How To Check For Bankruptcy In Georgia
Georgia court records are usually held in the custody of the Gwinnett County Clerk of the Magistrate, State, and Federal appellate courts.
The Clearks office website has online search tools to request case records and view the courts calendar. You can typically use the service to find any document or case information, providing the case n numbers and the parties involved.
You can also use an advanced case search function to request and search for documents and information on parameters such as presiding judge, court location, and court filing date.
An advanced case search function saves time and filters results by parameters like court filing date, court location, and the presiding judge.
You can typically request and search for information as a member of the public by visiting the Court Clerks office on Langley Drive, Lawrenceville, GA 30046, which is usually open between 8.00 AM and 5.00 PM Monday to Friday.
Once a case has been concluded, any member of the public can request and access information on any petition, including the creditors of an estate, the creditors, trustee, and debtors.
Your Creditors And Your Bankruptcy
You are required to list all of your creditors and send them a notice that states you are filing bankruptcy at the beginning of your filing. That means that if you owe money to individuals or entities in the community, they will become aware when you file bankruptcy just because you owe them money.
This notice requirement is really for your benefit, however. The automatic stay is only useful if the creditor knows you have filed bankruptcy. That is, a creditor can only be punished for continuing collection activities if it knows that you filed bankruptcy. As a result, it is vital that all of your creditors be made aware that you have filed.
Read Also: How Long Does Bankruptcy Stay On Record
What Are Bankruptcy Exemptions
Bankruptcy exemptions prevent debtors from losing all their assets to the bankruptcy process. These exemptions help the debtor maintain ownership of all or certain parts of specific assets required to maintain a basic standard of living.
Bankruptcy law provides several federal exemptions. However, states also offer varying exemptions to resident petitioners. Regardless, the requirements for applying these exemptions may differ between states. For instance, many states allow debtors to choose between federal and state exemptions but disallow a combination of both. Petitioners in states like Kentucky, New York, and New Hampshire may abandon federal exemptions in favor of state options and vice versa. However, states like California, Louisiana, and Colorado do not recognize federal exemptions.
Every three years, the amounts allowed under federal exemptions are adjusted due to changes in the Consumer Price Index. As of April 1, 2019, the following federal exemptions and amounts apply:
Homestead Exemption
Under federal law, a debtor can protect up to $25,150 of equity in their principal place of residence. The residential property may be a house, another type of dwelling, or personal residential property, such as a residential trailer. The homestead exemption only applies if the debtor lives on the property. This exemption is not usable on rental properties or other related investments.
Wildcard Exemption
Personal Property Exemptions
Benefit and Support Exemptions
Don’t Miss: How Long After You File Bankruptcy Can You File Again
How To Rebuild Credit After Bankruptcy
Accounts included in a bankruptcy filing wont be reported as unpaid or past due anymore on your credit reports. Assuming you pay new debts on time as you incur them, your credit rating will start to recover.
In the meantime, review your credit reports. Accounts that were discharged as part of your bankruptcy filing should be reported as discharged or included in bankruptcy on your credit reports. They should not show any money owed on them a balance of $0.
If there are errors in a credit report, contact the credit bureau to have the report corrected.
You can also start to rebuild your credit standing by obtaining a new credit card. You may have to resort to obtaining a secured credit card, which requires a deposit with the creditor. A third option is to have a family member or friend who has a good credit history apply for a card with you as a co-signer.
Rebuilding your credit is a gradual process. As you use a credit card and pay on time each month, other creditors will see your good financial habits on your credit report when its time to seek additional credit. It is best to avoid carrying a balance. If you must, it should not exceed 30% of the entire line of credit. You may review some tips to improve your credit score.
Read Also: Number Of Donald Trump Bankruptcies
Why Does Bankruptcy Appear On A Public Record Search

More than 500,000 Americans have filed for bankruptcy in recent years. Many individuals who have gone through difficult bankruptcy processes are unaware that their records are public information. In bankruptcy situations, privacy is not protected by state or federal law.
A person or organization can desire to carry out a bankruptcy filing public record search for several reasons, such as:
- A prospective employer wants to run a thorough background check.
