Tracking The Federal Deficit: May 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $132 billion in May, the eighth month of fiscal year 2021. Mays deficit was the difference between $463 billion of revenue and $596 billion of spending. To note, May spending was impacted by May 1 falling on a weekend, shifting certain payments into April that are normally paid at the beginning of May. If not for these timing shifts, the May deficit would have been $192 billion.
So far this fiscal year, the federal government has run a cumulative deficit of $2.1 trillion, the difference between $2.6 trillion of revenue and $4.7 trillion of spending. This deficit is 10% greater than at the same point in FY2020when only three months of pandemic-related spending had occurredand 179% greater than at this point in FY2019.
Analysis of notable trends: The pandemic response continues to disrupt normal spending and revenue patterns. Individual income taxes are usually paid in April however, in both 2020 and 2021, the federal government pushed back Tax Day due to COVID-19. This year, individual income taxes were due on May 17, compared to July 15 in 2020. Additionally, this year, estimated quarterly tax payments were due in April, whereas they were due in July in 2020. These shifting dates must be taken into account when considering year-over-year deficit comparisons.
The Federal Debt Ceiling
The federal debt ceiling is the legal amount of federal debt that the government can accumulate or borrow to fund its programs and pay for fees such as the national debt interest. Since its creation through the Second Liberty Bond Act in 1917, the debt ceiling has grown about 100 times. These instances have included permanent raises, temporary extensions, and revisions to what the debt limit can be defined as. When the debt ceiling isnt raised, the federal government is unable to issue Treasury bills and must rely solely on tax revenues to pay for its programs this has occurred 7 times since 2013.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: August 2022
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $217 billion in August 2022, the eleventh month of FY2022. This deficit was the difference between $304 billion in revenues and $521 billion in spending. August receipts were up by $36 billion , and outlays were up by $82 billion compared to a year ago. In 2021, August 1 fell on a weekend, shifting certain federal payments that would have otherwise been paid in August to July. If not for these timing shifts, the deficit in August 2022 would have been $13 billion less than August 2021s deficit. The following discussion excludes the effects of these timing shifts. Additionally, student loan debt cancellation was announced in August, but given the uncertainty around implementation, those outlay adjustments are not reflected in this months deficit projections.
Analysis of notable trends: Over the first 11 months of FY2022, the federal government ran a deficit of $944 billionbarely more than one-third the size of the $2.7 trillion deficit over the same period in FY2021. So far this year, revenues were $822 billion higher than over the same period in FY2021, increasing across all major sources. Individual income and payroll tax receipts increased by $742 billion . Unemployment insurance receipts also increased by $15 billion as states continued to replenish unemployment insurance trust funds following their depletion throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read Also: How Much Do Liquidators Pay For Inventory
Are The National Debt And The Budget Deficit The Same Thing
No, the deficit and the national debt are different things, although related. The national debt is the sum of a nations annual budget deficits, offset by any surpluses. A deficit occurs when the government spends more than it raises in revenue. To finance its budget deficit, the government borrows money by selling debt obligations to investors.
General Us National Debt Statistics
1. The outstanding national debt of the USA in 2021 was $28.43 trillion.
The growing public debt of the US has been a matter of concern for a long time. The annual national debt figures show that this problem has become particularly grave since the recession of 2008. The US national debt in 2008 was $10 trillion and has more than doubled since. Note that the US governments fiscal year ends in September.
2. In September 2022, the total US national debt hit $30.9 trillion.
The main reason for the growth of US debt over the years has been the spending on new governmental programs coupled with tax cuts. Between 2020 and 2022, however, the main factor was the governments COVID-19 response. Despite widespread worry about Americas growing debt, the concerned authorities have failed to control the rising figure.
3. The US interest on the national debt is projected to be $305 billion in 2022.
One of the greatest problems with having a large amount of debt owed to the public is the annual expenditure on interest payments. With the national debt year by year growing, this expenditure is also on the rise.
The USAs annual interest payment is larger than the entire GDP of over 160 countries. In 2022, this payment would account for 5% of the federal budget, taking away money from more important expenditures.
4. Adding unfunded obligations takes the federal governments total obligations to $202 trillion as of September 2022.
Don’t Miss: What Credit Cards Can You Get After Bankruptcy
Q& a: Everything You Should Know About The Debt Ceiling
The federal debt ceiling was raised in December of 2021 by $2.5 trillion to $31.381 trillion, which is expected to last until at least July of 2023. At that point, the Treasury Department may begin using accounting tools at their disposal, called extraordinary measures, to avoid defaulting on the governments obligations. At the point of exhaustion of those measures, absent a new agreement to either raise or suspend the debt ceiling, the Treasury will be unable to continue paying the nations bills. Congress could address the debt ceiling through reconciliation, which provides for passage of legislation with a simple majority vote in the Senate.
