Forms Of Government Borrowing
In addition to selling Treasury bills, notes, and bonds, the U.S. government borrows by issuing Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities and Floating Rate Notes . Its borrowing instruments also include savings bonds as well as the government account securities representing intergovernmental debt.
Other nations have borrowed from international organizations like the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank as well as private financial institutions.
National Debt Of The United States
| This article needs to be . Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
| This article is part of a series on the |
|
|
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms “national deficit” and “national surplus” usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the federal government spent trillions in virus aid and economic relief. The CBO estimated that the budget deficit for fiscal year 2020 would increase to $3.3 trillion or 16% GDP, more than triple that of 2019 and the largest as % GDP since 1945.
Hurricanes Katrina And Rita Growth Of China And India
In August of 2005, Hurricane Katrina hit the Gulf Coast, nearly destroying New Orleans and becoming one of the largest natural disasters in U.S. history. Hurricane Rita followed soon after.
The two storms caused more than $2 billion in damage, destroyed 275,000 homes, eliminated 400,000 jobs, killed over 1,000 people, and displaced hundreds of thousands of Americans.
This was also the year that China and India rose as world financial powers. For years, the U.S. had been outsourcing work to these countries because they offered cheap labor. Eventually, the strategy shifted to tapping these workforces for highly educated and skilled technical talent.
National Debt: $7.933 trillion
Read Also: Direct Liquidation Amazon Pallets
Does The Federal Reserve Sell United States Government Bonds
The Federal Reserve Bank is a private institution and not a part of the US Treasury. As such, the Fed does not have the right to issue government bonds.
However, it is allowed to buy bonds and it is by this mechanism that the Federal Reserve enabled the US Treasury to raise funds during the 2008 financial crisis without increasing interest rates.
Quantitative Easing
The US government needed a large amount of money to help refund banks that were in trouble. The Fed bought Treasury bonds from US banks and also directly from the Federal Financing Bank. As a result of this action, which is called quantitative easing, the Federal Reserve is now a major holder of US government debt.
Debt Grows Into The Trillions During 1980s And 1990s
![US National Debt (And Related Information) [OC] US National Debt (And Related Information) [OC]](https://www.bankruptcytalk.net/wp-content/uploads/us-national-debt-and-related-information-oc-national-debt.png)
At the start of the 1980s, an increase in defense spending and substantial tax cuts continued to balloon the federal debt. The national debt at the end of the Ronald Reagan era was $2.7 trillion.
The era under President Bill Clinton was marked with tax increases, reductions in defense spending and an economic boom that reduced the growth of debt, but it still reached a staggering $5.6 trillion by 2000.
Don’t Miss: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Tax Return
Risks To Economic Growth
Debt levels may affect economic growth rates. In 2010, economists Kenneth Rogoff and Carmen Reinhart reported that among the 20 developed countries studied, average annual GDP growth was 34% when debt was relatively moderate or low , but it dips to just 1.6% when debt was high . In April 2013, the conclusions of Rogoff and Reinhart’s study came into question when a coding error in their original paper was discovered by Herndon, Ash and Pollin of the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Herndon, Ash and Pollin found that after correcting for errors and unorthodox methods used, there was no evidence that debt above a specific threshold reduces growth. Reinhart and Rogoff maintain that after correcting for errors, a negative relationship between high debt and growth remains. However, other economists, including Paul Krugman, have argued that it is low growth which causes national debt to increase, rather than the other way around.
Commenting on fiscal sustainability, former Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke stated in April 2010 that “Neither experience nor economic theory clearly indicates the threshold at which government debt begins to endanger prosperity and economic stability. But given the significant costs and risks associated with a rapidly rising federal debt, our nation should soon put in place a credible plan for reducing deficits to sustainable levels over time.”
How Bad Is National Debt
Americans living with high levels of government and private debt tend to see saving in a positive light, while treating borrowing as a problem. In fact, they go hand in hand since borrowings come from savings and provide savers with the interest they earn from deferring consumption.
U.S. national debt provides corresponding low-risk assets for pension funds and families, and enables consumption in excess of production for the country as a whole.
