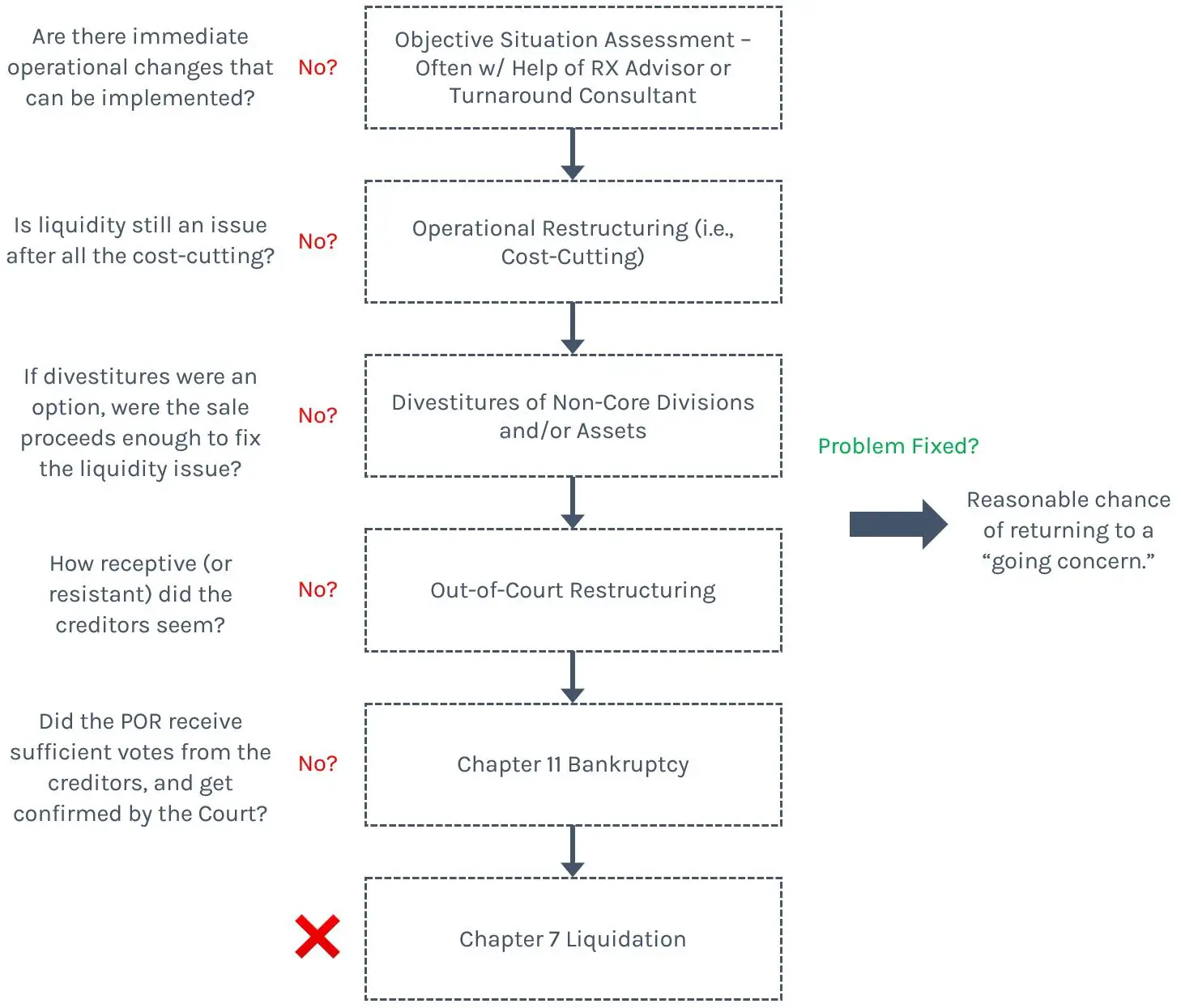
Through Thick And Thin
This reality created a challenge for the researchers. They could not simply compare Chapter 7 with Chapter 11 companies because the liquidated firms tend to be worse. Any differences in the fate of their assets might be due to the companies quality and not to the bankruptcy system. So how could the team figure out whether the Chapter 7 or 11 system is better for the economy?
The researchers solved this by taking advantage of a quirk of the legal process. Bankruptcy cases are randomly assigned to judges. And when a firm files for Chapter 11, the judge has some discretion over leaving it in Chapter 11 or converting it to Chapter 7.
