What Causes The National Debt To Increase
Sometimes the government needs to increase spending to stabilize the economy, and protect Americans and businesses from unexpected economic conditions.
During The Great Recession , for example, Congress passed legislation injecting $1.8 trillion into the economy. But that pales in comparison to the $4.5 trillion the Trump and Biden administrations have pumped into the economy since the Covid pandemic began in March 2020.
However, there are other reasons the national debt increases, even during years where spending is moderate and the economy is in good shape.
You May Like: How In Debt Is The United States
Tracking The Federal Deficit: April 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $225 billion in April, the seventh month of fiscal year 2021. Aprils deficit was the difference between $439 billion of revenue and $663 billion of spending. If not for a shift in the timing of some payments because May 1 fell on a weekend, Aprils deficit would have been $165 billion.
So far this fiscal year, the federal government has run a cumulative deficit of $1.9 trillion, the difference between $2.1 trillion of revenue and $4.0 trillion of spending. This deficit is 26% greater than at the same point last fiscal year and 252% greater than at this point in fiscal year 2019.
Analysis of notable trends: In normal years, spending and revenues typically follow similar monthly patternsan influx of individual income taxes arrives in April, corporate income taxes are paid quarterly, refundable tax credits are largely paid in February and March. These patterns allow analysts to gauge changes in federal finances by comparing each months spending and revenues to the same month in the prior year.
The New Deal & The Agricultural Adjustment Administration
In this year, approximately one-fourth of U.S. workers were unemployed, thanks to the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression. The New Deal was President Franklin Roosevelt’s effort to revive the economy and bring about reforms in industry, agriculture, labor, finance, and housing. Roosevelt drummed up support for the program in a series of fireside chats broadcast to the American people.
The Agricultural Adjustment Administration was one New Deal initiative. It sought to curtail farm production by subsidizing farmers who reduced their output. By 1936, payments totaling $1.5 billion had been paid out.
National Debt: $23 billion
Don’t Miss: When Will Bankruptcy Come Off My Credit Report
Tracking The Federal Deficit: March 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $658 billion in March 2021, the sixth month of fiscal year 2021. This months deficitthe difference between $267 billion in revenue and $925 billion in spendingwas $487 billion greater than last Marchs . The federal deficit has now swelled to $1.7 trillion in fiscal year 2021, 129% higher than at this point last year. While revenues have grown 6% year-over-year, cumulative spending has surged 45% above last years pacelargely a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, its economic fallout, and the federal governments fiscal response.
Analysis of Notable Trends: Adjusted for timing shifts, outlays in March 2021 were $517 billion greater than last March, an increase of 127%. Unemployment insurance, refundable tax credits, and the Small Business Administrations Paycheck Protection Program accounted for most of the increaseboth from March to March and from last fiscal year to this one. Spending on refundable tax credits was $346 billion higher in March 2021 than March 2020, mostly due to the payment of pandemic recovery rebates authorized by the Consolidated Appropriations Act and American Rescue Plan Act..
Less To Spend On Other Government Initiatives
The more money the U.S. has to spend on meeting its debt obligations as interest rates increase, the less financial capacity it could have to fund programs focused on education, veterans benefits and transportation.
This breakdown of the 2019 Federal Budget from the Council on Foreign Relations shows how the budget pie is only so big, so when one area increases , another must decrease.
Recommended Reading: Filing Bankruptcy On Car Loans
Will Rising Federal Debt Slow Economic Growth
There is always a lot of controversy around the implications of high government debt. Over the past 70 years, high government debt has generally been accompanied by weaker economic activity. The cause and effect can be debated, and there is also a bit of a chicken-and-egg, or “circular” argument: High and rising debt is a burden on growth, but low levels of growth also trigger an increase in government spending, higher budget deficits and higher debt.
