What Is A Gross Debt Service Ratio
Jamie Johnson is a sought-after personal finance writer with bylines on prestigious personal finance sites such as Quicken Loans, Credit Karma, and The Balance. Over the past five years, shes devoted more than 10,000 hours of research and writing to topics like mortgages, loans, and small business lending.
SDI Productions / Getty Images
Gross debt service ratio is the maximum amount of money you can afford to pay for housing each month. Its also referred to as a housing-expense ratio or front-end ratio. Its one of the tools your lender uses to determine whether you can afford a mortgage or a loan.
How Is Debt Service Calculated
Debt service is determined by calculating the periodic interest and principal payments due on a loan. Doing so requires knowledge of the loans interest rate and repayment schedule. Calculating debt service is important to determine the cash flow required to cover payments. Hence, it is useful to calculate annual debt service, which can then be compared against a companys annual net operating income.
Example Of Lender Terms
In the imagine below, MK Lending Corp has outlined its debt requirements for new mortgages. The columns highlighted yellow represent investors with a DSCR greater or equal to 1.0, while the orange columns represent investors with a DSCR less than 1.0. Because the yellow investors are less risky, their loan terms and LTV/CLTV terms are more favorable than the orange investors.
MK Lending Corp
Also Check: Will Filing Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment
What Is The Debt Ratio
The term debt ratio refers to a financial ratio that measures the extent of a companys leverage. The debt ratio is defined as the ratio of total debt to total assets, expressed as a decimal or percentage. It can be interpreted as the proportion of a companys assets that are financed by debt. A ratio greater than 1 shows that a considerable amount of a company’s assets are funded by debt, which means the company has more liabilities than assets. A high ratio indicates that a company may be at risk of default on its loans if interest rates suddenly rise. A ratio below 1 means that a greater portion of a company’s assets is funded by equity.
Debt Service Ratio Example
Lets say youve decided to purchase your home and you want to make sure you can qualify for a mortgage. Youre planning to finance a home valued at $300,000 with a 10% down payment .
Based on your credit score and the current market interest rates, you learn that you could get a rate of 4% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. If you pay $120 per month for homeowners insurance and $500 per month for property taxes, then your monthly payment would be $1,909.
But to ensure youll actually qualify for the loan, you want to calculate your debt service ratio.
First, the debt service on your new mortgage would be $1,909 per month, which comes to $22,908 per year. If you have a gross income of $90,000 per year, then your DSCR on your mortgage is 3.93, which is considered in the healthy range. Your DTI would be 25%.
But when it comes to qualifying for a mortgage, its far more than just the debt service on your mortgage that matters. Lenders look at your entire debt picture to see how your mortgage would fit into it.
Lets say you also have a student loan with a minimum monthly payment of $250 and an auto loan with a minimum monthly payment of $325.
When you add in those debts, your total monthly debt obligations come to $2,484, for an annual debt service of $29,808. Based on your annual income, your total DSCR is 3.02, while your DTI would be 33%.
Read Also: What Happens To Secured Debt In Bankruptcy
How To Improve Your Debt Service Coverage Ratio
Do you have a poor debt service coverage ratio and want to improve it? There are a number of different things that you can do. First off, you can increase revenues. Consider boosting prices or negotiating higher contracts with your clients. You can also consider reducing your companys operating expenses. Think about cutting overheads or tightening up your marketing budget.
What Certain Debt Ratios Mean
From a pure risk perspective, lower ratios are considered better debt ratios. Since the interest on a debt must be paid regardless of business profitability, too much debt may compromise the entire operation if cash flow dries up. Companies unable to service their own debt may be forced to sell off assets or declare bankruptcy.
A higher debt ratio makes it more difficult to borrow money. Lenders often have debt ratio limits and do not extend further credit to firms that are overleveraged. Of course, there are other factors as well, such as , payment history, and professional relationships.
On the other hand, investors rarely want to purchase the stock of a company with extremely low debt ratios. A debt ratio of zero would indicate that the firm does not finance increased operations through borrowing at all, which limits the total return that can be realized and passed on to shareholders.
While the debt-to-equity ratio is a better measure of opportunity cost than the basic debt ratio, this principle still holds true: There is some risk associated with having too little debt. That’s because debt is a cheaper form of financing than equity financing. This is the process by which corporations raise capital by selling additional shares to address short-term needs.
