Is China Economy Bigger Than Us
As per projections by IMF for 2021, United States is leading by $6,033 bn or 1.36 times on an exchange rate basis. The economy of China is Int. $3,982 billion or 1.18x of the US on purchasing power parity basis. According to estimates by World Bank, China’s gdp was approx 11% of the US in 1960, but in 2019 it is 67%.
Does China Own The United States
For its part, China owned 191,000 acres worth $1.9 billion as of 2019. … Indeed, there has been a tenfold expansion of Chinese ownership of farmland in the United States in less than a decade. Six states Hawaii, Iowa, Minnesota, Mississippi, North Dakota and Oklahoma currently ban foreign ownership of farmland.
Pak’s Economic Crisis Is Well Known Lanka Also Just Saw A Dramatic Change In Govt Followed By Massive Revolt By Public Over Sky
- Follow us:
After Pakistan and Sri Lanka falling under severe debts of Chinese loans, Bangladesh has now sounded an alert, warning developing countries to think twice over taking more loans through Chinas Belt and Road Initiative as global inflation and slowing growth add to the strains on indebted and vulnerable emerging markets.
Pakistans economic crisis is well known and Sri Lanka also just saw a dramatic change in government followed by massive revolt its public over deep financial burdens, sky-rocketing inflation triggered by depleting foreign reserves. Nepal, too, is said to be foreseeing an economic crisis and earlier this year banned the import of vehicles and other luxury items, due to declining foreign exchange reserves.
ALSO READ: How Rajapaksa Clan And Chinese Loans Put Sri Lanka on Expressway of Economic Collapse
One factor common between these countries is that they are all part of Chinas BRI global infrastructure development strategy aimed at investment by Beijing in nearly 70 countries. The Chinese government, through BRI, invests in building ports, roads, bridges, dams, power stations, railroads, etc. China is known to have BRI deals with all three countries, two of which are already reeling under a massive economic crisis and the remaining foreseeing one.
Also Check: Do You Have To Go To Court To File Bankruptcy
What Would Happen If China Called In Us Debt
China is one of the biggest owners of U.S. debt.
As of early 2020, China owned almost US$1.1 trillion in U.S. debt, which makes the country the second-largest buyer of American debt. Even though Japan is the number one buyer, this hasnt generated any worries since Japan is seen as a friendly nation. In contrast, the communist government of China owning so much U.S. debt has been a huge cause of concern, with some worrying that Beijing might use it as leverage against the United States. So will China ever call in its U.S. debt to hurt America?
Us Debt: How Big Is It And Who Owns It

US federal debt is still a record high. This week it passed a milestone: the fourth straight year the deficit has passed the $1tn mark. As of today, the national debt stands at $16,066,241,407,385.80 .
Its an issue thats sure to come up in the first presidential debate this Wednesday.
So, how does the US borrow money? Treasury bonds are how the US and all governments for that matter borrow hard cash: they issue government securities, which other countries and institutions buy. So, the US national debt is owned mostly in the US but the $5.4tn foreign-owned debt is owned predominantly by Asian economies.
Under President Obamas first term, that figure has gone up from $3tn, a rise of 74.1%. Under George W Bush, it went up too by 85% over the whole two terms and 64% in his second term alone.
Holders of US Treasury bonds, $bn
The US Treasury releases the figures on this every quarter we have made them more useable. So, who has the most?
It reflects a US national debt which has grown starkly, from $7.8tn in 2005 to busting through the US debt ceiling of $14.294tn last year according to these day by day figures.
The full data is below. What can you do with it?