In other words, one argument holds that a high and rising burden of debt crimps economic growth due to the “crowding-out” effect . A competing argument is that economic growth generally has been slowing over the past several decadesdriven by demographics, globalization/competition, technology/innovation, and low inflationwhich has led to increased government spending to try to boost growth, thereby increasing the deficit and, in turn, debt levels. The chart below represents the broadest measure of government debt, including federal government debt, state and local debt, and government-sponsored enterprise debt . Courtesy of the strength of the economic rebound coming out of the lockdown phase of the pandemicat the federal, state and local levelsgovernment debt as a percentage of gross domestic product has moved lower, which is good news .
National Debt Statistics By Decade
17. The national debt increased from $907 billion to $2.85 trillion in the 1980s.
We already mentioned the increase of the US federal debt percentage-wise during Ronald Reagans presidency. However, during this decade, there was also a high increase in the dollar amount.
During his term, Reagan lowered the taxes and yet increased military spending. The defense budget was increased by 43% which caused high budget deficits.
18. The US national debt amounted to $5.7 billion in 1999.
At the start of the decade, the national debt was approximately $3 trillion dollars. If we look at the US debt to the penny using official data from the Treasury, we can see that the decade ended with the national debt reaching $5.7 trillion.
President Bill Clinton signed the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993. Its aim was to decrease the budget deficit as well as the national debt. It is sometimes referred to as the Deficit Reduction Act, as this act decreased the debt to GDP ratio. It was the first time since the 1960s that the federal government had a budget surplus in 1998 due to this act.
19. The national debt increased by around $8 trillion from 2000 to 2010.
And lets not forget the impact the Great Recession had on the budget deficit!