- When considering a persons application for a license to practice in their field, a professional licensing committee will frequently inquire .
- A credit card or loan provider almost always does a credit check to evaluate eligibility for authorizing a loan or credit limit.
- A person thinking about investing in a certain firm will typically want to know more about its financial history.
You May Like: What Happens When A Company Files For Bankruptcy
Dont Ignore Your Debt Problems
Although tax liens and judgments might not appear on your credit reports today, there are still plenty of reasons to avoid them.
Its true you probably didnt wake up one morning and decide you were no longer going to pay your bills. Thats not the way financial and credit problems start for most people.
Still, even if youre struggling with bills you cant pay, you can avoid many tax liens and judgments simply by communicating with the agency or company to whom you owe the debt. The IRS, for example, offers payment plans for taxpayers who cant afford to pay their tax bills in full. Your creditors might be willing to settle your debt for less, as well.
One fact is clear. When youre in over your head financially, ignoring your problems isnt the answer.
Talk to your creditors or consider getting legal help or credit counseling. In extreme cases, bankruptcy might be your best option. Whatever financial challenge youre facing, youll be far better off to face it head on and deal with the consequences, rather than ignoring your problem and allowing it to grow.
What Is The Difference Between Chapter 7 And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy In Florida
Aside from the names, below are some of the differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 in Florida:
- Chapter 7 allows debtors to liquidate their properties and assets to settle the debts, while Chapter 13 allows debtors to retain control of their properties and assets and develop a repayment plan.
- Chapter 7 can be filed by both individuals and businesses, while Chapter 13 can only be filed by individuals with regular income.
- Debtors who file Chapter 7 bankruptcy will have their unsecured debts discharged, while debtors who file Chapter 13 may have to make full or partial repayment of their unsecured debts.
Don’t Miss: Credit Card Debt In America 2021
Is Bankruptcy Discharge Public Record
Yes. But that doesnât mean that people are guaranteed to find out about it.
Many people worry that other people will find out that they have filed for bankruptcy. Because a bankruptcy filing is a court proceeding, any bankruptcy discharge is public record. But, just because a bankruptcy filing is public record doesn’t mean you should let that hold you back from deciding to get relief.
Who Is Required To Be Informed Of Your Bankruptcy
The most obvious party that will be informed of your bankruptcy is your creditors.
When filing bankruptcy, you will compile a list of creditors who will be informed as they need to put an automatic stay on your debt, which means that all creditors are required to stop their debt collecting activity.
Your lawyer is required to list everyone you owe money to.
Surprisingly enough, you have to tell companies that have nondischargeable debts too.
For example, you must tell student loan companies that you are filing bankruptcy, even though the student loans dont go away in bankruptcy.
Child support recipients and any co-signers or codebtors must also must be told about it.
You May Like: Can You File Bankruptcy On Business Taxes
Read Also: Can A Home Equity Loan Be Discharged In Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy Is A Public Record But Public Records Are Not Easily Accessed
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy filing is a public record. Your bankruptcy case will be filed in court and the public does have the power to access it. However, searching and reviewing public records is not that easy. To obtain bankruptcy records, you will need to search an online platform that contains nationwide bankruptcy filings. To gain access to the portal, you must register and pay for each page of the documents you obtain. As such, few people outside of bankruptcy professionals will ever see your filing.
Your bankruptcy will additionally be visible on your credit report. Your credit report could be accessed by potential employers, rental agencies, and other financing offices. Accordingly, with your permission, certain individuals could access your bankruptcy history in this manner. The bankruptcy will appear on your credit report for ten years.
In Practice, Few Will Know of Your Bankruptcy
If you are among the millions of Americans drowning in debt, you will need to weigh all the potential benefits of divorce against the potential drawbacks. Acknowledge that bankruptcy is a matter of public record, but also recognize that your bankruptcy will not suddenly be known by your friends and neighbors. Contact a bankruptcy attorney today for assistance with assessing whether you may benefit from filing for bankruptcy.
