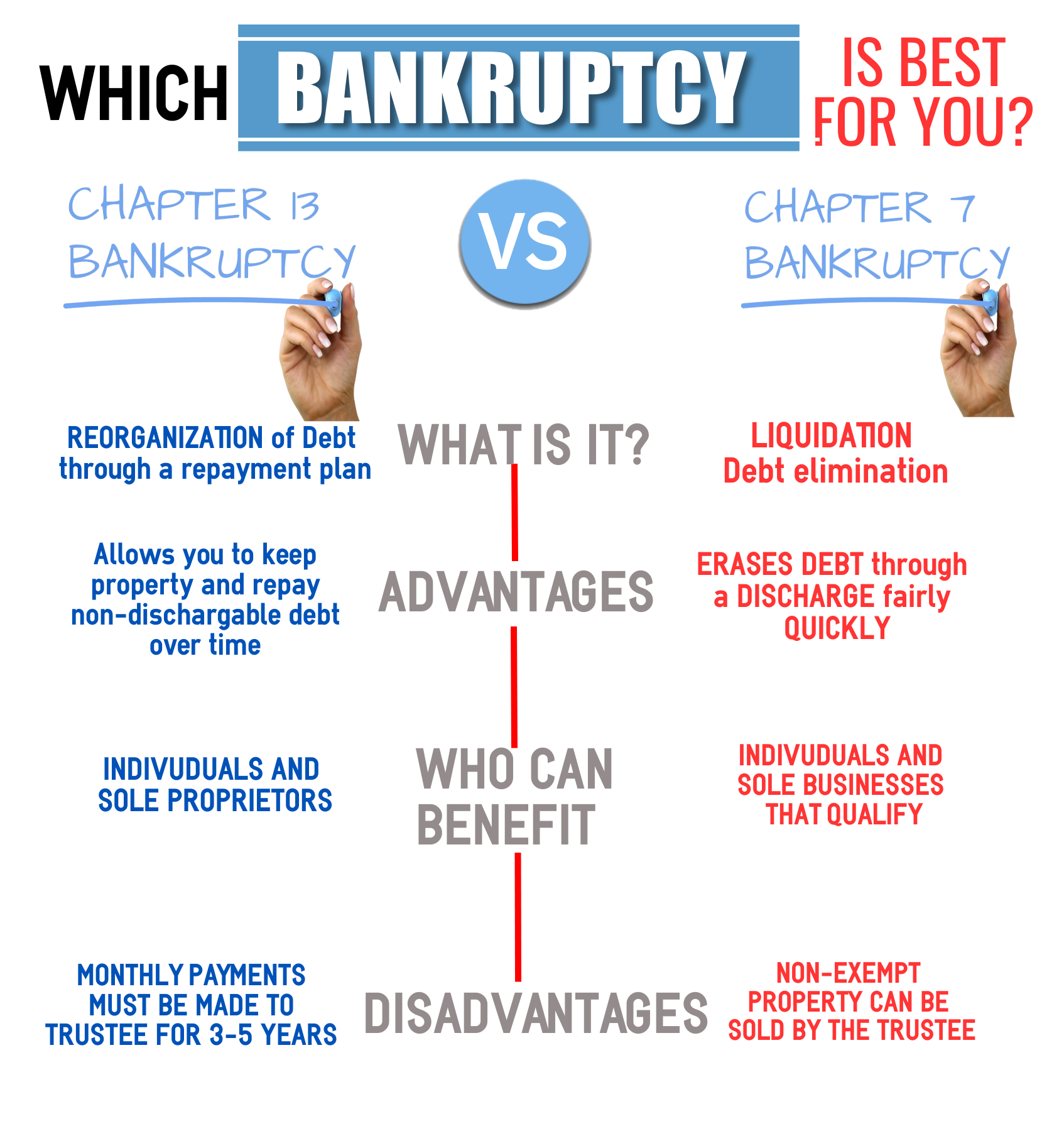
The Downsides Of Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Since Chapter 7 bankruptcy is by far the most common – and often preferred – type of bankruptcy, letâs start with a look at some of its downsides.
The bankruptcy trustee can sell any property not protected by an exemption
Bankruptcy exemptions protect most âbasicâ property – things like clothing, furniture, retirement accounts, and – at least up to a certain amount – cars. The state youâre filing bankruptcy in determines the type of bankruptcy exemptions youâre able to use. That’s because the Bankruptcy Code gives each state the option to require their residents to use state law instead of bankruptcy law to protect their belongings. If you own non-exempt property and donât want it to be used to pay at least a portion of your debts, a Chapter 7 âliquidation bankruptcyâ may not be right for you. Chapter 13 allows you to keep nonexempt property.