At the same time, nothing more than simple arithmetic is required to see the pace of the recent growth of government debt as unsustainable. That’s the term the U.S. Treasury used in the Financial Report of the U.S. Government for Fiscal Year 2021, after calculating that under prevailing trends the federal debt-to-GDP ratio would increase from 100% in 2021 to 701% by 2096.Economists and policy analysts on the left often differ from those on the right in evaluating the tradeoffs between the everyday utility of government debt and its growing risks amid rapid accumulation.
Critics of public debt often contend it can crowd out private investment, a theory not supported by U.S. credit markets developments in recent decades. In contrast, economists using Modern Monetary Theory argue government borrowing can improve economic outcomes if it fosters public investment that expands the economy’s productive potential.
Don’t Miss: Will Business Bankruptcy Affect Me Personally
What Is The Current Us Debt Clock
Debt Held by the Public at the end of November 2021: $22.7 trillion Debt Held by the Public at the end of November 2020: $21.3 trillion Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, debt held by the public has increased by 30 percent. Once the situation has stabilized, policymakers should turn their focus to the countrys underlying fiscal situation.
What Is Household Debt
Household debts are defined as money owed by individuals to financial institutions. This debt can be in the form of , loans, mortgages, or lines of credit.
Many people carry some form of debt, and its important to understand how these debts work before taking on any new obligations.
There are two main types of debt: unsecured and secured. Unsecured debt is not backed by any collateral, which means that the lender has no claim on your assets if you default on the loan. One of the most common types of unsecured debts is credit card debt.
Secured debt is backed by collateral, which gives the lender a claim on your assets if you default on the loan. Mortgage loans would be a good example of secured loans.
Debt can also be classified as revolving or non-revolving. Revolving debt has no set repayment schedule, which means you can borrow and repay the debt as you please.
Non-revolving debt has a set repayment schedule, which means you must repay the debt in full by a certain date. One of the most popular non-revolving debts would be student loans.
Also Check: Can You File Bankruptcy Without Assets
How Has The Covid
According to the Congressional Budget Office, debt held by the American public will rise to 98% of GDP due to the economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic and legislative actions taken as a result. The CBO says that the main driver of the increased debt is a federal budget shortfall of $3.3 trillion, the largest since 1945.
Federal Debt: Total Public Debt As Percent Of Gross Domestic Product
Observation:
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Release: Debt to Gross Domestic Product Ratios
Units: Percent of GDP, Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Quarterly
Notes:
Federal Debt: Total Public Debt as Percent of Gross Domestic Product was first constructed by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis in October 2012. It is calculated using Federal Government Debt: Total Public Debt and Gross Domestic Product, 1 Decimal :GFDEGDQ188S = /GDP)*100
You May Like: How To File Bankruptcy In Kansas
Can The United States Pay Off Its National Debt
The current US debt, at around $30 trillion, is unlikely to be paid off with any speed. In fact, as the worlds principal reserve currency, there are some ways in which the American national debt is good for other countries: Foreign investors can purchase US Treasury bonds to help fund their own countries.
The most likely way that the United States can pay off its debt is through budget surpluses, which boost a countrys GDP. However, the last time the US had a budget surplus was 2001.
