Alternatives To Chapter 7
Debtors should be aware that there are several alternatives to chapter 7 relief. For example, debtors who are engaged in business, including corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships, may prefer to remain in business and avoid liquidation. Such debtors should consider filing a petition under chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code. Under chapter 11, the debtor may seek an adjustment of debts, either by reducing the debt or by extending the time for repayment, or may seek a more comprehensive reorganization. Sole proprietorships may also be eligible for relief under chapter 13 of the Bankruptcy Code.
In addition, individual debtors who have regular income may seek an adjustment of debts under chapter 13 of the Bankruptcy Code. A particular advantage of chapter 13 is that it provides individual debtors with an opportunity to save their homes from foreclosure by allowing them to “catch up” past due payments through a payment plan. Moreover, the court may dismiss a chapter 7 case filed by an individual whose debts are primarily consumer rather than business debts if the court finds that the granting of relief would be an abuse of chapter 7. 11 U.S.C. § 707.
Debtors should also be aware that out-of-court agreements with creditors or debt counseling services may provide an alternative to a bankruptcy filing.
New Chapter 14 Bankruptcy Code Recommended By The United States Treasury Department
Would Handle Liquidation of Failing Financial Firms and Limit the Use of Orderly Liquidation Funds as Established in the Dodd-Frank Act
In February 2018, the United States Treasury Department issued the Orderly Liquidation Authority and Bankruptcy Reform Report advocating for the enhancement of the Bankruptcy Code, specifically as it applies to financial institutions. This report is in stark opposition to the CHOICE Act proposed by a conservative group of lawmakers in the U.S. House of Representatives that seeks to undo much of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act and fully repeal the orderly liquidation authority established in Dodd-Frank.
Under Dodd-Frank, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation is authorized to control the assets of a failing financial institution that has the risk of disrupting the United States financial markets. The OLA provides the FDIC with funds generated from fees on financial institutions to be used to break apart the assets of the banks taken over by the FDIC. Proponents support this structure because it uses bank fees instead of taxpayer dollars to handle the disassembly of failing banks and reduce the impact to financial markets. Opponents of OLA argue that risky bank behavior is incentivized by essentially providing a guarantee fund.
This blog post was drafted by Matthew Wine, an attorney in the Spencer Fane LLP Kansas City, MO office. For more information, visit spencerfane.com.
Rule 3009 Declaration And Payment Of Dividends In A Chapter 7
In a chapter 7 case, dividends to creditors shall be paid as promptly as practicable. Dividend checks shall be made payable to and mailed to each creditor whose claim has been allowed, unless a power of attorney authorizing another entity to receive dividends has been executed and filed in accordance with Rule 9010. In that event, dividend checks shall be made payable to the creditor and to the other entity and shall be mailed to the other entity.
Notes of Advisory Committee on Rules1983
This rule is derived from former Rules 308 and 1135. The preparation of records showing dividends declared and to whom payable is subject to prescription by the Director of the Administrative Office pursuant to Rule 5003. The rule governs distributions to creditors having priority as well as to general unsecured creditors. Notwithstanding the detailed statutory provisions regulating the declaration of dividends, a necessarily wide discretion over this matter has been recognized to reside in the court. See 3A Collier, Bankruptcy 65.03 : 1 Proceedings of Seminar for Newly Appointed Referees in Bankruptcy 173 . Although the rule leaves to the discretion of the court the amount and the times of dividend payments, it recognizes the creditors’ right to as prompt payment as practicable.
The rule does not permit variance at local option. This represents a marked change from former Bankruptcy Rule 308.
Notes of Advisory Committee on Rules1993 Amendment
Recommended Reading: How Does Filing Bankruptcy Affect Your Tax Return
Rule 3019 Modification Of Accepted Plan In A Chapter 9
Modification of Plan Before Confirmation . In a or chapter 11 case, after a plan has been accepted and before its confirmation, the proponent may file a modification of the plan. If the court finds after hearing on notice to the trustee, any committee appointed under the Code, and any other entity designated by the court that the proposed modification does not adversely change the treatment of the claim of any creditor or the interest of any equity security holder who has not accepted in writing the modification, it shall be deemed accepted by all creditors and equity security holders who have previously accepted the plan.
Modification of Plan After Confirmation in a Subchapter V Case . In a case under subchapter V of chapter 11 , a request to modify the plan under §1193 or of the Code is governed by Rule 9014, and the provisions of this Rule 3019 apply.
Notes of Advisory Committee on Rules1983
This rule implements §§942, 1127 and 1323 of the Code. For example, §1127 provides for modification before and after confirmation but does not deal with the minor modifications that do not adversely change any rights. The rule makes clear that a modification may be made, after acceptance of the plan without submission to creditors and equity security holders if their interests are not affected. To come within this rule, the modification should be one that does not change the rights of a creditor or equity security holder as fixed in the plan before modification.