It turns out that different judges have different interpretations of the law and tend toward either Chapter 7 or 11. This means that similar companies could be assigned to Chapter 7 or 11 depending on which judge oversaw their case, creating something close to a randomized experiment. So Iversons team was able to compare the outcomes of cases assigned to judges who favor Chapter 7 with the outcomes of otherwise-identical cases assigned to judges who favor Chapter 11.
Areas Where Bankruptcy Wont Help
Once a plan is confirmed in a Chapter 11 business bankruptcy case, all the debtors dischargeable debt is forgiven.
In the case of individual bankruptcy cases, a dischargeable debt is only forgiven after the debtor completes all their payments under the reorganization plan.
The only matters that can continue while a Chapter 11 bankruptcy case is pending are the following types of legal proceedings:
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Process
You can file a Chapter 11 voluntarily, or three or more creditors can force you to file.
The bankruptcy trustee may be assigned to your case. They are an employee of the Department of Justice that plays a significant role in monitoring the progress of your Chapter 11 case and supervising its administration. The U.S. trustee is responsible for monitoring the debtor in possessions operation of the business and submitting operating reports and fees. Bankruptcy trustees become the C.E.O. of the debtor, exercising such day-to-day control as they deem appropriate. Their duties include evaluating and making recommendations about various debtor demands under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code.
The business has four months to develop a reorganizational plan, but it can take 18 months. If the time limit surpasses this, then creditors can propose a plan. The creditors have to vote on the approval of the program. They are known as a creditors committee, a group of people representing a companys creditors in a bankruptcy proceeding.
There are three classes of creditors: priority, secured and unsecured. It is a payment hierarchy. The ones highest on the rung, the priority creditors, get paid first. It continues down the chain until all claims are resolved.
Most repayment plans take six months to two years, but there is no time limit.
Whats the exclusivity period?
Don’t Miss: How To Report Bankruptcy Fraud Anonymously
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Vs Chapter 7
| Chapter 11 | |
|---|---|
| Discharge takes four to six months | |
| Debtor retains assets and pays debts from future monthly income | Trustee sells assets to pay off debts |
| Debtor reorganizes debts and finances | Loan balances are not reduced |
| Very expensive | There are no monthly payments |
Chapter 11 bankruptcy allows a business to continue its operations while paying off its debts. This is in contrast to a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, also known as a “liquidation bankruptcy.” With Chapter 7, a business’s or individual’s assets are sold. The trustee uses the proceeds to pay debts, which often means ceasing operations for a business.
Consult With Our Portland Bankruptcy Attorneys Today
If you are dealing with crippling debt and youre considering filing for bankruptcy, deciding whether to file for bankruptcy under Chapter 7 vs Chapter 11 can be a tough decision to make. It can affect how you deal with home foreclosure, wage garnishment, or car repossession.
Not all types of bankruptcy are the same. Before proceeding with bankruptcy, it is best to review your financial situation with an experienced Portland bankruptcy attorney. Our Portland bankruptcy attorneys are experienced in both Chapter 7 and Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. Dont hesitate to contact our legal team at Michael D. OBrien & Associates PC today! We can help you assess your situation and give you a fresh start.
You May Like: How To Remove Chapter 7 Bankruptcy From Credit Report
How Do I Pay Creditors Back In A Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Case
Debts are handled differently in Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 cases. Debtors in Chapter 7 cases do not pay creditors back. If the bankruptcy trustee sells property as part of the administration of the case, unsecured creditors receive a share of the money. Debtors in Chapter 11 cases pay back different classes of creditors in different ways through a bankruptcy plan. The Debtor routinely makes regular payments to creditors after filing a Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceeding.
Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Infographics
Lets see the top differences between chapter 7 vs chapter 11 bankruptcy.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be HyperlinkedFor eg:
The key differences are as follows
#1 Type
In Chapter 7, liquidation of assets occurs, whereas, in chapter 11, restructuring of loan repayment takes place.
# 2 Processing Time
In chapter 7, the whole process of liquidation takes 4 to 6 months to wind up, whereas, in chapter 11, its a long run process because, during the time of restructuring debt repayment, there are chances that company debt payment duration can be extended.
# 3 Closure
In chapter 7, a company or individual is not able to run operation, whereas, in chapter 11, the company get the chance to run operations again.
# 4 Advantages
In chapter 7, no repayment plan debtor can start from starting again without having any debt limitation. In chapter 11, the company gets the chance to stand again and run its operations.
You May Like: Can You Get A Car Loan After A Bankruptcy
What Is Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
In this chapter, restructuring debt, repayments take place. The debtor files bankruptcy under this chapter to save their asset. This way of filing bankruptcy helps in avoiding the liquidation of assets.
- The company or a business file for this chapter is when the company can run its operation but cannot pay its debts. So this gives a chance to the company or an individual to stand again and run the business. There are some terms and conditions for filing Chapter 11. A company should generate regular income to run its operations, and the restructured payment plan should be submitted to the court.
