortgage payments. The court will usually grant a lender’s request to lift an automatic stay in order to continue foreclosure proceedings on the home.
You May Like: What Is Filing For Bankruptcy Mean
What Are The The Differences Between Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Challenging situations arise in peoples lives every day. Some of these circumstances mean that bills can no longer be paid. Individuals may have good intentions of paying their bills, but do not have the means to do so. When this happens, bankruptcy can be a source of relief. Bankruptcy is sometimes the most viable option. The question becomes whether Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 is better to file. We will review your finances to help you determine whether a chapter 7 or chapter 13 is best for you.
Dealing With Secured Creditors
With Chapter 7, you are generally allowed to either keep or surrender any collateral. So you can decide that you can no longer afford your mortgage or vehicle payment and give up the house or car and discharge the remaining debt. Or you can arrange to continue making the payments and keep the collateral. If you are behind on those payments, you will have limited time to catch up, depending on the discretion of the creditor.
Contrast that with Chapter 13, under which you can usually stretch out payment of your mortgage or vehicle arrears over the entire three-to-five year repayment plan. Also, you may be able to save a tremendous amount by cramming down the balance on an older vehicle loan to the value of the vehicle.
Don’t Miss: How Long To Wait To File Bankruptcy Again