Don’t Miss: How To File For Bankruptcy For Credit Card Debt
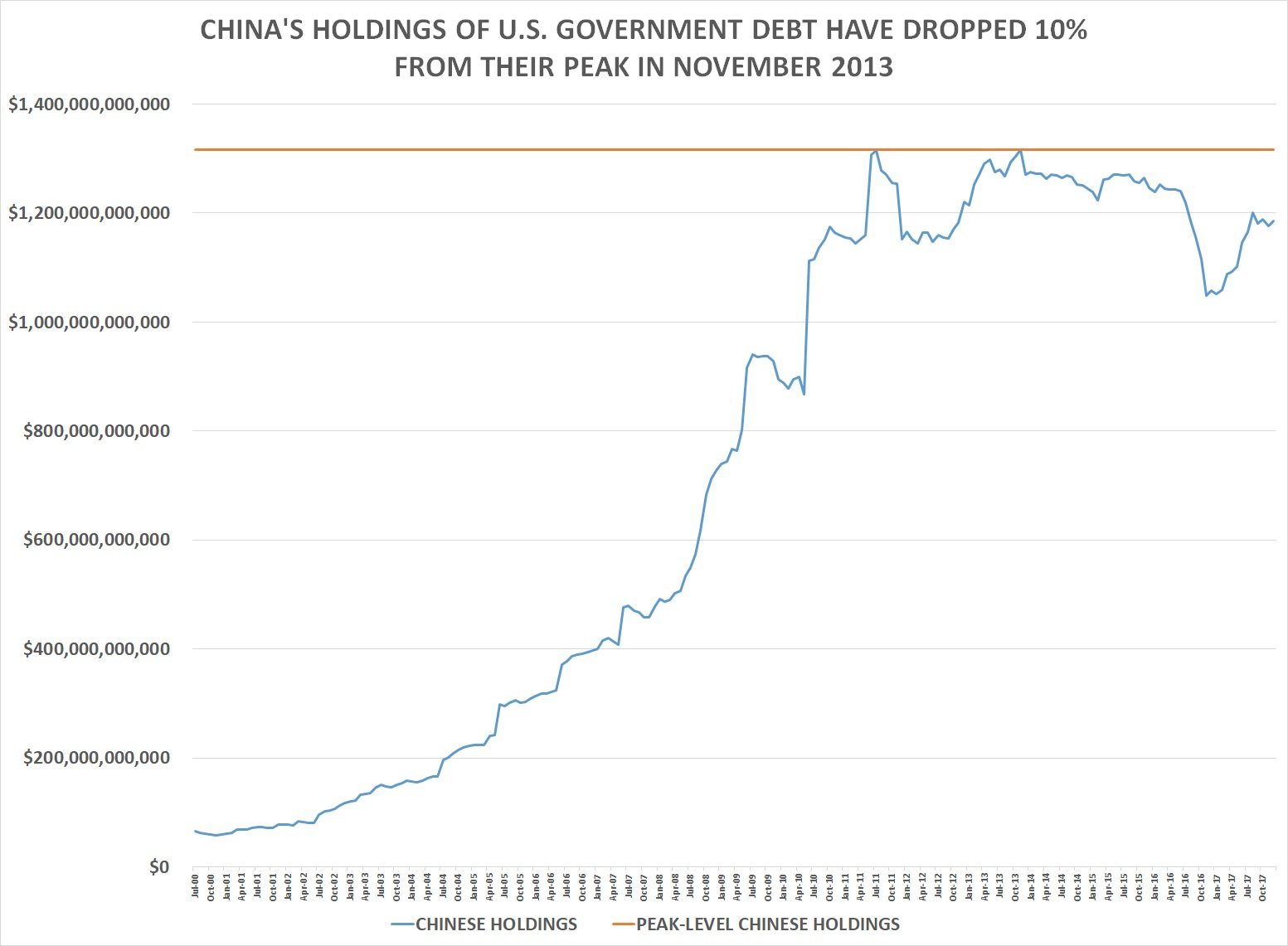
Concerns Over Chinese Holdings Of Us Debt
According to a 2013 Forbes article, many American and other economic analysts have expressed concerns on account of the People’s Republic of China’s “extensive” holdings of United States government debt as part of their reserves. The National Defense Authorization Act of FY2012 included a provision requiring the Secretary of Defense to conduct a “national security risk assessment of U.S. federal debt held by China.” The department issued its report in July 2012, stating that “attempting to use U.S. Treasury securities as a coercive tool would have limited effect and likely would do more harm to China than to the United States. An August 19, 2013 Congressional Research Service report said that the threat is not credible and the effect would be limited even if carried out. The report said that the threat would not offer “China deterrence options, whether in the diplomatic, military, or economic realms, and this would remain true both in peacetime and in scenarios of crisis or war.”
Slashed Us Debt Holdings Change Scene
More dollar liquidity to keep financial stability, diversify forex reserves
China’s trimmed US debt holdings can help the nation gain more dollar liquidity to maintain financial stability and reduce its reliance on dollar reserves, economists and experts said on Wednesday.
Noting that China is the second-biggest foreign holder of US Treasuries, they said the falling foreign holdings of US Treasuries reflect dampening investor confidence in dollar-denominated assets due to radical monetary tightening and elevated inflation in the United States.