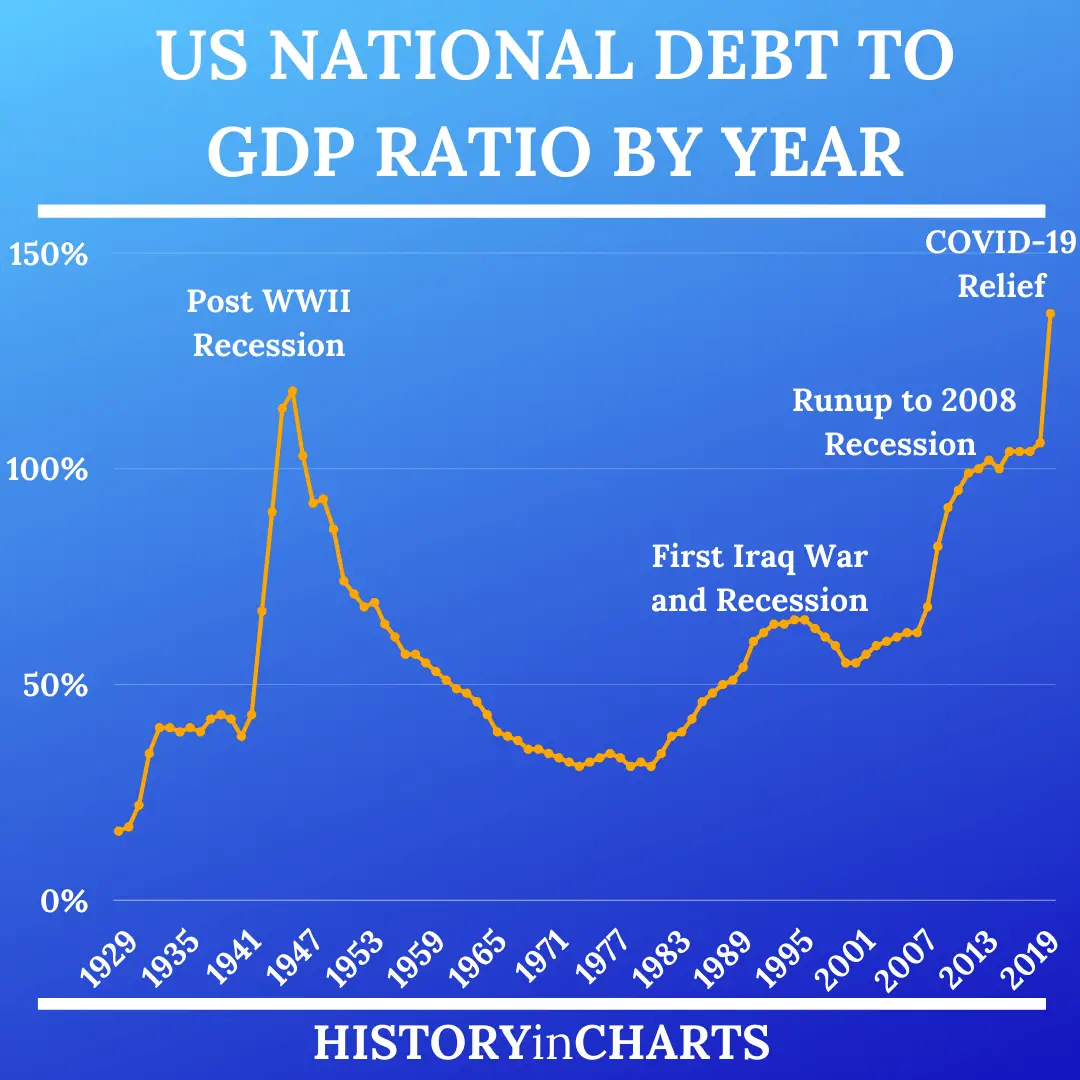
20. The current debt to GDP ratio is 127.52%. the highest since the 1940s.
21. The highest national debt to GDP ratio was 135.64% in Q2 2020.
Recommended Reading: What Is The National Debt Of Usa
Tracking The Federal Deficit: October 2020
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $284 billion in October, the first month of fiscal year 2021. This deficit is the difference between $238 billion of revenue and $522 billion of outlays. Because November 1 fell on a weekend this year, however, certain payments that would normally be made in November were instead shifted to October, increasing the size of this months deficit. Without those payments, Octobers deficit would have been $230 billion.
Either way, this Octobers deficit is a large increase from last Octobers figure of $134 billion. The year-over-year surge in the deficit is the sum of slightly lower revenues3% lower than last October, mostly due to lower receipts of individual income taxesand much greater outlays37% greater than last October , mainly because of the ongoing response to the COVID-19 pandemic and its economic fallout.
FY2020
The National Debt In Perspective
Consider what it means when the graph says 100%. It means the national debt equals one year of Gross Domestic Product . So if we used the full value of what the US produces for one year just to pay off that debt, that would just do it. And 50% means the debt would be paid off in six months of using the full output.
That sounds outlandishly huge, but consider a family making $100,000 a year that buys a $250,000 house with 20% down and takes a $200,000 mortgage. No one considers this unusual or risky. But that family would be off the top of the graph at 200%. It would take all they made for two years to pay off their debt. And the US has a slight advantage over most families. It can print money. So there is zero chance of default.
And only about 1/4 of the national debt is owed to foreigners. Another 40% is owed to Americans, for example, pension plans own quite a bit of it. And the rest is owed by the US governments General Fund to other Government Trust Funds, like the Social Security Trust Fund and the militarys pension fund.
Click for an explanation of the Green Line, balanced budgets, tax cuts and a bit of Keynesian stimulation.
You May Like: Can You File Bankruptcy On Student Loans In Michigan
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Obligations Excluded
Under normal accounting rules, fully owned companies would be consolidated into the books of their owners, but the large size of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac has made the U.S. government reluctant to incorporate them into its own books. When the two mortgage companies required bail-outs, White House Budget Director Jim Nussle, on September 12, 2008, initially indicated their budget plans would not incorporate the government-sponsored enterprise debt into the budget because of the temporary nature of the conservator intervention. As the intervention has dragged out, pundits began to question this accounting treatment, noting that changes in August 2012 “makes them even more permanent wards of the state and turns the government’s preferred stock into a permanent, perpetual kind of security”.
What Makes The Debt Bigger
The leading federal spending categories currentlySocial Security, Medicare/Medicaid and defenseare the same as in the 1990âs, when national debt was much lower relative to GDP. The U.S. remains the worldâs largest economy and one of the richest countries. How, then, did the debt situation deteriorate? Numerous factors are in play.