What is the debt ceiling?
The debt ceiling is the legal limit on the total amount of federal debt the government can accrue. The limit applies to almost all federal debt, including the roughly $24.3 trillion of debt held by the public and the roughly $6.9 trillion the government owes itself as a result of borrowing from various government accounts, like the Social Security and Medicare trust funds. As a result, the debt continues to rise due to both annual budget deficits financed by borrowing from the public and from trust fund surpluses, which are invested in Treasury bills with the promise to be repaid later with interest.
When was the debt ceiling established?
How much has the debt ceiling grown?
Why is Congress debating this now?
What are extraordinary measures?
Interest On The National Debt And How It Affects You
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past events that have had a lasting impact.
The interest on the national debt is how much the federal government must pay on outstanding public debt each year. The national debt includes debt owed to individuals, to businesses, and to foreign central banks, as well as intragovernmental holdings.
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Did Donald Trump File For Bankruptcy
Stats On The Us National Debt By Year
- In June 2022, the total US public debt hit $30.46 billion.
- The US interest on the national debt is projected to be $305 billion in 2022.
- The US per capita national debt in 2021 stood at $85,552.
- Interest payments are the US governments 6th largest budgetary expense as of 2022.
- Japan holds the most of the US national debt .
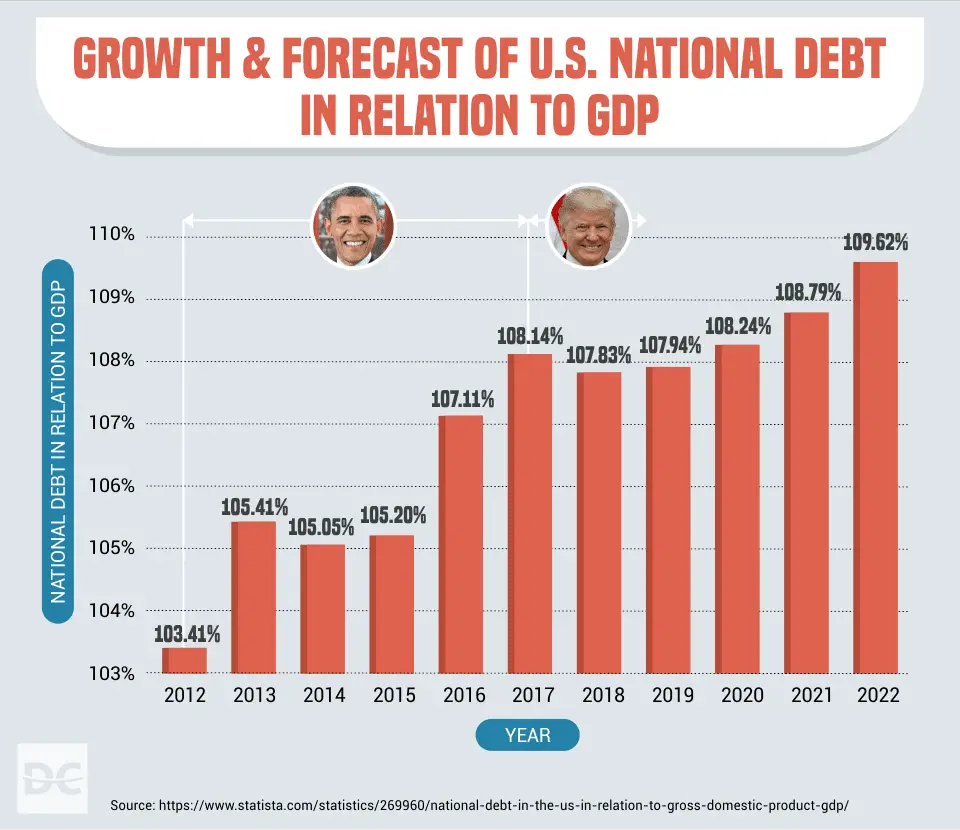
- In terms of Dollar value, Barack Obama was the US President who grew the debt burden the most.
- The wars in Afghanistan and Pakistan have cost the US more than $2.3 trillion.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: September 2019
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated a surplus of $83 billion in September, the final month of Fiscal Year 2019. This brings the total FY2019 deficit to $984 billion,26 percent higher than last years deficit. If not for timing shifts of certain payments, this years deficit would have been21 percent larger than the deficit inFY2018. On an apples-to-apples basis, total revenues inFY2019increased by4 percent , while spending increased by7 percent , compared to the prior fiscal year.
