Appointment Of Bankruptcy Trustee
Once your case is filed you are appointed a bankruptcy trustee. They handle the paperwork, questions, and monitor your case from beginning to end.
Your trustee must, by law, make you aware of the possible bad outcomes that can happen. They should tell you that:
- You cannot file Chapter 13 for four years
- Your credit score will decline after the bankruptcy discharge
- Reaffirming a debt has consequences
You will be told about these risks at or before the meeting of the creditors . Ask questions if you do not understand one of the topics.
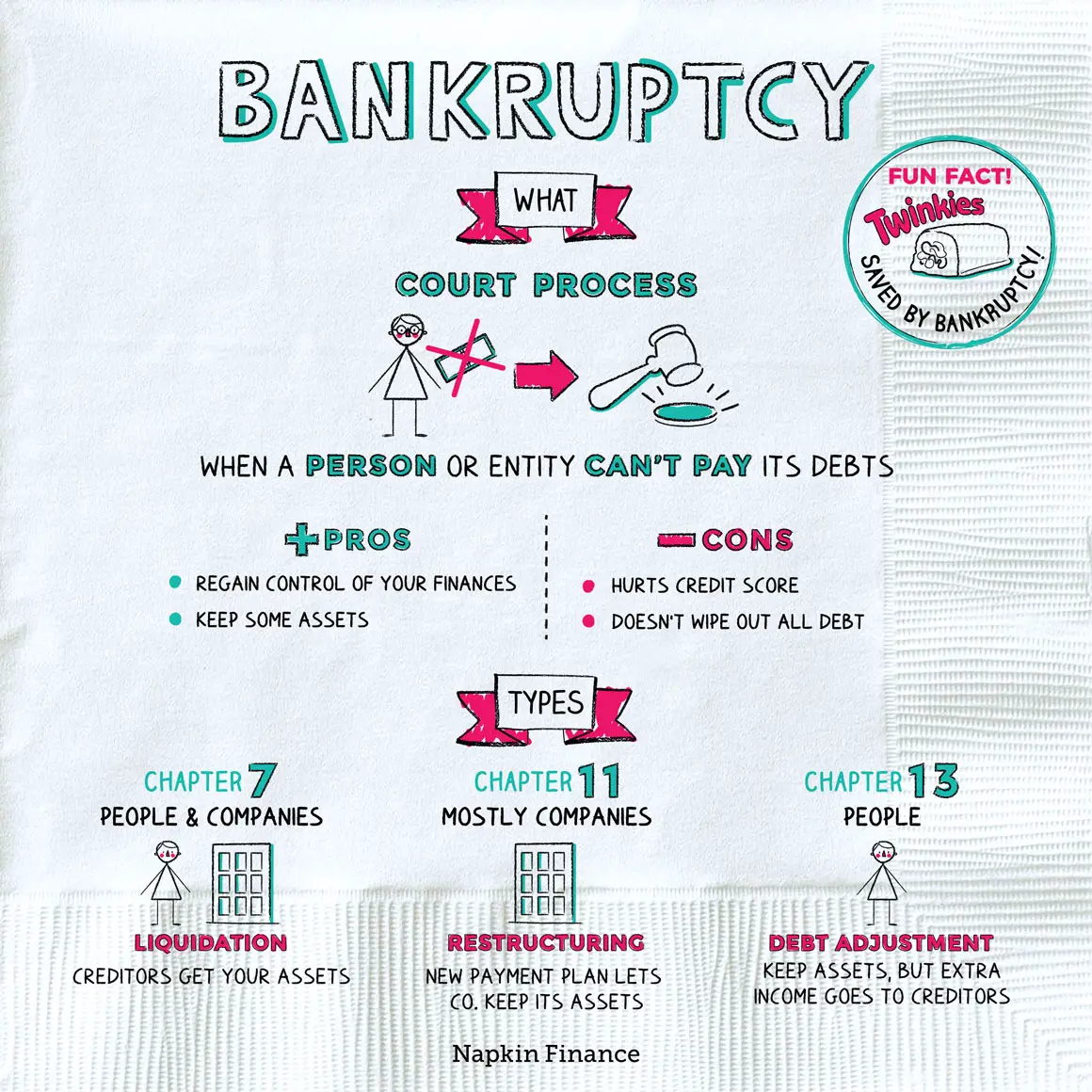
Different Types Of Bankruptcy
For individuals, there are two main types of bankruptcy cases. Most individual debtors file for Chapter 7, which can also be described as âstraightâ bankruptcy or âliquidation.â Under this plan all non-exempt assets are converted to cash , and secured creditors may have the item they financed turned over to them , unless the debtor reaffirms the debt with the courtâs approval prior to obtaining a discharge. Chapter 13, also called âreorganization,â is an option for people with regular income and debts that are less than the limits allowed by law. When you complete a Chapter 13 plan, you have the satisfaction of keeping your assets, paying your creditors, and possibly discharging some of your debts.