Also Check: How To File Bankruptcy Yourself In South Dakota
Impeachment Of President Clinton
President Bill Clinton’s second term in the White House was marked by a strong economy and a reversal of the budget deficit. However, his affair with a White House intern led to his impeachment in December of 1998. Clinton was later acquitted on charges of perjury and obstruction of justice.
National Debt: $5,656 trillion
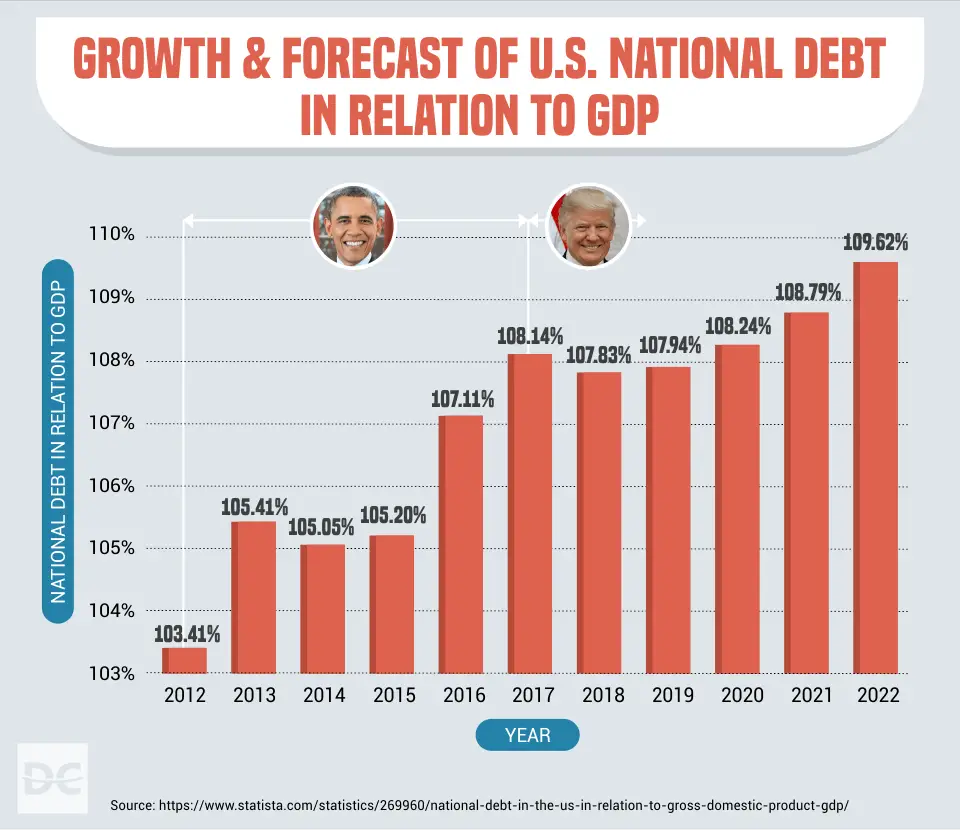
How The Debt Compares To Gdp Plus Major Events That Impacted It
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past events that have had a lasting impact.
The U.S. national debt grew to a record $31.12 trillion in October 2022. It has grown over time due to recessions, defense spending, and other programs that added to the debt. The U.S. national debt is so high that it’s greater than the annual economic output of the entire country, which is measured as the gross domestic product .
Throughout the years, recessions have increased the debt because they have lowered tax revenue and Congress has had to spend more to stimulate the economy. Military spending has also been a big contributor, as has spending on benefits such as Medicare. In 2020 and 2021, spending to offset the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic also added to the debt. In 2022, tax increases on the wealthy and corporations decreased the future debt outlook, but student loan forgiveness increased it.
One way to look at the national debt is by comparing it to GDP each year, as well as other major events that have impacted it. Below, we’ll dive into the U.S. national debt per year and what caused it to grow over time.
Read Also: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Future In Canada
Tracking The Federal Deficit: August 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $173 billion in August, the eleventh month of fiscal year 2021. Because August 1 fell on a weekend this year, certain large federal payments that typically pay out on the first of the month were shifted into late July. If not for this timing shift, the August deficit would have been $233 billion$60 billion greater than reported. Monthly revenues rose 20% compared to last August, primarily due to increased income and payroll tax receipts. Spending increased by 4% year over year, driven by changes in pandemic response spending.