- In this case, the court appoints a trustee to reorganize loan repayment and make some changes in terms and conditions of repayment terms
- Through this, the debtor can efficiently manage their loan repayment. It also helps the debtor to negotiate repayment plans with creditors. New terms and conditions form for both creditors and debtors regarding loan repayment.
How Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Works
Chapter 7 is the type of bankruptcy that most people imagine when they think of bankruptcy: Through a court-appointed trustee, Chapter 7 bankrupts usually individuals rarely businesses sell their nonexempt assets to clear as much of their unsecured debt as possible. The rest, with exceptions such as taxes and student loans, is wiped out.
This mutual destruction is why Chapter 7 bankruptcy also is commonly known as liquidation bankruptcy. However, a 2018 survey by the American Bankruptcy Institute revealed that 93% of applicants who properly filed exemption paperwork were able to protect all of their assets. All. Of. Their. Assets. Thats #AllOfTheirAssets.
Whats the trick? Debtors must qualify for Chapter 7 by surviving a bankruptcy means test. Is your monthly income lower than the median for a household of your size in your state? Youre in. File exemptions properly fingers crossed and become one of the 93-percenters.
Who doesnt qualify? Applicants with above-median incomes who, after paying allowed expenses, have money left to address at least a portion of their unsecured debts.
Recommended Reading: Bankruptcy Attorney Twin Falls Idaho
What Is The Difference Between Bankruptcy Cases Filed Under Chapters 7 11 12 And 13
Chapter 7: Often called the liquidation chapter, chapter 7 is used by individuals, partnerships, or corporations who are unable to repair their financial situation. In chapter 7 asset cases, the debtor’s estate is liquidated under the rules of the bankruptcy code. Liquidation is the process through which the debtor’s non-exempt property is sold for cash by a trustee and the proceeds are distributed to creditors.
Chapter 11: Often called the reorganization chapter, chapter 11 allows corporations, partnerships, and some individuals to reorganize, without having to liquidate all assets. In filing a chapter 11, the debtor presents a plan to creditors which, if accepted by the creditors and approved by the court, will allow the debtor to reorganize personal, financial or business affairs and again become a financially productive individual or business.
Chapter 12: Chapter 12 is designed for “family farmers” or “family fishermen” with “regular annual income.” It enables financially distressed family farmers and fishermen to propose and carry out a plan to repay all or part of their debts. Under chapter 12, debtors propose a repayment plan to make installments to creditors over three to five years. Generally, the plan must provide for payments over three years unless the court approves a longer period “for cause.”
More information regarding the difference between chapters can be found in the Bankruptcy Basics Manual.
Chapter 1: Subchapter V
In 2019, the U.S. Congress passed the Small Business Reorganization Act of 2019. The Subchapter V of Chapter 11 makes filing more accessible and more affordable both for individuals and business owners.
Chapter 11: Subchapter V resembles Chapter 13 more than Chapter 11. This is because it requires less creditor involvement in the bankruptcy process.
Also Check: Does A Bankruptcy Trustee Check Records
What Happens To Your Property In Bankruptcy
Whether you can keep your property in bankruptcy depends on whether you file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
For the most part, you keep your property in Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
If you file under Chapter 7, you may have to give up some property . This mostly depends on whether your property is exempt. To learn more, be sure to check out our section on . If your property serves as collateral for a debt , there are other considerations.
Below you’ll find articles explaining what happens to your property in both Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy, and links to other sections with more in-depth articles.
Which Debts Cannot Be Eliminated Through Bankruptcy

Some types of debt generally cannot be discharged through bankruptcy. There are rare exceptions, depending on the facts in an individual case. Debts that typically cannot be discharged include:
- Debts for personal injury or death you caused while driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs
- Debts you failed to list in your bankruptcy filing.
You May Like: Can You File Bankruptcy On Business Taxes
Are Businesses Required To Complete Credit Counseling/debtor Education
Sole proprietors must complete an approved credit counseling course before they file for bankruptcy in their own names. They must also take a second debtor education course after filing for bankruptcy. Owners of corporations, LLCs and other business entities generally are not subject to these requirements. We can determine if these steps are necessary for your small business.
First Meeting Of Creditors And Bankruptcy Court
Barring when creditors dispute a discharge, few must attend a hearing in a bankruptcy court for a personal bankruptcy filing. Instead, there is a “First Meeting of Creditors,” which is a meeting that takes place around 30 to 40 days into the filing process. As the name suggests, creditors may attend this meeting, but they rarely do instead, they tend to have their attorneys work with the debtor’s attorney another reason it is wise to hire an attorney for the bankruptcy process.