You May Like: What Does It Mean When A Bankruptcy Is Discharged
What Is The Debt Service Ratio
The debt service ratiootherwise known as the debt service coverage ratiocompares an entity’s operating income to its debt liabilities. Expressing this relationship as a ratio allows analysts to quickly gauge a company’s ability to repay its debts, including any bonds, loans, or lines of credit. This is an especially important calculation for bankers, who may be deciding whether or not to allow a business to take on more debt.
The name of the ratio stems from debt service, which is the amount of money required over a period of time to repay debts. A common timeframe for debt service is a year.
What Is Debt Service
Debt service refers to the total cash required by a company or individual to pay back all debt obligations. To service debt, the interest and principal on loans and bonds must be paid on time. Businesses may need to repay bonds, term loans, or working capital loans.
In some cases, lenders may require companies to hold a debt service reserve account . The DSRA can act as a safety measure for lenders to ensure that the companys future payments will be met. Individuals may need to service debts such as mortgage, credit card debt, or student loans. The ability to service debt for both companies and individuals will impact their options to receive additional debt in the future.
Don’t Miss: How Long Bankruptcy Remain On Credit
Gross Debt Service Ratio Formula And Calculation
The formula that’s used to calculate the gross debt service ratio is fairly straightforward. It looks like this:
Gross Debt Service Ratio = Principal + Interest + Taxes + Utilities / Gross Annual Income
Utilities can include any amounts paid toward electric, water, or natural gas service. If you’re planning to purchase a property, you may be able to contact the electric company, water company, and gas company to get information about average utility costs. You can also look up information about local property taxes to estimate what you might pay for those.
Why Is Debt Service Coverage Ratio Important
The DSCR plays a crucial role lending decisions especially for commercial property loans and loans to small businesses. A business with a higher DSCR may be considered a more prudent borrower whereas a company with a lower DSCR may be considered a higher risk of default.
A favorable DSCR may not just improve your odds of securing a loan, but can also help you negotiate more favorable loan terms or access a wider variety of financing options.
For businesses themselves, the DSCR can provide good insight into the company’s financial health. Business owners can check-in on the DSCR periodically to see how the company is doing on that front. Any continued trends of declining DSCR can prompt a rethink of business strategies, gearing them more towards reduction of debt or improvement of operating income.
Also Check: Can You Get Student Loans After Bankruptcy
Problems With The Debt Service Coverage Ratio
An issue regarding this ratio is that a negative outcome can result when a property is transitioning to new tenants, so that it is generating sufficient cash by the end of the measurement period, but was not doing so during the beginning or middle of the measurement period. Thus, the metric can yield inaccurate results during transition periods.
How Total Debt Service Ratio Works

When applying for a mortgage or any other type of loan, all borrowers should be aware that the total debt service ratio is a key factor driving approval or rejectionand it is just as important as a stable income, timely bill payment, and a strong .
Remember, the lower your TDS ratio, the better your chances of approval. Borrowers with higher TDS ratios are more likely to struggle to meet their debt obligations than borrowers with lower ratios.
All lenders will compare your TDS to their benchmark TDS rangeusually from 36% to no more than 43%before they decide whether you can manage an additional monthly payment on top of all other bills. Many lenders prefer a ratio of 36% or less for loan approval most do not give mortgages to borrowers with TDS ratios that exceed 43%.
Lenders prefer borrowers with total debt service ratios of 36% or less borrowers with TDS ratios that exceed 43% are rarely approved for mortgages.
Recommended Reading: Clothing Pallets For Sale
Ways To Improve Your Dscr
- Increase your sales. You can do this by expanding your customer base, increasing the frequency of purchases, or selling higher-priced items.
- Reduce your expenses. You can do this by negotiating better terms with suppliers, cutting costs in other business areas, or improving your operational efficiency.
- Finally, you can also improve it by reducing the amount of debt.
- The last option is to refinance your current debt obligations to reduce your interest payments.
#DidYouKnow
There are two types of Debt Service Coverage Ratios:
- Gross Debt Service
- Total Debt Service
When you apply for a business loan, many lenders use both as a preliminary assessment to determine if you are already in debt.
About The Authortrue Tamplin Bsc Cepf
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance , author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website, view his author profile on , or check out his speaker profile on the CFA Institute website.
