Lowering Your Debts And Financial Obligations
To accelerate your debt repayment and consequently lower your DTI ratio, there are only four effective options to consider:
Repay the debts on your own using one of the four methods we describe in our DIY section.
Work directly with your creditors to lower your interest rates.
This is most commonly effective with credit card and store card accounts. If you have a credit card with a 29% interest rate and yet you have made payments on time for the past year or more, call the cards customer service department and explain how you are less of a risk now than you were a year or two ago, having proved so by making on-time payments for a year. If they refuse to lower your rate, let them know you will be transferring your balance to a different card company, although you would prefer not to. In most cases, credit card companies would rather lose out on a small portion of the interest you pay by lowering your rate than the entire amount of the interest you would pay by having it paid off by a balance transfer.
Once you secure a lower interest rate, continue to make your current monthly payments, even if the credit card company asks for less each month. Sending even $50 extra a month to a $5,000 credit card balance can accelerate your payoff from 15 years down to 3 years or less.
How To Get The Best Loan Interest Rates
You may be able to improve your chances of obtaining the most favorable interest rate on a loan in a few ways:
- Improve your credit score: The most competitive interest rates are generally available to those with the highest credit scores.
- Opt for a shorter repayment timeline: The best interest rates will always accompany the shortest-term loans. You will pay less interest over time if you can afford the payments.
- Reduce your debt-to-income ratio: Your debt-to-income ratio is the debt you pay each month as a percentage of your gross monthly income. It is nearly as significant as your credit score when qualifying for a competitive loan.
Add Up All The Minimum Payments You Make Toward Debt In An Average Month Plus Your Mortgage Payment
You dont need to factor in common living expenses or paycheck deductions contributions). But you should include all types of debt, like:
Mortgage payments Personal loans Timeshare payments
Youll also include recurring monthly paymentslike rent, child support or alimonyeven though they arent technically considered debt.
Confusing? We get it . But think about it like thisto get an accurate picture of how much youre spending each month, lenders look at more than just your debt to decide if theyll approve you for new credit.
So, to sum it up, include all your monthly minimum debt payments and recurring or legally binding payments in your debt-to-income ratiobut not basic monthly bills.
Read Also: Liquidation Pallets Salt Lake City
Work On Paying Down Debt
Paying off loans and bringing down debt balances can improve your debt-to-income ratio. To free up cash flow you can use to pay down your debt faster, give your budget a second look.
You may find ways to cut down on monthly expenses such as by:
- Shopping for a lower-cost cell phone plan
- Reducing how often you get food delivery or takeout
- Canceling streaming services you no longer use
When deciding which debt to pay down first, borrowers often use one of two strategies. The debt avalanche method involves targeting your highest-interest debt first, while continuing to make minimum payments on all other debts. This strategy helps you save money on interest over time. The other method, debt snowball, has borrowers focus on the debt with the lowest balance first, while keeping up with the minimum payments on other debts. It helps borrowers stay motivated by giving them small wins on their path to getting out of debt.
If youre unsure how to approach your debt, you could sign up for free or low-cost debt counseling with a certified credit counselor. These professionals can provide personalized financial advice, help you create a budget and provide useful tools that can teach you about money management. You can search for a certified credit counselor through the Financial Counseling Association of America or the National Foundation for Credit Counseling .
How To Calculate Debt
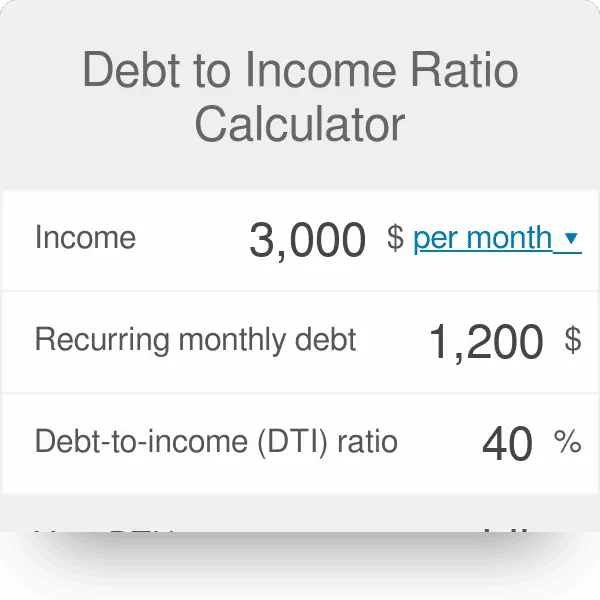
The debt-to-income formula is simple: Total monthly debt payments divided by total monthly gross income . Then, multiply that number by 100. That final number represents the percentage of your monthly income used towards paying your debts.