This meeting is not overseen by a bankruptcy judge, but by a bankruptcy trustee, a person who is in charge of managing an individual’s bankruptcy. Trustees are usually appointed by the U.S. Department of Justice. In some Chapter 11 filings, a chief restructuring officer is used in place of a trustee.
In either type of filing, the person seeking liquidation or reorganization swears an oath to truthfully answer a trustee’s questions. Most of the time, this meeting is very short unless the trustee or chief restructuring officer is confused or suspicious about certain information the debtor has provided.
Don’t Miss: Is It Too Late To File Bankruptcy
What Is Chapter 11 Bankruptcy What You Need To Know
Are you feeling frustrated by sleepless nights due to a failing business and dont know what to do?
According to statistics published in 2019 by the Small Business Administration , about 20% of business startups fail in the first year. Nearly half succumb to business failure within five years. By year 10, only about 33% survive.
There is a solution.
Chapter 11 Vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Both allow businesses to continue operating under reorganization plans. But both have different costs, eligibility, and time to complete.
Chapter 11 can be done by any business or individual with no debt level limits or required income.
Chapter 13 is a wage earners plan for individuals with stable incomes and specific debt limitations. This chapter also includes a trustee who handles all the payments and distributes them to creditors and takes three to five years to complete.
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Can You File Bankruptcy In Your Life
What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
In this chapter 7 bankruptcy liquidation of assets takes place. The debtor pays his debts by selling his/her personal assets. The debtor pays his secured loan on a priority basis because creditors can claim for collateral like a car loan, home equity loan, mortgage, etc. After paying secured loansSecured LoansSecured loans refer to the type of loans approved and received against a guarantee or collateral. If they fail to do so, the lending institution acquires the collateral to compensate for the amount that the borrowers were allowed.read more if still some money is left to the debtor, he pays unsecured loans like a credit card, unsecured personal loan, etc.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be HyperlinkedFor eg:Source: Chapter 7 vs Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
How Long Does It Take To Complete A Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Case
The time to complete a Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 bankruptcy case is very different.
A Chapter 7 case for individuals can be completed in four to six months. Chapter 11 cases for individuals can last several years.
A business that files under Chapter 11 is in bankruptcy for several years in most cases. A Chapter 7 for a business could be completed in a year or two, depending on the size of the business.
Also Check: Do Married Couples Have To File Bankruptcy Together
Chart Of Differences Between Chapter 7 And 11 Bankruptcy
This table highlights some primary differences between Chapters 7 and 11, and Chapter 11, Subchapter V.
|
Chapter 7 |
||
|
The trustee can sell nonexempt property. Doesn’t provide a way to catch up on missed payments to avoid foreclosure or repossession. The personal assets of partnership partners can be at risk. Filing for bankruptcy opens the door for creditor litigation. |
Prohibitively expensive for most small businesses. Filing for bankruptcy opens the door for creditor litigation, although the risk is lessened by the ability to negotiate with creditors. |
Filing for bankruptcy opens the door for creditor litigation, although the risk is lessened by the ability to negotiate with creditors. |
Your Property In Bankruptcy

-
What happens to your property in bankruptcy, including your house and car, will depend on whether you file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. In Chapter 7, you’ll lose your house or other property that isn’t protected by an exemption. In Chapter 13, you’ll keep all of your property, including your house, but you’ll pay for nonexempt property that isn’t covered by a bankruptcy exemption through the Chapter 13 repayment plan.
-
Bankruptcy exemptions determine what you get to keep during and after bankruptcy, including your home, car, retirement account, or personal belongings. But you’ll have to comply with exemption rules. Find out which state exemption laws will apply in your bankruptcy case, or whether you can choose the federal bankruptcy exemptions instead.
-
If you are married and considering bankruptcy, you should consider how your bankruptcy filing will affect your spouse and the property you own together. The answers depend on what type of case you file, whether you file alone or with your spouse, how you own your property, and the laws of your state about marital property.
View More Articles
Also Check: Bank Of America Foreclosed Homes
Other Options For Individuals And Sole Proprietors
If a filer would lose important property in Chapter 7, negotiating debt directly with creditors and selling assets might be the better option. Also, Chapter 13 has mechanisms not available in Chapter 7 that will allow filers to do the following:
- pay off nondischargeable debt over time without fear of collection actions
- discharge marital property settlements
- reduce secured debt on a car, rental property, or other collateral to the property value using a “cramdown” procedure , and
- erase an unsecured junior mortgage on a residential home using a lien stripping mechanism.
Find out when Chapter 13 works better than Chapter 7.