It doesnât help with expensive car loans if you want to keep the car
Even though bankruptcy law allows you to keep your not-yet-paid-off car even after filing a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, youâll likely be stuck with the same car loan. After signing a reaffirmation agreement, most Chapter 7 filers are stuck with the same high interest rate on their loan and often owe much more on it than the car is worth. This can seriously lessen the positive impact your fresh start will have on your monthly budget.
It doesnât help with non-dischargeable debt or past due mortgage obligations
You Will Keep Future Income
In general, the property you acquire or will acquire after filing for Chapter 7 is not included in the bankruptcy estate.
These forms of property acquired within 180 days after filing for Chapter 7 will become part of the bankruptcy estate:
- Inherited property
- Proceeds from a life insurance policy
Do We Have Chapter 7 Or Chapter 13 Bankruptcy In Canada
I have always thought one of the disadvantages of living next to the largest economy in the world is the fact that Canadians end up using American terms for things they may be looking for. The use of Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy wording is an excellent example.
Since many people use these insolvency terms in Canada, I will give a brief explanation of how the different compare.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Bankruptcy Petition Preparer
Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 13
When deciding between Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 13 bankruptcy, itâs important to consider:
-
the types of debt you have ,
-
if any of your personal property would be considered a nonexempt asset,
-
if your regular monthly income is enough to cover your living expenses, and
-
the difference between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 on your credit report
Bankruptcy can be a powerful poverty fighting tool and help thousands of families get back on their feet every month. If youâre facing wage garnishment, know the Bankruptcy Codeâs âautomatic stayâ protects you from any future garnishment as soon as your case is filed. If youâre not sure whether bankruptcy is right for you, keep doing what youâre doing and research. You may even consider signing up for a free credit counseling session to learn more.
Donât be discouraged – or embarrassed – by the idea of filing bankruptcy. If COVID-19 and its impact on everyone in the United States and around the world has shown us anything, it’s that life happens. Bankruptcy laws exist to give you a fresh start. Thereâs no shame in using this legal tool, just like Walt Disney, Abraham Lincoln, and Henry Ford did when they needed help.
Filing Chapter 7? Upsolve may be able to help…
Reasons To File For Chapter 7 Bankruptcy

Just as there are good reasons to file for Chapter 13 bankruptcy, there are many reasons why filing for Chapter 7 may be in your best interest. Depending on the facts of your case, it may be possible to have debts discharged in as little as 60 days.
Your Debts Are Mostly Eligible for Discharge
If you have mostly credit card or medical debt that you can no longer pay, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is usually the most helpful in getting rid of it quickly. You may also be able to discharge payday loan or personal loan debt as well. As a general rule, if the debt is unsecured, it can in most cases be eliminated through a liquidation bankruptcy.
You Are Looking to Get Rid of Debt Quickly or You Are Unable to Repay With a Payment Plan
In a Chapter 7 case, you may be able to discharge your debt without paying anything in a matter of weeks. As they are generally exempt, you may be able to keep your IRA or 401 even after your case is finalized. For those who are unable to pay creditors, getting a quick discharge is critical as all contact and collection efforts must generally stop unless you reaffirm your commitment to pay a particular debt.
Filing bankruptcy may enable a debtor to get a fresh financial start. However, prior to filing, it might be worthwhile to talk with a bankruptcy lawyer who may be able to explain the differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy and which options are available to you.
Read Also: How To Buy A New Car After Bankruptcy
Which Is Better: Chapter 7 Or Chapter 13
Which form of bankruptcy is best for you depends on your financial situation and goals.
To determine whether Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy is best for you, consult with a bankruptcy attorney. Youll want to ensure that your problem debts can be handled by bankruptcy and that you’re in a position to make the most of the fresh start that bankruptcy offers.
Most consumers opt for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, which is faster and cheaper than Chapter 13. The vast majority of filers qualify for Chapter 7 after taking the means test, which analyzes income, expenses and family size to determine eligibility. Chapter 7 bankruptcy discharges, or erases, eligible debts such as credit card bills, medical debt and personal loans. But other debts, like student loans and taxes, typically arent eligible. And Chapter 7 doesnt offer a route to get caught up on secured loan payments, like a mortgage or auto loan, and it doesnt protect those assets from foreclosure or repossession.
In some instances, a bankruptcy trustee an administrator who works with the bankruptcy courts to represent the debtor’s estate may sell nonexempt items, meaning belongings that are not protected during bankruptcy. Nonexempt items vary according to state law.