Say you make $3,000 a month before taxes and household expenses. Your monthly debts include $1,200 for rent, $200 in student loan payments, and $100 in car payments, for a total of $1,500. Divide your total monthly debt payments by the total monthly income, $3,000, and the result is 0.5 or 50%. This means that 50% of your monthly income goes towards paying back your debts.
Don’t Miss: Government Debt Relief Loans
Dti Formula And Calculation
The debt-to-income ratio is a personal finance measure that compares an individualâs monthly debt payment to their monthly gross income. Your gross income is your pay before taxes and other deductions are taken out. The debt-to-income ratio is the percentage of your gross monthly income that goes to paying your monthly debt payments.
The DTI ratio is one of the metrics that lenders, including mortgage lenders, use to measure an individualâs ability to manage monthly payments and repay debts.
How Debt Affects Your Income And Credit
Establishing credit requires a solid long-term history of success repaying loans and other debts. Young people rely on incremental credit-building opportunities to build the catalogs of consistent credit success required to secure future financing. Each positive entry is a step toward creditworthiness, providing greater assurances for future lenders.
Starting with the most basic forms of credit: Mobile phone contracts, student loans, credit cards, and store cards, credit histories are built one transaction at a time. Timely payments are the first order of business for repaying any debt, since late payments are entered on your record. Depending on your lender, some flexibility might be built in to your account, like grace periods for late payments or other considerations. Eventually though, your propensity for paying late works against you.
Read Also: How To Access Bankruptcy Court Filings
What Debt To Income Ratio Is Good For Getting A Mortgage
When seeking out a mortgage, the stakes are even higher. Often, lenders who provide you with a home loan want to know that youll be able to pay them back. Thats why most lenders want to see your debt to income ratio to be below 43%. Anything higher will be seen as too risky for most mortgage providers.
Where Should Debt to Income Ratio Be?
So, where should your debt to income ratio be? The truth is, everyones finances are different, so your ideal ratio may be different than someone elses. Despite that, its still best to keep your DTI under 40% if its possible. If your ratio is higher than that, then there are likely steps you can take to reduce your ratio and improve your financial status.
Pay More Than The Minimum
Pay off your debt and save on interest by paying more than the minimum every month. The key is to make extra payments consistently so you can pay off your loan more quickly. Some lenders allow you to make an extra payment each month specifying that each extra payment goes toward the principal. Before you begin, check the terms of your loan to determine whether additional fees or prepayment penalties may apply.
Also Check: Will Filing Bankruptcy Affect My Credit
What’s The Difference Between Your Debt
Debt-to-credit and DTI ratios are similar concepts however, it’s important not to confuse the two.
Your debt-to-credit ratio refers to the amount you owe across all revolving credit accounts compared to the amount of revolving credit available to you. Your debt-to-credit ratio may be one factor in calculating your credit scores, depending on the scoring model used. Other factors may include your payment history, the length of your credit history, how many credit accounts you’ve opened recently and the types of credit accounts you have.
Your DTI ratio refers to the total amount of debt you carry each month compared to your total monthly income. Your DTI ratio doesn’t directly impact your credit score, but it’s one factor lenders may consider when deciding whether to approve you for an additional credit account.
Familiarizing yourself with both ratios may give you a better understanding of your credit situation and help you anticipate how lenders may view you as you apply for credit.
What Factors Impact Dti
Lenders usually consider two components when they figure DTI ratios. They include:
-
Front-end ratio: This ratio, also called the housing ratio, shows what percentage of your monthly gross income goes toward housing expenses, such as monthly mortgage payments, property taxes, homeowners insurance and homeowners association dues.
-
Back-end ratio: This ratio shows what portion of your income is needed to cover monthly debt obligations, your mortgage payments and housing expenses. This includes credit card bills, car loans, child support, student loans and any other revolving debt that shows on your credit report.
Other monthly bills and financial obligations such as utilities, groceries, insurance premiums, health care expenses, day care, etc., are not part of this DTI calculations. They are not factored into a lenders decision to lend your money.
You May Like: How Does Debt Consolidation Work
Also Check: How To Declare Bankruptcy With No Money
How To Calculate Your Debt
You can calculate your debt-to-income ratio in four easy steps:
Tips To Improve Your Debt

Reducing your debt-to-income ratio may seem self-explanatory, but paying down debt is often easier said than done. Follow these tips to make a meaningful, timely impact on your debt-to-income ratio before you apply for a mortgage or another major loan:
Also Check: What Happens To Employees When A Company Files Bankruptcy
Multiply That Number By 100 To Get A Percentageand Thats Your Debt
Lets look at an example:
Bob pays $600 a month in minimum debt payments plus $1,000 per month for his mortgage payment. Before taxes, Bob brings home $5,000 a month. To calculate his DTI, add up his monthly debt and mortgage payments and divide it by his gross monthly income to get 0.32. Multiply that by 100 to get a percentage.