Their comments followed data from the US Treasury Department that China’s holdings in US Treasury securities had decreased for six consecutive months to $980.8 billion as at the end of May, down from $1.0034 trillion in April and dropping below the $1 trillion mark for the first time in 12 years.
The decline in China’s holdings came as part of the global trend of trimming holdings of US debt. Total foreign holdings of US Treasury securities stood at $7.4216 trillion as at the end of May, down from $7.4553 trillion in April and marking the lowest level since May 2021.
Japan, the leading holder of US debt, held $1.2128 trillion in US Treasury securities as at the end of May, the third straight month of decline and compared with $1.2185 trillion in April.
“Real yields have been very negative, which has been offset by a strong dollar. But there are concerns that this is not sustainable,” McCaffery said.
Don’t Miss: Can You File Bankruptcy On Credit Cards Alone
United States Of America
- State and local government pension funds: $342.8 billion
- U.S. savings bonds: $141.1 billion
Why would individual Americans, businesses and local governments continue to loan money to the United States? Doesn’t it seem risky to put money into an institution that’s already $28 trillion in the hole? Believe it or not, investing in the government isn’t a high-risk proposition. While the federal government is hemorrhaging thousands of dollars by the second in order to pay interest on its debts, the U.S. has a vested interested in not defaulting on its loans. America’s credit rating would drop, and the booming market for U.S. debt could dry up. How would the U.S. government function without its international credit card? Let’s hope we never find out.
Originally Published: Jul 26, 2011
Could Chinas Massive Public Debt Torpedo The Global Economy
China might be the to the world, but it is also riddled with debt. Between public and corporate debt, China is one of the most indebted large economies in the world. Even worse, its state-owned banks are sitting on mountains of bad debts and non-performing loans, particularly in the real-estate sector. And this is just on the surface. Underneath lies a staggering quantity of murky debt, off-balance-sheet lending, wealth management products, and local government funding vehicles. All told, Chinas debt is considerably larger than it appears at first glance, and so high that some analysts feel it is at dangerous levels and could spill over, doing severe damage to the world economy. What does this say about the stability of the global economy and Western anxieties about Chinas rise to a preeminent place in world affairs?
If the Chinese economy falters, it will affect all of its significant trading partners, which basically means the entire world. Countries around the globe will suffer from slower and more expensive exports as well as reduced demand for imports. Companies in China are suffering from supply chain disruption, higher input costs, pollution curbs, and logistical issues due to pandemic measures, such as fuel rationing, electricity rationing, and disruption at ports. Factory-gate prices, the price of products at the factory, have been steadily rising. All of these circumstances have driven factory inflation to its highest level in 13 years.
Recommended Reading: What Debts Are Not Discharged In Bankruptcy
Negative Real Interest Rates
Since 2010, the U.S. Treasury has been obtaining negative real interest rates on government debt, meaning the inflation rate is greater than the interest rate paid on the debt. Such low rates, outpaced by the inflation rate, occur when the market believes that there are no alternatives with sufficiently low risk, or when popular institutional investments such as insurance companies, pensions, or bond, money market, and balanced mutual funds are required or choose to invest sufficiently large sums in Treasury securities to hedge against risk. Economist Lawrence Summers states that at such low interest rates, government borrowing actually saves taxpayer money and improves creditworthiness.
In the late 1940s through the early 1970s, the U.S. and UK both reduced their debt burden by about 30% to 40% of GDP per decade by taking advantage of negative real interest rates, but there is no guarantee that government debt rates will continue to stay this low. Between 1946 and 1974, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio fell from 121% to 32% even though there were surpluses in only eight of those years which were much smaller than the deficits.
Chinas Us Debt Holdings Fall Below $1 Trillion
Mainland China reduced its holdings of United States debt by US$23 billion to US$980.8 billion in May from April, the first time the total dropped below the US$1 trillion mark in 12 years, the US Treasury Department said on July 18. Chinas US debt holdings have dropped for six consecutive months.
Japan, the current largest holder, and more than 10 other holders of US Treasuries also disposed of their US debts to some degree.
What caused the US debt to fall out of favor?
Wang Yongzhong, director and researcher of the International Commodities Research Office of the Institute of World Economics and Politics of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, told Guancha.com that the United States sanctions and freezing of assets of countries such as Russia and Afghanistan had caused concern about the safety of the US debt investments.
Another reason, he said, was that high inflation in the US has also led to a reduction in the US Treasury yield.