What To Expect In Your Bankruptcy Filing
Bankruptcy filing is a complex process, and any errors made during the initial phase of your bankruptcy case can significantly increase the time required for the bankruptcy case to unfold. An experienced attorney will be invaluable as you begin the bankruptcy filing process. They will help you gather the documentation you will need to provide to the bankruptcy court and prepare you for each stage of your case.
The first phase of filing for bankruptcy is the initial petition. Once you file for bankruptcy, an automatic stay is placed on your assets and property that will prevent creditors from continuing with their collection efforts. This alone can be a major relief, especially if you have dealt with repeated calls and other collection efforts for months. However, the initial filing is only the first step in securing bankruptcy status.
Recommended Reading: How Many Bankruptcies Has Donald Trump Filed
Bankruptcy Lawyer Vs Bankruptcy Trustee
Of course there are differences between how bankruptcy law works in the US and in Canada. The most obvious is the fact that in the US, to file either Chapter 7 bankruptcy or Chapter 13 the first step is to hire an . The lawyer helps you prepare the documents in order to apply to the Court for approval of your plan. The creditors have the right to appear in Court and proposal alternate arrangements, after which the Court issues an Order and assigns your file to a Bankruptcy Trustee.
In Canada you attend directly at a Bankruptcy Trustees office in order to file personal bankruptcy or a consumer proposal. Lawyers and the Court only become involved in very complex cases after you file. .
The Canadian approach was designed to reduce the costs of filing bankruptcy or a consumer proposal so that more of your money can go to repaying your debts.
If you reside in Canada and you require relief from your debts then you should research personal bankruptcy and consumer proposals. If the article starts referring to Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, youre likely on a US page and need to refine your search.
Choosing The Right Type Of Bankruptcy
Your income and assets will determine the bankruptcy chapter you file. For instance, too much income might preclude you from filing a simple Chapter 7 case. Or, if you have property you’d lose in Chapter 7 that you’d like to keep, you can protect it in Chapter 13.
In Chapter 7 bankruptcy, the bankruptcy trustee has the power to sell your nonexempt property to pay back your creditors. As a result, Chapter 7 might be costly if you own a lot of assets. By contrast, Chapter 13 bankruptcy allows you to keep all of your property in exchange for paying back a portion or all of your debts through your repayment plan.
Further, if certain conditions are satisfied, Chapter 13 bankruptcy offers debtors additional benefits that aren’t available in Chapter 7 such as the ability to:
- save a home subject to foreclosure–or a car from repossession–by catching up on missed payments
- reduce the principal balance of your car loan or investment property mortgage with a cramdown, or
- eliminate your second mortgage or another unsecured junior lien through lien stripping.
Here are a few scenarios that explore which bankruptcy strategy would be best:
Don’t Miss: How To Get Bankruptcy Court Documents
Pros Of Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Debtors who earn too much to qualify for Chapter 7 may yet score bankruptcy protection under Chapter 13. This means, among other things, calls and other contacts from creditors and collections agencies stop the moment the application is filed. Other plusses include:
- You get time to pay back your creditors, oftentimes with lower payments than you faced before declaring bankruptcy.
- Once your plan is complete, creditors who were not repaid in full cannot pressure you into making them whole.
- Under Chapter 13, a debtor has the length of the plan to catch up on past-due amounts owed on houses, vehicles, or loans secured by collateral. Repossession schemes stop under Chapter 13, and the valuables need not be liquidated as they would in a Chapter 7 filing.
- Through a Chapter 13, you may be able to renegotiate secured debts such as a car loan and in some cases can pay a lower interest rate and lower car payment.
- Chapter 13 filers also have the life of their plan to pay overdue income taxes and domestic support obligations such as child support and alimony.
- Chapter 13 protects the debtors cosigners on personal loans.
- In a Chapter 13 case, the debtor may be allowed to pay the bankruptcy attorneys fee in an installment plan, rather than in advance.
- Unlike Chapter 7, which limits the frequency of filing, you may file for a Chapter 13 plan repeatedly.
Chapter 7 Vs Personal Bankruptcy
When a person finds themselves in deep financial trouble in the United States they may file personal bankruptcy under Chapter 7, Title 11 of the United States Code. Overtime this has simply come to be known as Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
In Canada it is simply called filing for bankruptcy. The law is known as the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act of Canada, or BIA for short, but the only people that refer to the law are professionals working in this area.