So, Bobs debt-to-income ratio is 32%.
Now, its your turn. Plug your numbers into our debt-to-income ratio calculator above and see where you stand.
How To Calculate A Personalized Debt
Your personalized debt-to-income ratio should account for recurring, unavoidable personal or family expenses not included in the Step 2 definition of debts. Such expenses might include:
- Health insurance
- Home insurance, if not bundled in escrow
- Childcare costs, if you have young kids in a single-parent or two-earner household
- Income taxes, if not wholly withheld from your paycheck
- Utility and communications expenses
Obviously, the more expenses you include, the closer youll come to simply rehashing your households budget.
You can avoid that by concentrating on the largest obligations: in most cases, health insurance and childcare. Before calculating your personalized debt-to-income ratio, subtract your health insurance costs and childcare costs from your gross income.
If you qualify for tax credits or deductions related to either expense, add those back in. Depending on your income, you may qualify for a tax credit equal to 20% to 35% of qualifying daycare or other supervisory expenses for children and dependents under age 13, capped at $3,000 in expenses for one child and $6,000 in expenses for two or more children. The full credit is only available to lower-income parents. If you earn more than $43,000 per year, your credit is capped at 20%.
Recommended Reading: How To File Bankruptcy Without Losing Your Home
Add Up Your Monthly Debt Payments
Once youve determined your monthly gross income, you can focus on your monthly debt payments. This is the money thats taken out of your paycheck each month. Expenses like groceries and utilities generally are not included. Once youve figured out all of your monthly debts, take the sum of each value.
Example: You owe $1,000 in rent, $300 in student loans and $100 for a credit card payment. You would then add 1,000, 300 and 100. This would result in monthly debt payments of $1,400.
$1,000 + $300 + $100 = $1,400
Recommended Reading: Can You File Bankruptcy Just For Credit Cards
Why It Matters
A good credit score shows that youve responsibly managed your debts and consistently made on-time payments every month.
Your credit score matters because it may impact your interest rate, term, and credit limit. The higher your credit score, the more you may be able to borrow and the lower the interest rate you could receive.
For example, with a good or excellent credit score, you might qualify for a lower interest rate and monthly payment on a loan of $15,000. The example below explains how your credit rating may impact your annual percentage rate and monthly payment. Rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
Recommended Reading: What Happens At Bankruptcy Meeting Of Creditors
What Is A Debt
Debt-to-income ratio is the ratio of total debt payments divided by gross income expressed as a percentage, usually on either a monthly or annual basis. As a quick example, if someone’s monthly income is $1,000 and they spend $480 on debt each month, their DTI ratio is 48%. If they had no debt, their ratio is 0%. There are different types of DTI ratios, some of which are explained in detail below.
There is a separate ratio called the credit utilization ratio that is often discussed along with DTI that works slightly differently. The debt-to-credit ratio is the percentage of how much a borrower owes compared to their credit limit and has an impact on their credit score the higher the percentage, the lower the credit score.
Why is it Important?
DTI is an important indicator of a person’s or a family’s debt level. Lenders use this figure to assess the risk of lending to them. Credit card issuers, loan companies, and car dealers can all use DTI to assess their risk of doing business with different people. A person with a high ratio is seen by lenders as someone that might not be able to repay what they owe.
There are two main types of DTI:
Front-End Ratio
Back-End Ratio
How To Reduce Your Debt
Here are few things to consider if you want to reduce your debt-to-income ratio or learn how to use credit wisely:
Avoid Taking On New Debt
Avoiding debt can help build your financial well-being, according to the CFPB. And because your DTI ratio depends on your amount of debt versus your income, taking on more debt without growing your income will increase your DTI ratio. So itâs a good idea to apply only for the credit you need and avoid taking on new debt.
Pay Down Existing Debt
There are a few different strategies for paying off debt. The CFPB talks about the snowball and highest-interest-rate methods. But there are many more strategies for handling loan paymentsâsuch as consolidating debtâthat you might explore, too.
Before you make any decisions, consider talking to a qualified financial professional to figure out a debt management plan for your specific situation. You might even have access to some financial planning services through your employer or retirement plan administrator.
Pay More Than the Minimum
The CFPB recommends paying more than the minimum payment on your credit cards whenever possible. This may help you reduce your credit card debt faster and minimize charges. It can also help your , which can be an important factor in calculating your credit scores.
Use a Budget
Read Also: Filing Bankruptcy In Mn