Bankruptcy is a serious step. If you choose to file Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, you will probably need to hire an attorney. Be sure to find an attorney who has experience handling the type of bankruptcy case you plan to file. The following overview of Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 will give you some idea of whatâs involved.
How To File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Filing Chapter 7 bankruptcy involves collecting information about yourself and using this information to fill out your bankruptcy forms. Whether you plan on filing now or aren’t sure yet, check out Upsolve’s 10-Step Guide on How to File Bankruptcy for Free to learn more about how to prepare for and file a Chapter 7 bankruptcy case.
Recommended Reading: Can You File Bankruptcy On A Judgement Against You
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Exemptions
In addition, the ability to keep your possessions in a bankruptcy is called an exemption and in this case, an exemption is a good thing. For one thing, exemptions are made for various types of items that you need for your survival, like food, housing, clothing, transportation etc. However, it does vary case to case.
For example, when you file for Ch 7 bankruptcy, exemptions in Arizona are a little different than in other states. At Chapter Bankruptcy Law, our Arizona Chapter 7 lawyers will help you identify exempt property within the current Arizona bankruptcy laws. These chapter 7 bankruptcy exemptions are information that is important. For instance, Arizona bankruptcy law does not allow you to choose exemptions allowed under federal bankruptcy laws.
Therefore, bankruptcy exemptions in a ch 7 is definitely something that you should explore. In fact, your Henderson bankruptcy attorney can explain to you in detail what things you are able to keep and what things may have to go when considering declaring bankruptcy. In any case, our experienced debt relief expert knows how to make the most of your bankruptcy exemptions.
Will I Receive A Discharge In Bankruptcy

Certain types of debt automatically do not get discharged in bankruptcy, like certain taxes, student loans, most government fines and penalties, court restitution orders, domestic support obligations , and debts in connection with divorce decrees, among others.
For other types of debts, creditors have the right to file a lawsuit in the Bankruptcy Court, called adversary proceedings, against the debtor to determine if these debts are dischargeable. Creditors can sue debtors for a judgment in the court determining that their debts will not be eliminated in bankruptcy.
Here are some examples of debts that could be excepted from discharge with a bankruptcy court order:
- Actual fraud or false representations
- Consumer debts owed to a single creditor above the dollar limits specified in the Bankruptcy Code for luxury goods or services
- Debts for malicious injury of the debtor to another person or entity or property of another person or entity
- Money or cash advances above the dollar limit specified in the Bankruptcy Code incurred within the time period specified in the Bankruptcy Code
- Renewals or refinancing of credit obtained under false pretenses
You May Like: Florida Foreclosures Suspended 2021
What Happens If My Income Is Above The Median Income In New York For A Family Of My Size Does That Mean I Cannot File For Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
When your income is above the median income for New York state for a family of your size, the means test results will determine your chapter 7 bankruptcy eligibility.
Just because your income is above the median doesnt mean that youre excluded from Chapter 7. You can subtract actual expenses to help determine whether you have enough income left over after you pay your expenses and to repay all or part of your debt.
The means tests are a complicated calculation and thats why it may be in your best interest to speak with a bankruptcy law professional. The experienced NY bankruptcy attorneys at Macco Law can help you get the legal advice you seek with your means test.
Need More Bankruptcy Help
Did you know Nolo has been making the law easy for over fifty years? It’s trueand we want to make sure you find what you need. Below you’ll find more articles explaining how bankruptcy works. And don’t forget that our bankruptcy homepage is the best place to start if you have other questions!
|
Our Editor’s Picks for You |
|
More Like This |
Also Check: How To Buy Wholesale Pallets
Adversary Claims And Objections
If a creditor believes its debt should not be discharged, it may file an adversary case during the bankruptcy proceeding. The most common ground for a creditor filing an adversary case is fraud.