What Is The Downside Of Filing For Bankruptcy
There are several disadvantages to filing for bankruptcy. Although the bankruptcy system provides respite to persons with heavy debt, interested petitioners should be mindful of the following downsides.
You May Like: What Happens When You Declare Bankruptcy In Texas
The Pacer System & Court Records
A bankruptcy filing becomes public record after you submit your bankruptcy petition. Someone from the court will upload your documents and bankruptcy schedule into the Pacer system.
The PACER system is a program used by the federal courts to keep track of any and all court documents. Any kind of paperwork that goes through a court will usually be added to the PACER system, and can therefore be accessed by the public. To access the system, you need to create a PACER account and pay a small fee per page that is viewed.
What Happens If I Declare Personal Bankruptcy
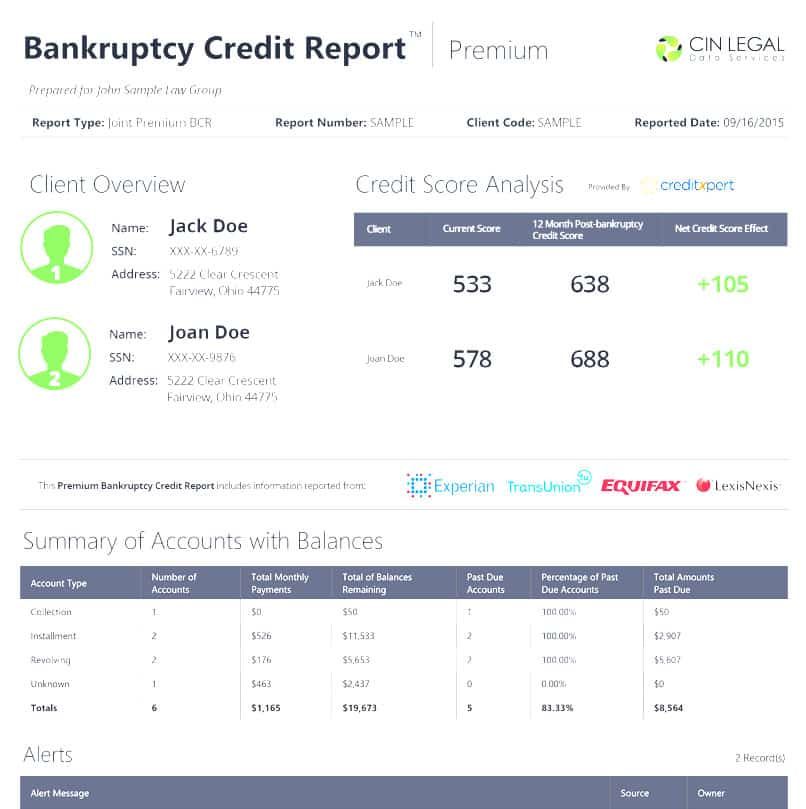
What happens when you file. When you file for bankruptcy, you get an automatic stay, which puts a block on your debt. Such stays prevent creditors and collections agencies from pursuing debtors for amounts owed. While the stay is in place, your wages cant be garnished and creditors cant go after any secured assets.
You May Like: Did The Nra Filed For Bankruptcy
You May Like: Can You Refinance While In Bankruptcy
How To Get North Carolina Bankruptcy Records
Persons interested in getting a bankruptcy record in North Carolina must follow systematic instructions peculiar to these public records. The two means of getting a bankruptcy record are viz:
- Online requests
- In-person and mail requests
An online search for bankruptcy records
When court staff receive a bankruptcy filing, the standard case management procedure is to keep a physical copy of each document. Courts also upload digital scans of the documents to an electronic repository. This electronic repository is the public access to court electronic records system .
Using PACER, any interested requester with access to the internet may access bankruptcy records. An advantage of PACER over in-person requests is that the user may get public records regardless of the District in charge of the bankruptcy case. Besides, the system is available round-the-clock, and the access fee is cheaper. PACER charges $0.10 per page viewed. The user may also print the documents accessed.