How Does The National Debt Affect Me
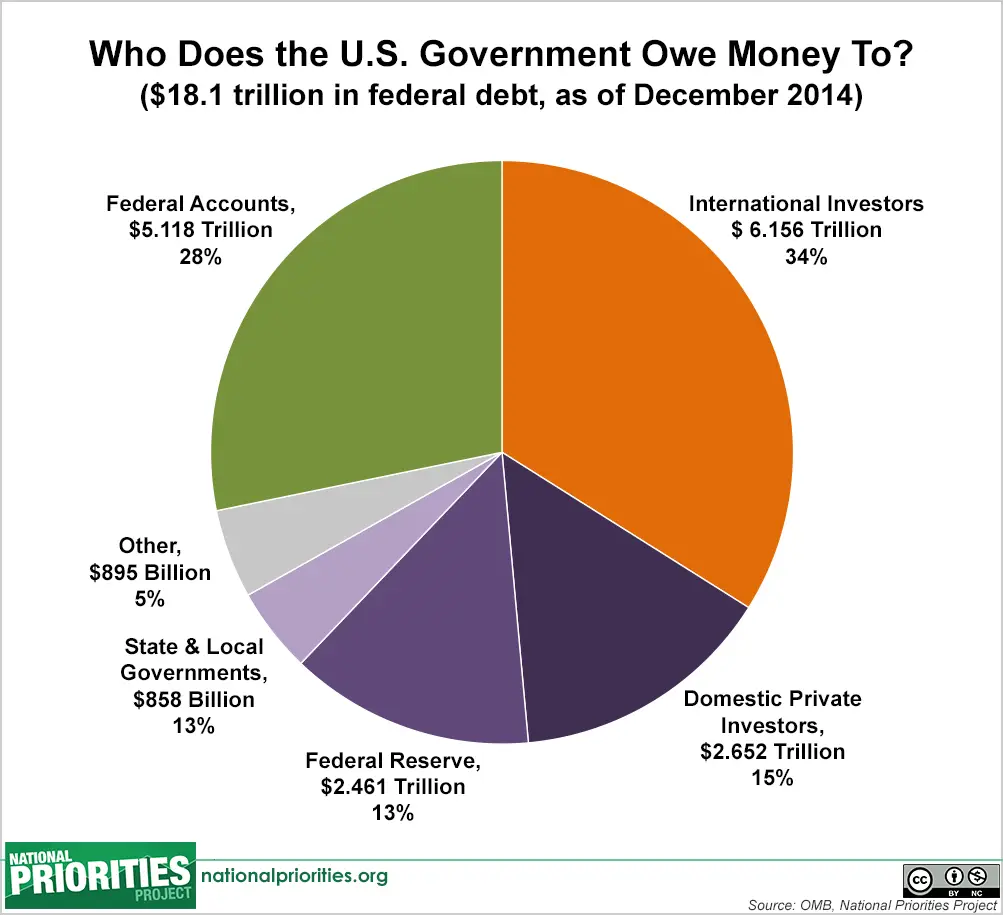
Interest payments also have an important role as they grow in step with the national debt. As the government allocates more funds towards paying off interests, other investment areas could get crowded out. Areas such as education, research and development, and infrastructure may not progress at sufficient or adequate levels due to interest payments. Interest payments currently take many of the dollars that are raised through federal income, estate, and federal excise taxes. Net worth is also an important and interesting factor that can be affected by the national debt.The cost of borrowing money to purchase large assets such as homes will increase due to the Federal Reserves interest rates. Interest rates will push down the prices of homes as individuals will struggle to qualify for mortgage loans this will then lower prices on home values.
Read Also: How Much To File Bankruptcy In Va
What Are The Primary Drivers Of Future Debt
The main drivers are still mandatory spending programs, namely Social Securitythe largest U.S. government programMedicare, and Medicaid. Their costs, which currently account for nearly half of all federal spending, are expected to surge as a percentage of GDP because of the aging U.S. population and resultant rising health expenses. Yet, corresponding tax revenues are projected to remain stagnant.
Meanwhile, interest payments on the debt, which now account for nearly 10 percent of the budget, are expected to rise, while discretionary spending, including programs such as defense and transportation, is expected to shrink as a proportion of the budget.
President Trump signed off on several pieces of legislation with implications for the debt. The most significant of these is the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Signed into law in December 2017, it is the most comprehensive tax reform legislation in three decades. Trump and some Republican lawmakers said the bills tax cuts would boost economic growth enough to increase government revenues and balance the budget, but many economists were skeptical of this claim.
The CBO says the law will boost annual GDP by close to 1 percent over the next ten years, but also increase annual budget shortfalls and add another roughly $1.8 trillion to the debt over the same period. In addition, many of the provisions are set to expire by 2025, but if they are renewed, the debt would increase further.
National Debt And Budget Deficit
The federal government creates an annual budget that allocates funding towards services and programs for the country. This is made up of mandatory spending on government-funded programs, discretionary spending on areas such as defense and education, and interest on the debt. The budget deficit can be thought of as the annual difference between government spending and revenue. When the government spends more money on programs than it makes, the budget is in deficit.