Fraud in this context is not criminal. In this context, fraud means that the debtor abused their relationship with the creditor and the bankruptcy process. Fraud supporting a creditors discharge objection could, for example, refer to a bankruptcy debtor who used a credit card to buy property or take cash advances prior to filing bankruptcy when the debtor was financially insolvent.
If a debtor incurred a debt when the debtor planned to file bankruptcy, the creditor could have a basis to set aside a discharge of that debt for fraud during an adversary case.
What Are The Alternatives To Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
You May Like: When Did My Bankruptcy Get Discharged
What Will Happen To Nonexempt Property
If, after the 341 creditors meeting, the trustee determines that you have some nonexempt property that you can’t protect, you might have to surrender it or provide the trustee with like property or its equivalent value in cash.
If the property isn’t worth very much or is cumbersome for the trustee to sell, the trustee will “abandon” it. You’d get to keep it, even though it is nonexempt.
Keep in mind that bankruptcy exemptions vary by state. You can find out more in Bankruptcy Exemptions and Your Property.
What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Chapter 7 bankruptcy, also known as a straight or liquidation bankruptcy, is a type of bankruptcy that can clear away many types of unsecured debts. If you’re far behind on your bills and don’t have the means to afford monthly payments and living expenses, filing Chapter 7 bankruptcy could be a last resort to help you reset your finances. However, you may have to give up some of your possessions, and it will have a long-lasting negative impact on your creditworthiness.
You May Like: Does Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Include Student Loans
How Long Does A Chapter 7 Case Last
A chapter 7 case begins with the filing of the case and ends with the closing of the case by the court.
If the debtor has no nonexempt money or property for the trustee to collect, the case will most likely be closed shortly after the debtor receives his discharge, which is usually about four months after the case is filed. If the debtor has nonexempt money or property for the trustee to collect, the length of the case will depend on how long it takes the trustee to collect the assets and perform his other duties in the case.
How Is A Debtor Notified That His Discharge Has Been Granted
Most courts send a form called Discharge of Debtor to the debtor and to all creditors.
This form is a copy of the court order releasing the debtor from his dischargeable debts and it usually serves as notice that the debtors discharge has been granted. It is usually mailed about four months after the case is filed, unless the trustee or a creditor has filed an objection to the discharge of the debtor, in which case a hearing must be held so that the court can rule on the objection.
If the debtors discharge is not granted, the court must inform the debtor of the reasons for not granting it.
Don’t Miss: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Spouse
What Debts Are Not Released By A Chapter 7 Discharge
All debts of any kind or amount, including debts incurred in other states, are released by a Chapter 7 discharge, except those listed below. The following types of debts cannot be discharged under Chapter 7:
How Chapter 7 Works
A chapter 7 case begins with the debtor filing a petition with the bankruptcy court serving the area where the individual lives or where the business debtor is organized or has its principal place of business or principal assets. In addition to the petition, the debtor must also file with the court: schedules of assets and liabilities a schedule of current income and expenditures a statement of financial affairs and a schedule of executory contracts and unexpired leases. Fed. R. Bankr. P. 1007. Debtors must also provide the assigned case trustee with a copy of the tax return or transcripts for the most recent tax year as well as tax returns filed during the case . 11 U.S.C. § 521. Individual debtors with primarily consumer debts have additional document filing requirements. They must file: a certificate of credit counseling and a copy of any debt repayment plan developed through credit counseling evidence of payment from employers, if any, received 60 days before filing a statement of monthly net income and any anticipated increase in income or expenses after filing and a record of any interest the debtor has in federal or state qualified education or tuition accounts. Id. A husband and wife may file a joint petition or individual petitions. 11 U.S.C. § 302. Even if filing jointly, a husband and wife are subject to all the document filing requirements of individual debtors.
Also Check: What Happens At Bankruptcy Meeting Of Creditors
What Do You Lose And What Can You Keep In Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
If you file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you may lose your nonexempt belongings, property that has a lien on it and property you offered as collateral for a loan.