So far this fiscal year, the federal government has run a cumulative deficit of $2.7 trillion, the difference between $3.6 trillion in revenue and $6.3 trillion in spending. This deficit is 10% lower than over the same period in FY2020, but more than 150% larger than the FY2019 deficit at this point in the year.
Analysis of Notable Trends: With one month to go until the close of fiscal year 2021, the federal government is on track to record a somewhat smaller deficit than last year. The economic recovery has buoyed revenues, and the tapering of some large pandemic relief programs has slowed growth in outlays.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: November 2020
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $146 billion in November, the second month of fiscal year 2021. This deficit was the difference between $365 billion of spending and $219 billion of revenue. Spending in November, however, was artificially lowered by the fact that November 1 fell on a weekend, causing $63 billion worth of payments that would normally be made in November to be made in October instead. If those payments had been made in November as usual, this months spending and deficit would each have been $63 billion greater, or $428 billion and $209 billion . In the first two months of this fiscal year, the federal government has run a deficit of $430 billion, $87 billion more than at this point last fiscal year. Compared to this point last fiscal year, spending has run 9% higher while revenues have fallen by 3%.
Revenues also fell by 3% from last November, mostly reflecting a drop in withheld individual income and payroll taxes due to lower levels of employment.
Recommended Reading: When Does A Company File For Bankruptcy
Is Rising Debt Inflationary
Although it’s not supported by any historical data, there is an elevated concern expressed about high debt and whether it, in and of itself, leads to serious and persistent inflation. The visual below looks at every decade since the 1970seach color-coded. It shows the relationship between debt as a percentage of gross domestic product and the inflation rate, as measured by the core personal consumption expenditures measure . As shown, as debt growth expanded as a share of GDP, inflation moved lower, not higher. There is a more recent debate about how much of the past year’s inflation surge is due largely to COVID-19-specific supply/demand dislocations vs. the blow-out of the budget deficit as fiscal stimulus ramped up to ease the strains of the COVID recession. The answer is probably both.
What Is National Debt
The term national debt refers to the outstanding financial obligations of a country. Such obligations may also be called government debt, federal debt, or public debt. The national debt of the United States is what the federal government owes creditorsincluding debt held by the public and federal government trust funds. U.S. national debt totaled $31.1 trillion as of October 2022, a record high.
Recommended Reading: Debt To Income Ratios
Stats On The Us National Debt By Year
- In September 2022, the total US public debt hit $30.9 billion.
- The US interest on the national debt is projected to be $305 billion in 2022.
- The US per capita national debt in 2021 stood at $85,552.
- Interest payments are the US governments 6th largest budgetary expense as of 2022.
- Japan holds the most of the US national debt .
- In terms of Dollar value, Barack Obama was the US President who grew the debt burden the most.
- The wars in Afghanistan and Pakistan have cost the US more than $2.3 trillion.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: January 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $165 billion in January, the fourth month of fiscal year 2021. This months deficitthe difference between $552 billion of spending and $387 billion of revenuewas $132 billion greater than last Januarys. But federal finances deteriorated more than the raw numbers suggest. Adjusting for shifts in the timing of some payments, the deficit this January would have been $211 billion greater than last Januarys. The federal deficit has now reached $738 billion so far this fiscal year, an increase of 120% over the same point last year . Compared to the same point last fiscal year, cumulative revenues have ticked up 1%, but cumulative spending has surged 27%mostly due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the federal response to it.
Increased spending so far this fiscal year has likewise mostly resulted from pandemic relief. About 60% of the increase in cumulative year-to-date spending has come from refundable tax credits and unemployment insurance benefits . Outlays from the Public Health and Social Services Emergency Fund are also up $26 billion compared to the first four months of fiscal year 2020, and Medicaid spending is $29 billion greater.
Revenues rose 4% from last January, thanks to greater revenue from individual income, payroll, and corporate income tax revenue.
You May Like: Bankruptcy And Medical Bills