Types Of Bankruptcy Proceedings
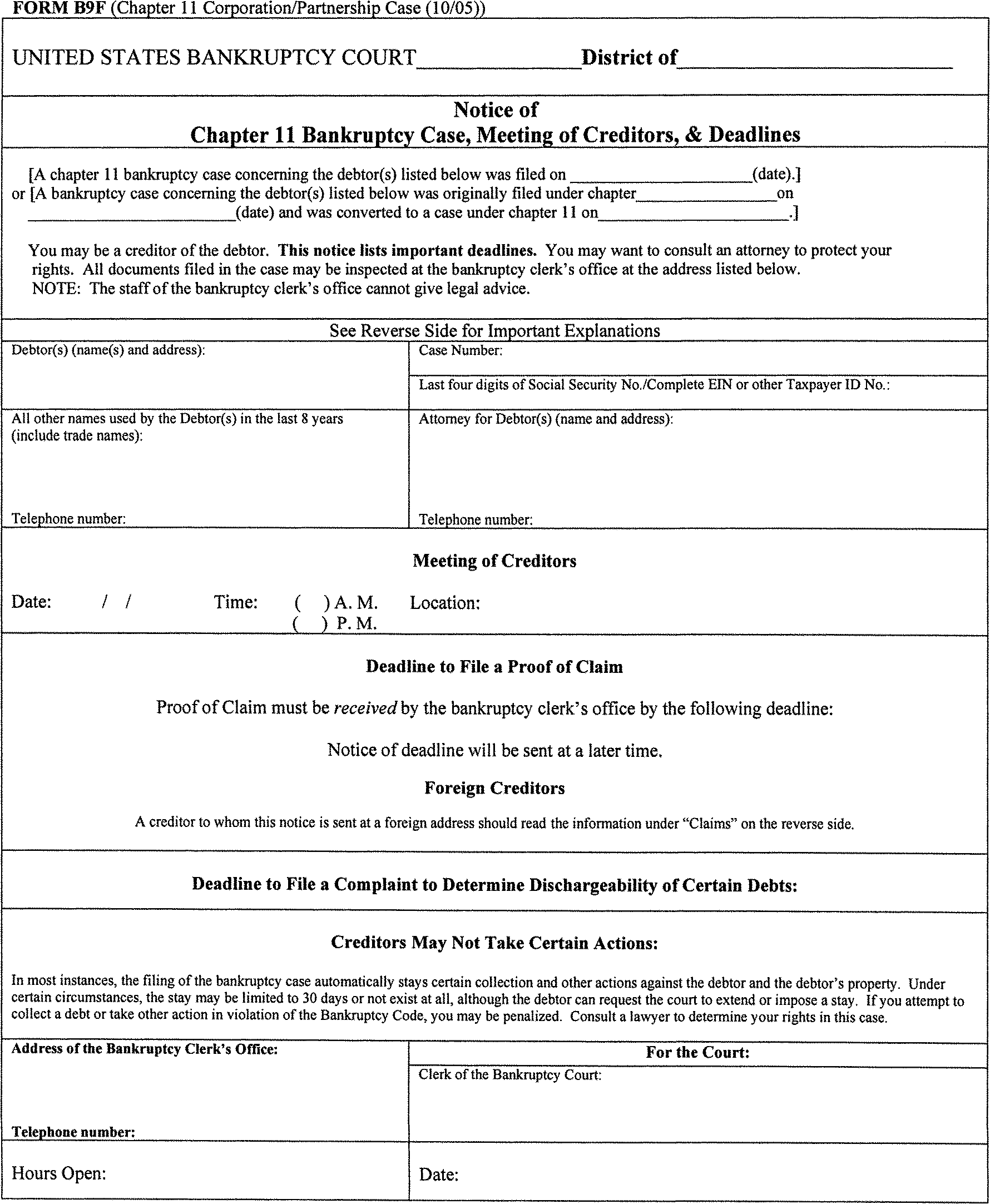
There are several different types of bankruptcy cases, each with its own rules and forms. They are generally referenced by the chapter number in the U.S. Bankruptcy Code in which the type of bankruptcy is discussed.
The most common forms of bankruptcy are:
The rules and procedures for Chapter 15 bankruptcy are, for example, outlined in Chapter 15 of the Bankruptcy Code.
All types of bankruptcy negatively affect credit and can make it challenging to get new credit.