Analysis of Notable Trends for Fiscal Year 2019: Corporate income tax revenue increased by 14 percent relative to 2018, although that year notably was tied for the lowest corporate revenue level as a share of the economy since 1965, a result of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 . Customs duties increased by 71 percent versus last year due to the imposition of tariffs, specifically on certain imports from China. On the spending side, outlays from the refundable earned income and child tax credits increased by 14 percent versus last year, reflecting expansions enacted in TCJA. Finally, payments for net interest on the public debt rose by an alarming 14 percent , largely due to higher short-term interest rates and a growing federal debt burden on which those interest payments are owed.
Also Check: Jud Ct Gov Foreclosure
What Causes The National Debt To Increase
Sometimes the government needs to increase spending to stabilize the economy, and protect Americans and businesses from unexpected economic conditions.
During The Great Recession , for example, Congress passed legislation injecting $1.8 trillion into the economy. But that pales in comparison to the $4.5 trillion the Trump and Biden administrations have pumped into the economy since the Covid pandemic began in March 2020.
However, there are other reasons the national debt increases, even during years where spending is moderate and the economy is in good shape.
You May Like: How In Debt Is The United States
The National Debt In Perspective
Consider what it means when the graph says 100%. It means the national debt equals one year of Gross Domestic Product . So if we used the full value of what the US produces for one year just to pay off that debt, that would just do it. And 50% means the debt would be paid off in six months of using the full output.
That sounds outlandishly huge, but consider a family making $100,000 a year that buys a $250,000 house with 20% down and takes a $200,000 mortgage. No one considers this unusual or risky. But that family would be off the top of the graph at 200%. It would take all they made for two years to pay off their debt. And the US has a slight advantage over most families. It can print money. So there is zero chance of default.
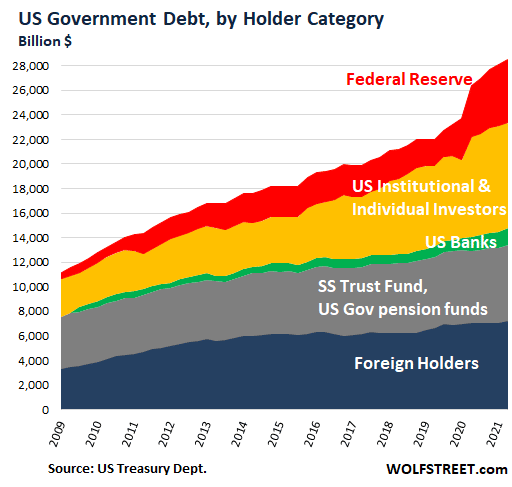
And only about 1/4 of the national debt is owed to foreigners. Another 40% is owed to Americans, for example, pension plans own quite a bit of it. And the rest is owed by the US governments General Fund to other Government Trust Funds, like the Social Security Trust Fund and the militarys pension fund.
Click for an explanation of the Green Line, balanced budgets, tax cuts and a bit of Keynesian stimulation.
Recommended Reading: How To Qualify For Bankruptcy In California
Why Is The Debt So High
As of March 2022, the U.S.s national debt stands at $30.2 trillion.Factors that contribute to the U.S.s high national debt include continued federal budget deficits, the government borrowing from the Social Security Trust Fund, the steady Treasury lending from other countries, low interest rates that promote increased investment, and raised debt ceilings.
Other factors that contribute to the high national debt include the inefficient healthcare system and the changing demographics of the country. Though the U.S. spends more than other countries on healthcare, health outcomes are not much better. In addition, the Baby Boomer generation are now becoming elders and seeking benefits and increased healthcare services. The government will spend, sometimes inefficiently, more on programs and services for the longer living older generations.
National Debt For Selected Years
| Fiscal year | |
|---|---|
| 130.6% | 21,850 |
On July 27, 2018, the BEA revised its GDP figures in a comprehensive update and figures back to FY2013 were revised accordingly.
On June 25, 2014, the BEA announced: “n addition to the regular revision of estimates for the most recent 3 years and for the first quarter of 2014, GDP and select components will be revised back to the first quarter of 1999.
Fiscal years 19402009 GDP figures were derived from February 2011 Office of Management and Budget figures which contained revisions of prior year figures due to significant changes from prior GDP measurements. Fiscal years 19502010 GDP measurements were derived from December 2010 Bureau of Economic Analysis figures which also tend to be subject to revision, especially more recent years. Afterwards the OMB figures were revised back to 2004 and the BEA figures were revised back to 1947.