Read Also: How Much To File Bankruptcy In Wisconsin
Definition And Example Of Gross Debt Service Ratio
Gross debt service ratio is the percentage of your gross income that goes toward housing. This ratio is often employed when lenders are determining if you can afford a mortgage and is one facet of your debt-to-income ratio.
- Alternate names: front-end ratio, housing-expense ratio
- Acronym: GDS ratio
Your lender determines your GDS ratio by dividing your total housing costs by your gross monthly income. If your GDS ratio exceeds 28% of your income, this could indicate that youre spending too much on housing costs.
For example, lets say your gross monthly income is $6,000 and you spend $2,000 on monthly housing costs. Your GDS ratio is 33%, which is higher than most lenders like to see. That doesn’t necessarily mean youll be denied a loan, but it will factor into your lenders decision.
Repay Any Outstanding Debt
When it comes to important things like trying to qualify for a mortgage, the amount of debt you have does matter. Everything adds up, and when it comes to the various ratios formula, every debt does count. So, before you secure your mortgage, look to pay down any outstanding principal and interest debt and attempt to repay lines of credit, for example.
You May Like: How Long Does Bankruptcy Stay On Your Credit Score
What Is The Debt Service Coverage Ratio Used For
The following can use the Debt Service Coverage Ratio:
- Small business owners to assess their business ability to make debt payments and evaluate their companys growth possibilities
- Lenders to determine if they should approve a loan to a small business
- Investors assess a small business financial stability and decide if the investment is risky or worthy
How To Calculate Debt Service Coverage Ratio
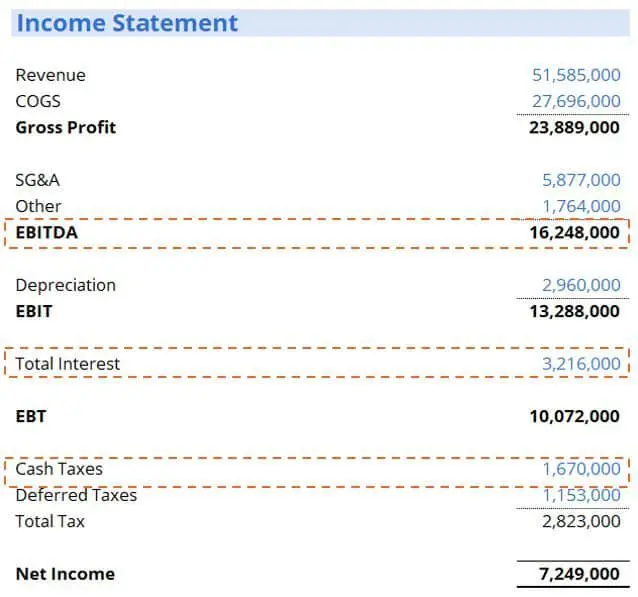
Lets look at an example. Assume the client below had $20 million in long-term debt plus $5 million in current portion of long-term debt . Based on that information, plus whats been provided in the income statement below, what is the borrowers DSCR?
We would plug the numbers into our DSCR formula and calculate as follows:
Also Check: How To File For Bankruptcy Without A Lawyer In Florida
How To Calculate The Debt Service Coverage Ratio
The debt service coverage ratio shows how much EBITDA a company generates for every dollar of interest and principal paid.
The ratio is typically calculated with this formula:
EBITDA
Despite its simple formula, the debt service coverage ratio is often miscalculated. For this indicator to be useful, you have to make sure youre calculating it with the right inputs, Sood says.
Other Common Dsc Adjustments
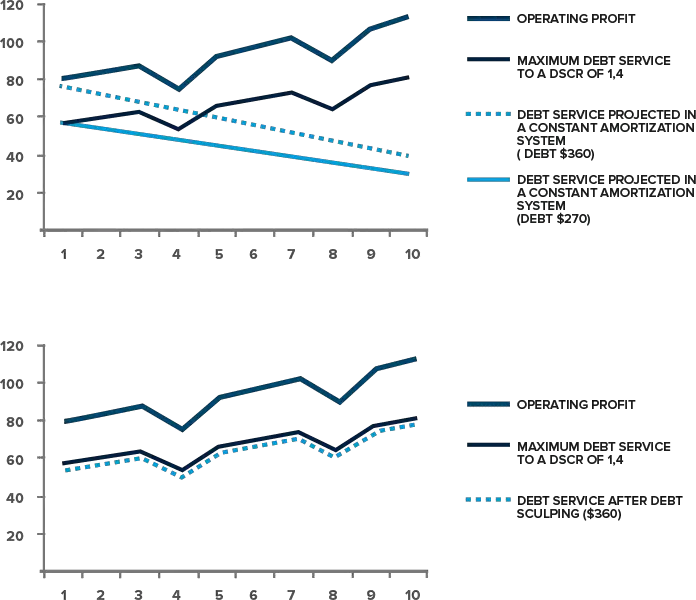
Debt Service Coverage formulas and adjustments will vary based on the financial institution thats calculating the ratio as well as the context of the borrowing request.