Read Also: Has Mark Cuban Ever Filed For Bankruptcy
Your Credit Could Take A Hit
The other major consequence of a Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the impact to your credit. A Chapter 7 bankruptcy can stay on your credit reports for up to 10 years from the date you file.
That doesnt mean youll never be able to open a credit card or take out a mortgage again, but it does mean you might have to pay a lot more in interest rates and fees when borrowing.
Who Controls The Business In A Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Filing
In a Chapter 11 filing, the owners of the business continue to operate the business. The debtor is considered the âdebtor in possessionâ because generally no trustee is involved. The debtor in possession has the exclusive right to propose a bankruptcy plan of reorganization for a certain period of time.
Unsecured creditors may form a creditors’ committee to ensure the bankruptcy plan meets their best interests under the bankruptcy laws. After a certain period of time, creditors are able to file a competing plan. The debtor’s bankruptcy plan can propose different treatment for creditors’ claims and even cram down secured creditors by changing the terms of the repayment, including the interest rate.
Ultimately, the court determines what’s in the best interest of creditors and approves a bankruptcy plan and related disclosure statements following a confirmation hearing.
In a Chapter 7 case the trustee takes over to close down the business. This typically involves selling off all of the debtorâs assets for the benefit of unsecured creditors. The trustee has a duty to act in the best interest of the unsecured creditors while administering the case. The trustee may operate the business for a short time if that generates more money for the creditors.
Read Also: How To Become A Bankruptcy Lawyer
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Repayment Plan
Chapter 13 debtors create their own repayment plan, which must be written and submitted to the bankruptcy court at the outset of your case. The federal bankruptcy court provides a form for drafting a plan, or you can obtain one from a lower court in your area. The bankruptcy court must approve your plan for you to enter Chapter 13. The plan details your income, property, expenses and debts and includes a proposed payment plan.
A trustee will be assigned to review your plan, assess its compliance with bankruptcy laws, collect your payments and distribute them to creditors, and make sure all terms in your bankruptcy repayment plan are followed.
Your repayment plan will be divided into categories, which include:
How To File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
The most important factor in filing Chapter 7 bankruptcy is finding an experienced bankruptcy attorney. Once you decide on an attorney, you can refer creditors to your lawyers office. Filing the petition will trigger an automatic stay, which means creditors cant pursue lawsuits, garnish your wages or contact you about your debts. Heres a potential timetable:
If youre qualified, it will take 4-6 months to complete the bankruptcy process.
Here are the steps you must take when filing for bankruptcy:
Don’t Miss: Can Bankruptcy Stop A Judgement
If You’re Thinking About Bankruptcy You’ll Need To Consider Which Type Is Right For You Here Are The Highlights
By Cara O’Neill, Attorney
Once you’ve decided that bankruptcy is the right solution for your financial situation, you will need to decide which type of bankruptcy is most beneficial.
If you are an individual or a small business owner, then your most obvious choices are Chapter 7 “liquidation” bankruptcy or Chapter 13 “wage earners” or “reorganization” bankruptcy.
We’ll go over the pros and cons of each, the eligibility rules, and give you some information to help decide which would be best for you in your financial situation.
There are a select few other types of bankruptcies that are available under certain circumstances, and we will touch on those as well.
The Differences Between Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Those who are having trouble repaying their debts may opt to file for either Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy. Chapter 7 bankruptcy involves liquidating all non-exempt property and using the funds to repay creditors. Chapter 13 is a way for wage earners to reorganize existing debt to be repaid over three or five years.
Generally speaking, most debtors prefer to file for Chapter 7 over Chapter 13 because it tends to be easier and because it eliminates most unsecured debt. However, Chapter 13 is a good option for those who do not qualify for Chapter 7.
Also Check: How Many Times Has Trump Declared Bankruptcy
Power Over Special Unsecured Creditors
There are certain types of debt that are not discharged in bankruptcy, such as recent income taxes, all child and spousal support, student loans, and a few others. Under Chapter 7, if you have any of these debts, you need to deal with them after your case is finished.
This may be fine if the surviving debt is relatively small and discharging your other debts has made dealing with it manageable. Additionally, many types of unsecured debts are discharged under Chapter 7 bankruptcy. These include medical debt and .
Under Chapter 13, you can arrange to pay those kinds of special debts through a court-approved repayment plan which usually gives you more control, is based on what you can afford, and protects you from all your creditors throughout the process.
This continued protection can be especially important because otherwise, the law tends to give these kinds of creditors extraordinarily aggressive collection powers. Also, in some casessuch as income taxesyou will be able to pay less by avoiding ongoing interest and penalties.