Read Also: How To Buy Foreclosed Homes
What Is The Us Debt Ceiling
The United States Congress oversees all American government departments including the Treasury. Until 1917, the Treasury had to seek the approval of Congress for every bond auction. Since then, the debt-raising capability of the Treasury has been limited by a debt ceiling that is set by Congress.
The debt ceiling covers all US government debt, including intragovernmental holdings.
The debt ceiling is stated as an amount rather than a percentage of GDP.
What Are The Policy Options For Dealing With The Debt
Politicians and policy experts have put forward countless plans over the years to balance the federal budget and reduce the debt. Most include a combination of deep spending cuts and tax increases to bend the debt curve.
Cut spending. Most comprehensive proposals to rein in the debt include major spending cuts, especially for growing entitlement programs, which are the main drivers of future spending increases. For instance, the 2010 Simpson-Bowles plan, a major bipartisan deficit-reduction plan that failed to win support in Congress, would have put debt on a downward path and reduced overall spending, including military spending. It also would have reduced Medicare and Medicaid payments and put Social Security on a sustainable footing by reducing some benefits and raising the retirement age. However, Biden plans to address gaps in the U.S. social safety net, which could increase demand for more long-term funding.
Some optimists believe that the federal government could continue expanding the debt many years into the future with few consequences, thanks to the deep reservoirs of trust the U.S. economy has accumulated in the eyes of investors. But many economists say this is simply too risky. The debt doesnt matter until it does, says Maya MacGuineas, president of the bipartisan Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget. By taking advantage of our privileged position in the global economy, we may well lose it.
Recommended Reading: Does Filing Bankruptcy Affect Taxes Owed
The Types Of Presidential Decisions That Impact National Debt
Presidents can have a tremendous impact on the national debt. They can also have an impact on the debt in another presidentâs term. When President Trump took office in January of 2017, for the first nine months of his presidency, he operated under President Obamaâs budget which didnât end until September, 2017. So for most of a new presidentâs first year in office, he isnât accountable for the spending that takes place. As strange as this may seem, itâs actually by design to allow time for the new president to put a budget together when in office.
Coronavirus And The National Debt