Read Also: Bankruptcy Attorney Rockford Il
Rule 3013 Classification Of Claims And Interests
For the purposes of the plan and its acceptance, the court may, on motion after hearing on notice as the court may direct, determine classes of creditors and equity security holders pursuant to §§1122, 1222, and 1322 of the Code.
Notes of Advisory Committee on Rules1983
Sections 1122 and 1322 set the standards for classifying claims and interests but provide that such classification is accomplished in the plan. This rule does not change the standards rather it recognizes that it may be desirable or necessary to establish proper classification before a plan can be formulated. It provides for a court hearing on such notice as the court may direct.
Notes of Advisory Committee on Rules1991 Amendment
This rule is amended to include chapter 12
How Chapter 7 Works
A chapter 7 case begins with the debtor filing a petition with the bankruptcy court serving the area where the individual lives or where the business debtor is organized or has its principal place of business or principal assets. In addition to the petition, the debtor must also file with the court: schedules of assets and liabilities a schedule of current income and expenditures a statement of financial affairs and a schedule of executory contracts and unexpired leases. Fed. R. Bankr. P. 1007. Debtors must also provide the assigned case trustee with a copy of the tax return or transcripts for the most recent tax year as well as tax returns filed during the case . 11 U.S.C. § 521. Individual debtors with primarily consumer debts have additional document filing requirements. They must file: a certificate of credit counseling and a copy of any debt repayment plan developed through credit counseling evidence of payment from employers, if any, received 60 days before filing a statement of monthly net income and any anticipated increase in income or expenses after filing and a record of any interest the debtor has in federal or state qualified education or tuition accounts. Id. A husband and wife may file a joint petition or individual petitions. 11 U.S.C. § 302. Even if filing jointly, a husband and wife are subject to all the document filing requirements of individual debtors.
Don’t Miss: Warehouse Pallets For Sale
You Can Keep Property You’d Lose In Chapter 7
When you file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you get to keep property protected or “exempt” from creditors under state or federal law. The bankruptcy trustee appointed to your case will sell any “nonexempt” property that isn’t protected by a bankruptcy exemption and use the proceeds to pay creditors.
In Chapter 13 bankruptcy, you don’t have to give up any property. However, there’s a catch. You must pay its value through the repayment plan. So, if you have nonexempt property you can’t bear to part with and can afford to pay to keep it, Chapter 13 bankruptcy might be the better choice.
Which Type Of Bankruptcy Is Right For My Situation
Since the other types of bankruptcies are specifically geared toward certain individuals or businesses, most people only qualify for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. Heres a side-by-side comparison to show how theyre different:
The biggest difference between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy comes down to the persons assets and income level. For instance, if someone had a recent job loss or an unsteady income, they might fall into a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. But if the means test says they make enough money to pay back their debts, they would fall into a Chapter 13 instead. Someone might also apply for Chapter 13 if avoiding home foreclosure is a top priority, or they could go for Chapter 7 if timing is an issuesince its significantly faster than Chapter 13.
But bankruptcy is a nerve-wracking experience, and choosing between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 is like trying to pick the lesser of two evils. In both cases, privacy goes out the window. All your information literally gets laid out on a table for the court to look through. Then theres the fact that about half of Chapter 13 bankruptcy cases nationwide are dismissed because the debtor cant make the monthly payments.4
So, lets look at some ways you can avoid filing for bankruptcy altogether.
You May Like: California Central District Bankruptcy
Estimated Proofs Of Claim
The IRS files estimated proofs of claim if you have unfiled, past due federal tax returns. Its important to have an up-to-date proof of claim for any federal taxes you owe before confirmation of your Chapter 13 plan. This ensures you dont pay any more than you need to and minimizes discharge of the tax debt issues upon completion of the Chapter 13 plan.
To help the IRS quickly amend an estimated proof of claim, promptly provide the IRS bankruptcy specialist with a copy of each late filed return for each year on the proof of claim. This helps to avoid unnecessary litigation on the proof of claim or discharge of the liability.
The specialists name and contact information are in part 3 of page 3 of the proof of claim. Otherwise, call to get the name and phone number of the specialist handling your case.
The specialist will ordinarily amend the proof of claim within 21 days. If you havent heard from the specialist within 21 days of submitting your late filed returns, please call .
Take Care Of Necessities First
Before you do anything, you want to make sure the Four Walls are covered: food, utilities, shelter, and transportation. You wont have the energy to fight your way out of debt if you dont have a house to sleep in or food to eat. So make sure youre taking care of yourself and your family first. The collectors can wait.
Also Check: How Long Does The Bankruptcy Process Take
Advantages Offered In Chapter 13 But Not Chapter 7
Before exploring options afforded by Chapter 13, check whether you meet these criteria:
- You’re an individual or a sole proprietor. Partnerships, LLCs, and corporations can’t file for Chapter 13.