Examples of exempt property based on current federal limits for an individual include:
- A homestead exemption of $25,150
- Up to $4,000 on a vehicle
- Up to $1,700 in jewelry
- Up to $13,400 in personal property, such as books, household items, and clothes
- Funds in tax-exempt retirement accounts, such as a 401 or 403 accounts, and up to $1,362,800 in combined savings in IRAs and Roth IRAs
- Public benefits, such as Social Security, veterans benefits and unemployment
- Up to $2,525 in books and tools of trade
- Alimony and child support
- Certain insurance benefits
- An additional $1,325 in property of your choice, plus up to $12,575 of unused funds from your homestead exemption
Double these amounts if you’re married and file a joint tax return. Keep in mind that states may have different exemptions and limits that you can use when filing bankruptcy. For example, the homestead exemption for a single homeowner living in California starts at $75,000, but is unlimited in some other states.
A trustee can’t take property when its value is less than the exempt amount, which means you may be able to keep your home and vehicle.
A similar scenario could play out with other forms of secured debts, such as an auto loan. However, just because the trustee can’t take and sell these assets doesn’t mean you’ll get to keep them in the long run.
The Chapter 7 Discharge
A discharge releases individual debtors from personal liability for most debts and prevents the creditors owed those debts from taking any collection actions against the debtor. Because a chapter 7 discharge is subject to many exceptions, debtors should consult competent legal counsel before filing to discuss the scope of the discharge. Generally, excluding cases that are dismissed or converted, individual debtors receive a discharge in more than 99 percent of chapter 7 cases. In most cases, unless a party in interest files a complaint objecting to the discharge or a motion to extend the time to object, the bankruptcy court will issue a discharge order relatively early in the case generally, 60 to 90 days after the date first set for the meeting of creditors. Fed. R. Bankr. P. 4004.
The grounds for denying an individual debtor a discharge in a chapter 7 case are narrow and are construed against the moving party. Among other reasons, the court may deny the debtor a discharge if it finds that the debtor: failed to keep or produce adequate books or financial records failed to explain satisfactorily any loss of assets committed a bankruptcy crime such as perjury failed to obey a lawful order of the bankruptcy court fraudulently transferred, concealed, or destroyed property that would have become property of the estate or failed to complete an approved instructional course concerning financial management. 11 U.S.C. § 727 Fed. R. Bankr. P. 4005.
Don’t Miss: Is Direct Liquidation Legit
Is It Better To File A Chapter 7 Or 13
Whether you should file a Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 depends on your individual financial situation. If youre unable to pass the means test and your income is too high to qualify for Chapter 7, you may be eligible for Chapter 13 bankruptcy instead. With Chapter 7, your eligible debts will be discharged once youve finished filing however, you may lose some of your assets in the process. With a Chapter 13 filing, youll have to follow a three- to five-year payment plan before your debts are discharged, but it may be a way for you to avoid losing assets.
Section 362 Of This Title In This Subchapter
Notwithstanding section 362 of this title , SIPC may file an application for a protective decree under the Securities Investor Protection Act of 1970. The filing of such application stays all proceedings in the case under this title unless and until such application is dismissed. If SIPC completes the liquidation of the debtor, then the court shall dismiss the case.
Historical and Revision Notes
legislative statements
Section 742 of the House amendment deletes a sentence contained in the Senate amendment requiring the trustee in an interstate stock-brokerage liquidation to comply with the provisions of subchapter IV of chapter 7 if the debtor is also a commodity broker. The House amendment expands the requirement to require the SIPC trustee to perform such duties, if the debtor is a commodity broker, under section 7 of the Securities Investor Protection Act . The requirement is deleted from section 742 since the trustee of an intrastate stockbroker will be bound by the provisions of subchapter IV of chapter 7 if the debtor is also a commodity broker by reason of section 103 of title 11 .
senate report no. 95989
Section 742 indicates that the automatic stay does not prevent SIPC from filing an application for a protective decree under SIPA. If SIPA does file such an application, then all bankruptcy proceedings are suspended until the SIPC action is completed. If SIPC completes liquidation of the stockbroker then the bankruptcy case is dismissed.
Editorial Notes
Read Also: The Best Liquidation Sites