Fiscal years 19401970 begin July 1 of the previous year fiscal years 19802010 begin October 1 of the previous year. Intragovernmental debts before the Social Security Act are presumed to equal zero.
19091930 calendar year GDP estimates are from MeasuringWorth.com Fiscal Year estimates are derived from simple linear interpolation.
Audited figure was “about $5,659 billion.”
Audited figure was “about $5,792 billion.”
Audited figure was “about $6,213 billion.”
Audited figure was said to be “about” the stated figure.
Audited figure was “about $7,918 billion.”
Audited figure was “about $8,493 billion.”
You May Like: How To Get Student Loans Discharged In Bankruptcy
Tracking The Federal Deficit: August 2019
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated a $200 billion deficit in August, the eleventh month of Fiscal Year 2019. This makes for a total deficit of $1.067 trillion so far this fiscal year, 19 percent higher than over the same period last year. Total revenues so far in FY 2019 increased by 3 percent , while spending increased by 7 percent , compared to the same period last year.
Analysis of Notable Trends this Fiscal Year to Date: Trends in the major categories of revenue and spending continued from previous monthscompared to last year, individual income and payroll taxes collectively rose by 3 percent , while spending for the largest mandatory programs collectively increased by 6 percent . Revenues from customs duties increased by 72 percent , primarily due to new tariffs imposed on certain imports from China. Estate tax revenue decreased by 25 percent due to the 2017 tax cuts which doubled the value of the estate tax exemption. Additionally, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac remitted $16 billion more in payments to the Treasury this year. Finally, net interest payments on the federal debt continued to rise, increasing by 14 percent versus last year due to higher interest rates and a larger federal debt burden.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: February 2020
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated a $235 billion deficit in February, the fifth month of fiscal year 2020. Februarys deficit is a $1 billion increase from the $234 billion deficit recorded a year earlier in February 2019. Februarys deficit brings the total deficit so far this fiscal year to $625 billion, which is 15% higher than the same period last year . Total revenues so far in FY2020 increased by 7% , while spending increased by 9% , compared to the same period last year.
Analysis of Notable Trends inThis Fiscal Year to Date: Through the first five months of FY2020, individual income tax refunds fell by 6% , increasing net revenue, as the timing of refund payments varies annually. Customs duties rose by 14% , partly due to tariffs imposed by the current administration, primarily on imports from China. On the spending side, net interest on the public debt increased by 6% even amidst historically low interest ratesbecause the overall debt burden has risen. Outlays for the Department of Veterans Affairs rose by 7% because of rising participation in veterans disability compensation, growing average disability benefits, and increasing spending on a program that helps veterans receive treatment in non-VA facilities.
Recommended Reading: Different Types Of Bankruptcies For Businesses
Tracking The Federal Deficit: February 2019
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated a $227 billion deficit in February, the fifth month of Fiscal Year 2019, for a total deficit of $537 billion so far this fiscal year. Februarys deficit is 5 percent higher than the deficit recorded a year earlier in February 2018. Total revenues so far in Fiscal Year 2019 decreased by 0.3 percent , while spending increased by 8.5 percent , compared to the same period last year.
Analysis of Notable Trends this Fiscal Year to Date: Income tax refunds were down by 10 percent from October-February 2019 compared to the same period in Fiscal Year 2018, and corporate income tax receipts were down by 19 percent from October-February 2019 relative to the same period in Fiscal Year 2018. The dip in corporate revenues is primarily attributable to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. On the spending side, Department of Homeland Security outlays decreased by 31 percent due to a relative decrease in disaster spending versus last year. Conversely, net interest payments on the national debt were up 15 percent from October-February 2019 compared to the same period in Fiscal Year 2018.
United States Government Debt: % Of Gdp
Key information about United States Government Debt: % of GDP
- United States Government debt accounted for 124.9 % of the country’s Nominal GDP in Jun 2022, compared with the ratio of 127.1 % in the previous quarter.
- US government debt to GDP ratio data is updated quarterly, available from Mar 1969 to Jun 2022.
- The data reached an all-time high of 132.4 % in Mar 2021 and a record low of 31.8 % in Sep 1974.
Related information about United States Government Debt: % of GDP
- In the latest reports, US National Government Debt reached 30,928.9 USD bn in Sep 2022.
- The country’s Nominal GDP reached 6,312.1 USD bn in Jun 2022.
View United States’s Government Debt: % of GDP from Mar 1969 to Jun 2022 in the chart:
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Buy Liquidation Pallets