- You meet debt requirements. In Chapter 13, your debt can’t exceed certain limits. If it does, you’ll use Chapter 11 bankruptcy. You can view the current Chapter 13 debt limits here.
If these factors don’t preclude you from filing, you might be able to take advantage of these exclusive Chapter 13 benefits.
Requirements For Chapter 11 Bankruptcy

The Small Business Reorganization Act of 2019, which went into effect on Feb. 19, 2020, added a new subchapter V to Chapter 11 designed to make bankruptcy easier for small businesses, which are defined as entities with less than about $2.7 million in debts that also meet other criteria, according to the U.S. Department of Justice.
The act imposes shorter deadlines for completing the bankruptcy process, allows for greater flexibility in negotiating restructuring plans with creditors, and provides for a private trustee who will work with the small business debtor and its creditors to facilitate the development of a consensual plan of reorganization.
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, signed into law by the president on March 27, 2020, raised the Chapter 11 subchapter V debt limit to $7,500,000. The change applies to bankruptcies filed after the CARES Act was enacted and sunsets one year later.
Because Chapter 11 is the most expensive and complex form of bankruptcy, most companies explore all alternative routes before filing for one.
Don’t Miss: New Foreclosure Law In California
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Bankruptcy
Declaring bankruptcy can help relieve you of your legal obligation to pay your debts and save your home, business, or ability to function financially, depending on which kind of bankruptcy petition you file. But it also can lower your credit rating, making it more difficult to get a loan, mortgage, credit card, buy a home or business, or rent an apartment.
If you’re trying to decide whether you should file for bankruptcy, your credit is probably already damaged. But it’s worth noting that a Chapter 7 filing will stay on your for 10 years, while a Chapter 13 will remain there for seven. Any creditors or lenders you apply to for new debt will see the discharge on your report, which can prevent you from getting any credit.
Will I Lose My Car If I Declare Bankruptcy
If you bought your car with a loan, your vehicle may be seized as collateral during a bankruptcy proceeding. However, you can usually keep your car by reaffirming your car loan and continuing to make payments. Similarly, you can usually keep your home if you declare bankruptcy, even if you owe money on it, as long as you continue making the payments and donât have more equity than you are permitted under state and federal bankruptcy laws.
Recommended Reading: Can You File Bankruptcy On A Civil Lawsuit
You Can Strip Off A Junior Home Mortgage
Chapter 13 offers a powerful benefit if your residential home is worth less than you owe. Chapter 13’s “lien stripping” mechanism lets you remove a “wholly unsecured lien” from your home. A wholly unsecured lien would be a junior loan that wouldn’t receive a penny if you were to sell your house.
For instance, suppose you owe $500,000 on your first mortgage and $70,000 on a second junior mortgage, but your house is worth only $460,000. If you sold the house, the sales proceeds wouldn’t fully pay the first mortgage, so there’d be nothing to pay toward the second. The second would qualify as a wholly unsecured junior mortgage, and you could eliminate the lien and essentially the loan using Chapter 13’s lien stripping procedure.
The “automatic stay” is an order that stops creditors from:
- “garnishing” your wages and taking money out of your paycheck
- “levying” on your bank account by instructing the bank to withdraw funds
- foreclosing on your house
- repossessing your car, and
- moving forward with a civil lawsuit requesting a money judgment.
But the automatic stay doesn’t always apply. For instance, your creditors can still collect spousal and child support. Also, you might need to file a motion asking the court to put the stay in place or extend it if:
- you filed bankruptcy the previous year because the stay will be limited to 30 days, or
- you filed two or more cases the previous year because the stay won’t go into effect.
Preface: Implementing The Dodd
The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System is responsible for implementing numerous provisions of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 . The Dodd-Frank Act requires, among other things, that the Board produce reports to the Congress on a number of potential reform topics.
See the Board’s website for an overview of the Dodd-Frank Act regulatory reform effort and a list of the implementation initiatives recently completed by the Board as well as several of the most significant initiatives that the Board expects to address in the future .
Also Check: What Is The Automatic Stay In Bankruptcy
What Are The Different Types Of Bankruptcies
11 Min Read | Nov 16, 2022
Youre sitting at the kitchen table, staring down collection notices and wondering how youre going to make things work. Maybe youve recently lost your job and the debt is piling up to an overwhelming amount. And then you think itthat word you never thought youd have to consider: bankruptcy.
Sometimes your situation seems so hopeless that bankruptcy looks like your only option. We know you might feel scared and backed into a corner, but bankruptcy isnt a decision to make lightly. Its important to know exactly what bankruptcy is and what the different types of bankruptcies are so you can make the best decision for your situation.