The U.S. government has taken efforts to offset the effects of worldwide health pandemic by borrowing money to invest in individuals, businesses, and state and local governments. Of these responses, the CARES Act has been the largest stimulus package in U.S. history. This stimulus package included $2.3 trillion towards relief for large corporations, small businesses, individuals, state and local governments, public health, and education. In order to pay for the relief fund, the government needed to expand its debt to do so, the government borrowed money from investors through the sales of U.S. government bonds.
Also Check: B Stock Phone Number
Does The United States Have Too Much Debt
We are now addicted to debt to lubricate the wheels of our financial system. There is nothing wrong with debt per se, but it is safe to say that too much debt relative to how much revenue is being produced is a sign of economic problems. At the core of our current financial mess is how we use debt as a parachute for any problem.
President Andrew Jackson Cuts Debt To Zero
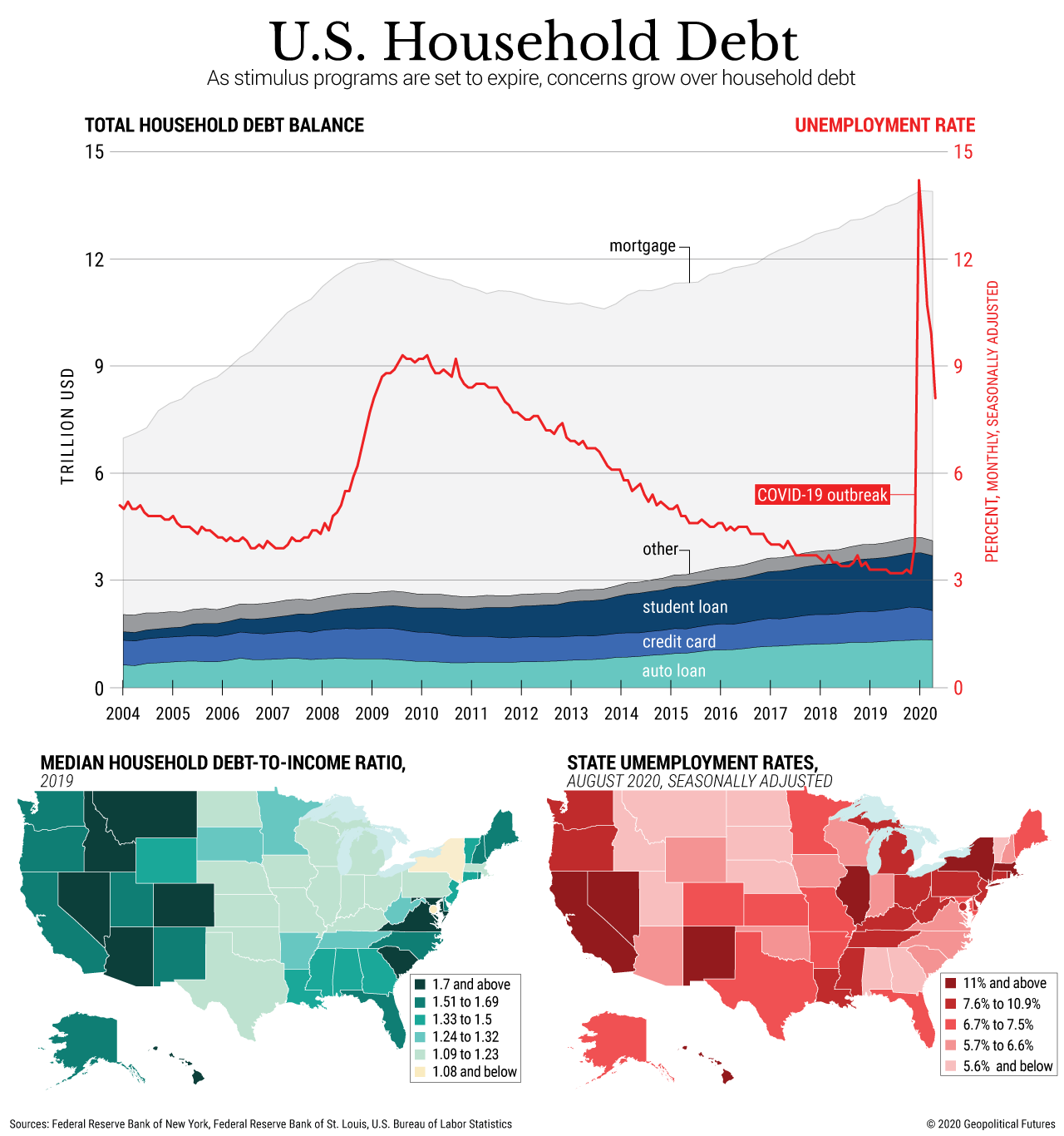
The War of 1812 more than doubled the nations debt. It increased from $45.2 million to $119.2 million by September 1815. The Treasury Department issued bonds to pay a portion of the debt, but it was not until Andrew Jackson became president and determined to master the debt that this national curse, as he deemed it, was addressed.
The time of prosperity was short-lived, as state banks began printing money and offering easy credit, and land value dropped.
Don’t Miss: How Long After Bankruptcy Can You Get A Mortgage
Us National Debt Statistics
- The current US national debt is $26,498,433,296,171 TreasureDirect – The debt to the Penny and Who Holds It
- Thatâs an increase of $3,326,434,162,341 since January 2nd 2020
- In 2020, national debt has increased $14,850,152,510 per day or $1.031 million per minute
- By December 31st 2020, the national debt is currently set to increase a further $2.15 trillion to $28,651,705,410,186
- The national debt per citizen equals $80,274 per person
- Between 2010 and 2020, national debt increased $9,157,778,722,542, an increase of 71.9%
- Since Jan 12nd 2020, national debt has increased more than $2.9 trillion
- National debt has increased for the last 64 years consecutively – the last time it fell was 1956 – 57
- The most expensive decade in American history was the 1860s, where national debt increased 3,726% from $64.8 million to $2.48 billion.
- 1836 – 37 saw the fastest ever increase in US national debt, soaring 882%. This was even quicker than the second fastest debt increase in history, 1835 – 1836, when it rose 798%
- National debt was almost eradicated in in the 1830s, dropping 99.4% during Andrew Johnsonâs Presidency
The U.S. national debt gets a lot of attention from the media and politicians. Still, few Americans truly understand what it means.