Some examples include:
For CAPEX heavy borrowers/industries
CAPEX stands for Capital Expenditure. Some businesses require constant reinvestment in order to remain competitive.
Some management teams elect to use cash on hand to support some or all of that CAPEX .
In these cases, thats cash thats gone and can no longer be used to service debt. Some more conservative lenders will adjust EBITDA accordingly when calculating DSC for CAPEX-heavy industries.
For private, owner-operated businesses
Because personal income tax rates can be quite high in many jurisdictions, some owner-operators of small and medium-sized businesses pay themselves a modest management salary and instead take compensation through dividends or by moving funds in and out of the shareholder loan accounts.
Adjusting for cash outflows that effectively represent ownerships compensation gives a more accurate picture of the companys ability to generate actual profits and cash flows for the purpose of retention in the company .
For specific types of credit requests
Consider a company thats been renting its warehouse but recently exercised an option to purchase the building. This companys historical income statements show rent expense, but that expense will no longer exist once it owns the building.
Recommended Reading: If You File For Bankruptcy Which Debts Are Forgiven
What Is The Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula
There are three things youll need to complete before calculating your companys debt service coverage ratio.
The easiest way to calculate your net operating income or EBITDA is by using your cash flow statement. In many cases, your accounting software application will calculate net income on your financial statements, but not always. First, locate your annual sales revenue, which for this example well say is $700,000. Next, youll need to add up all of your expenses for the year. For this example, lets use the following expenses:
Your net operating income calculation would be:
$234,000 + $155,000 + $15,000 + $40,000 + $22,000 = $466,000
Youll need to use this number when calculating your DSCR. Though the example above is using annual totals, many larger businesses find it useful to calculate the debt service coverage ratio every quarter or when looking to take on additional debt.
This needs to include all current loans and notes payable. For this example, well say that you currently have two outstanding loans with the following payments made annually:
Building loan $60,184
Business loan $12,550
This makes your annual debt payment total $72,734. When calculating debt payments, make sure that you include both principal payments as well as interest payments required. And for any new debt, be sure to consider the loan amount, loan payments, and principal repayment required.
Example Of The Total Debt Service Ratio
To see how your TDS ratio will be determined, just add up monthly debt obligations and divide them by gross monthly income. Here’s a hypothetical example: an individual with a gross monthly income of $11,000 and monthly debt obligations of $4,225 .
Divide the total debt obligation of $4,225 by income of $11,000 to get a TDS ratio of 38.4%, which is not much higher than the low benchmark and well below the max . This individual would most likely get a mortgage.
You May Like: Secu Houses For Sale
How To Calculate Debt Service Coverage
The formula for calculating debt service coverage ratio is very straightforward. The DSCR for real estate is calculated by dividing the annual net operating income of the property by the annual debt payment.
DSCR formula
- Debt Service Coverage Ratio = Net Operating Income / Debt Service
For example, if a rental property is generating an annual NOI of $6,500 and the annual mortgage payment is $4,700 , the debt service coverage ratio would be:
- DSCR = NOI / Debt Service
- $6,500 NOI / $4,700 Debt Service = 1.38
A DSCR of 1.38 means there is extra net operating income available than is needed to service the annual debt. On the other hand, a DSCR of 0.97 means that there is only enough net operating income available to pay for 97% of the annual debt payments.
Before we dig deeper into the debt service coverage ratio, lets review what to include and exclude when determining net operating income for a rental property.
How to determine NOI
Understanding how to accurately calculate net operating income is important because NOI has a significant impact on the debt service coverage ratio, the mortgage loan amount an investor can obtain, and the amount of income available to service the debt.
An NOI that is artificially high will overstate the amount of income available to service the debt, while an NOI that is low due to a miscalculation will understate the amount of income that can be used to pay the mortgage.
- Gross Operating Income = Potential Rental Income Vacancy Rates