However, a limitation of PACER is that sealed records are typically unavailable to public users. Furthermore, older bankruptcy records from before December 2003 are unavailable on the system. To access either, the requester must make an in-person request following the instructions in the next section.
In-person and mail requests:
Are Bankruptcy Records Public Information
Generally, bankruptcy records are publicly available unless sealed or expunged by the court. As per 11 U.S.C. § 107, interested persons can examine and obtain copies of bankruptcy records, including dockets and all papers filed in the bankruptcy case. However, identifying details and other information that may put an individual at risk of personal injury, identity theft, or unlawful injury to the property are protected from disclosure by the bankruptcy court. Examples of these details include:
- Bank account numbers
- Names of minors involved in the case
- Private contact details
In some cases, the bankruptcy court may seal or destroy the entire bankruptcy record if the judge finds that public availability may threaten an individuals safety. However, interested persons have to file a petition and explain how the entire file presents a threat and how “the need to seal records” outweighs the publics right to access the document. If the court determines that sealing is unnecessary, it may simply redact sensitive information instead of placing the record under seal. Public bankruptcy records are accessible by phone, in person at court depositories, and online.
Read Also: Can You Be Bonded After Bankruptcy
Us Bankruptcy Court Records Are Technically Public But Often Inaccessible
It is true that, as a court document, your petition for bankruptcy will be part of the public record. Federal and state court records are generally required to be available to the public. However, the federal Public Access to Court Electronic Records system isnt free. PACER charges the individuals and companies who use it for every search they run, and every page they view. Because of this, most of the people who use PACER are attorneys, credit companies, or lenders. Unless you are a celebrity, reporters and the general public wont care enough to pay the fee to access your personal bankruptcy records.
Types Of Bankruptcy Filings
Chapter 7: Liquidation
Chapter 7 is designed for individuals and businesses experiencing financial difficulty that do not have the ability to pay their existing debts. Under Chapter 7 a trustee takes possession of all of your property. You may claim certain property as exempt under governing law. A bankruptcy trustee then liquidates all non-exempt property and uses the proceeds to pay your creditors according to a distribution scheme required by the Bankruptcy Code.
The main purpose of filing a Chapter 7 case is to obtain a discharge of your existing debts. A bankruptcy discharge is a court order releasing you from liability for many types of debts. If, however, you are found to have committed certain kinds of improper conduct described in the Bankruptcy Code, your discharge may be denied by the court and the purpose for which you filed the bankruptcy petition will be defeated.
Even if you receive a discharge, there are some debts which are not discharged under the law. These include certain types of taxes, student loans, alimony and child support payments, debts fraudulently incurred, debts for willful and malicious injury to a person or property, and debts arising from a drunk driving charge. Generally speaking, a bankruptcy discharge does not remove liens from your property.
Chapter 11: Reorganization
Chapter 11 is designed for the reorganization of a business. It is also available to individual debtors who exceed the thresholds for Chapter 13 bankruptcies.
Also Check: Overstock Returns Customer Service
How To Get Massachusetts Bankruptcy Records
Copies of bankruptcy case documents, official documents, and claims registers are available to members of the public upon request. Interested persons can either access records through court-provided online databases or request physical copies from the courts.
Requesting Physical Copies
In Massachusetts, the bankruptcy court provides physical copies to requesters at 50 cents per page, payable at the time of pickup. If any entity requests physical copies but refuses to pick them up within three days, the request will be discarded. Therefore, all requesters should ensure that they pick up their requested copies when the court clerk informs them of their availability.
Individuals can also obtain certified copies of case documents if they are registered ECF Users. Registered users can obtain up to five certified copies for a single case or proceeding by filing a request with the court and paying the required fees. The court will then process the request and mail the requested certified documents to the attorney or entity.
Certified and paper copies may also be obtained in person at the court. For in-person requests, no inspection fee is required. The individual is only required to pay the printing or photocopy fee and the $11 certification fee. The court will only accept payments with a bank cashier’s check or money order made payable to “Clerk, United States Bankruptcy Court.”
Requesting Electronic Records
- Date and time of 341 Meeting
- Date of discharge,