US Treasuries themselves are risk assets, so our holdings are also declining, said Wang.
Wang said it was an overall trend that China would have a more flexible and diversified allocation of its overseas assets. However, he added that the US dollar remained a very important overseas asset for China.
Although the purchasing power of the US dollar has fallen sharply, it is still a strong currency, he said. Returns from other bonds, such as those in Europe and Japan bonds, are less than those of the US bonds.
You May Like: How Much Does Bankruptcy Affect Credit Score
How Big Is Chinas Off
Standard & Poors Global Ratings has stated Chinese local governments may have an additional CN¥ 40 trillion in off-balance sheet debt. Furthermore, debt owed by state-owned industrial firms is another 74% of GDP according to the International Monetary Fund.
According to a report by Institute of International Finance report published in January 2021, Chinas outstanding debt claims on the rest of the world rose from some US$1.6 trillion in 2006 to over US$5.6 trillion by mid-2020, making China one of the biggest creditors to low income countries.
What Is The Current National Debt
As of June 23, 2022, the total U.S. national debt was $30.4 trillion, after crossing the $30 trillion mark for the first time in February. At the end of 2019, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the national debt was $23 trillion. One year later, it had risen to $27.7 trillion. Since then, it has increased by more than $2 trillion.
Don’t Miss: How To File Bankruptcy In Georgia
China’s Use Of Usd Reserves
China has approximately $3.2 trillion in foreign exchange reserves as of November 2021. Like the U.S., it also exports to other regions like Europe. The euro forms the second biggest tranche of Chinese forex reserves. China needs to invest such huge stockpiles to earn at least the risk-free rate. With trillions of U.S. dollars, China has found the U.S. Treasury securities to offer the safest investment destination for Chinese forex reserves.
Multiple other investment destinations are available. With euro stockpiles, China can consider investing in European debt. Possibly, even U.S. dollar stockpiles can be invested to obtain comparatively better returns from euro debt.
However, China acknowledges that the stability and safety of investment take priority over everything else. Though the Eurozone has been in existence for around 18 years now, it still remains unstable. It is not even certain whether the Eurozone will continue to exist in the mid-to-long term. An asset swap is thus not recommended, especially in cases where the other asset is considered riskier.
Other asset classes like real estate, stocks, and other countries’ treasuries are far riskier compared to U.S. debt. Forex reserve money is not spare cash to be gambled away in risky securities for want of higher returns.
National Debt Of The United States
| This article needs to be . Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
| This article is part of a series on the |
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms national deficit and national surplus usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the federal government spent trillions in virus aid and economic relief. The CBO estimated that the budget deficit for fiscal year 2020 would increase to $3.3 trillion or 16% GDP, more than triple that of 2019 and the largest as % GDP since 1945.
Recommended Reading: Debt Relief Credit Card
You May Like: Can You Include Student Loans In Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Obligations Excluded
Under normal accounting rules, fully owned companies would be consolidated into the books of their owners, but the large size of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac has made the U.S. government reluctant to incorporate them into its own books. When the two mortgage companies required bail-outs, White House Budget Director Jim Nussle, on September 12, 2008, initially indicated their budget plans would not incorporate the government-sponsored enterprise debt into the budget because of the temporary nature of the conservator intervention. As the intervention has dragged out, pundits began to question this accounting treatment, noting that changes in August 2012 makes them even more permanent wards of the state and turns the governments preferred stock into a permanent, perpetual kind of security.
Also Check: Are Bankruptcy Courts Affected By Government Shutdown
What Is Us Debt And Why Do Other Countries Own It
To finance its ever-increasing expenses, the US federal government issues bonds and other debt instruments, known as Treasury securities, which institutions and other countries can buy. So, US debt colloquially refers to the value of the outstanding Treasury securities that the federal government has issued to finance its budget.
Holders of US Treasurys receive interest payments twice a year. When the bonds mature, meaning they reach their expiry date, their owner gets paid back in full.
Its completely normal for countries to buy other countries debt. Most governments dont default on their debts so its a low-risk asset to hold. But not all government bonds are born equal: Some are considered safer than others, based on a mix of market perception, how easy they are to buy and sell, and factors like a countrys credit rating.
The fact that China owns a lot of US debt makes sense. Its the second largest economy in the world. It has a massive trade surplus with Washington, meaning it exports more to the US than it imports from the US. So it can use its reserve of US dollars to buy Treasurys.
Don’t Miss: Can You Buy A Car In Bankruptcy