How Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Works
Pay even the slightest bit of attention to financial news and youll learn about Chapter 11 bankruptcy. All the major airlines have done it. So have General Motors and Chrysler. Krispy Kreme and Hostess did it. So did, back in the day, Marvel Comics.
In Chapter 11 bankruptcy, companies and certain individuals ask the court to help them get relief from creditors while staying afloat and holding onto assets. Generally, the debtor develops a plan to change the operation of its business with the idea of generating more profit and paying off debts. The debtor also gets the chance to renegotiate with creditors. Once the plan is approved by the court, it is put into motion.
Chapter 11 bankrupts win because they get a real fresh start, often while unloading certain legacy debts unsustainable pension plans, for instance that prevent them from getting into the black and staying there. Creditors win because they wind up getting far more than they would in a liquidation bankruptcy.
Individuals who choose Chapter 11 dont qualify for Chapter 7 because their income is too high, and they have too much debt to qualify for Chapter 13. Think: Hollywood headliners and professional sports stars.
Bitbns Introduces Zero Tds Cryptocurrency Systematic Investment Plans
This process involves the creditors and the business owner striking a court-approved deal to resume business and restructure the debt, renegotiate fees, take proactive cost cutting measures and other necessary actions to stabilise the business situation.
Both Chapter 7 and Chapter 11 require the company to appoint a trustee, but in Chapter 7, the trustee will work to sell the assets and distribute cash according to absolute priority, and in Chapter 11, the trustee will supervise the companys assets and allow the business to continue as a going concern.
Bankruptcy under Chapter 11 doesnt mean that the entire business debt is absolved, but rather that the debt is structured and an arrangement of paying it back with future earnings has to be made.
Why Celsius Filed Chapter 11?
According to a report from Wall Street Journal, Celsius has $162.547 million in cash and short term investments, and its bad debts amounts to $800,000.
Recently, Celsius repaid its loan from AAVE and freed up its crypto assets pledged there. Hence, Celsius has some cash and some assets, and if it can provide a solid restructuring plan, it might emerge as a successful crypto decentralised finance company again. As such, Celsius filed for Chapter 11 Bankruptcy to get a second chance in running its business, rather than shutting shop and selling whatever assets they have, and paying creditors in their absolute priority, which is what Chapter 7 Bankruptcy does.
Other Ways To Discharge Debt
Often creditors sell their unsecured debts to collection agencies, who then adopt aggressive tactics to collect on the debt, or as much of it as they can. There are ways to use the Fair Credit Reporting Act to get these unsecured debts voided, especially because collection agencies often lack the necessary documentation for legally enforcing debt obligations. This forum post has some good information on how to do that.
Don’t Miss: Where To Buy A Car After Bankruptcy
Who Should File For Chapter 11 Or Chapter 7
In most cases, individuals will want to file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy. Chapter 7 bankruptcy, in particular, is meant for individuals who are seeking a “fresh start,” but corporations may also file for Chapter 7 . This form of bankruptcy focuses on discharging as many debts as possible and liquidating assets to pay off a variety of remaining debts that cannot be discharged.
A minimum amount of debt is not required for someone to file either Chapter 11 or Chapter 7 bankruptcy. However, to file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, individuals need to pass a “means test,” usually by having a large amount of unmanageable debt and/or a low income that hinders debt repayment. Those who have a lot of disposable income are less likely to have their Chapter 7 filing approved.
Chapter 11, which is more expensive than Chapter 7, is typically intended for medium- to large-sized businesses, but smaller businesses and sole proprietors may also want to consider this type of bankruptcy. Unlike Chapter 7, Chapter 11 does not liquidate assets, only restructures debts. This allows a debtor to protect an important asset, such as a business, from liquidation. In the case of sole proprietorships and similarly small businesses, Chapter 11 bankruptcy affects both business and personal assets.
What Is The Difference Between Chapter 11 Vs Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
If filing for bankruptcy protection has become necessary, Chapter 11 grants the company an opportunity to restructure its debts and continue operating, whereas Chapter 7 is the straight liquidation and distribution of the sale proceeds of a company to its creditors.
- Under which type of circumstances might a company file for Chapter 7 rather than Chapter 11 ?
- What is the overarching purpose of Chapter 11 bankruptcies?
- How is the best interests test related to the Chapter 7 liquidation recoveries?
- Can Chapter 11 bankruptcies also end up in liquidation?
Also Check: What To Bring To Bankruptcy Attorney
Chapter 11 And Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Chapter 11 and Chapter 13 filings are similar. Chapter 13 is for individuals, as is Chapter 11, though the latter was originally designed for corporations. The main difference between the two is the amount of money the debtor owes. There is no limit to the amount of money owed by debtors filing for Chapter 11. When filing for Chapter 13, a debtor needs steady income, unsecured debt that is less than $269,250 and secured debt less than $807,750. After filing, the debtor appoints a trustee to create a payment plan proposal. It is then up to the court to accept the repayment plan, alter it, or create an entirely new plan. A plan can take three to five years to pay back once decided upon.Contact us today to learn more about our bankruptcy lawyer services in Las Vegas!Main photo by Jonathan Kos-Read
Are Businesses Required To Complete Credit Counseling/debtor Education
Sole proprietors must complete an approved credit counseling course before they file for bankruptcy in their own names. They must also take a second debtor education course after filing for bankruptcy. Owners of corporations, LLCs and other business entities generally are not subject to these requirements. We can determine if these steps are necessary for your small business.
You May Like: What Is The Current Debt Of The United States
Can I Keep My Property During Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
Yes, youll likely get to keep your home during a Chapter 11 bankruptcy. But only up to a certain amount.
A Chapter 11 personal bankruptcy allows up to $1,184,200 in secured debt mortgage and car payments. It also allows $394,725 in unsecured debt such as credit cards.
Assets such as property can also be written down. For example, if you own a property worth $98,000 but owe $150,000 on the loan, the principal balance of the mortgage can be reduced to the value of the property. The new mortgage would be $98,000.
Chapter 11 also allows the interest rate on the loan to be reduced and repayment terms can be extended. That could drop your monthly mortgage payments.
Personal Bankruptcy Options Chapter 7
As far as personal bankruptcy options go, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common type. This is a liquidation bankruptcy where a Chapter 7 trustee is assigned to your personal bankruptcy case. This trustee has the power to sell any of your assets that are not protected by bankruptcy exemptions. In most Chapter 7 bankruptcy cases, people are able to discharge the majority of their general unsecured debts such as credit cards, loans, medical bills, and other debts which are not secured against property, and are not certain types of priority unsecured debts.
Individual and joint debtors may qualify for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy case if they pass the means test. This is a calculation to determine if your income is more than the average income of a household of your same size in your county. If you do pass the means test, then you may choose Chapter 7 over other kinds of bankruptcy. However, if you have exposed equity in your assets, or are concerned that the Chapter 7 trustee assigned to your case will believe that you have exposed equity in your assets, then you may want to consider a reorganization bankruptcy under Chapter 13 or Chapter 11.
Recommended Reading: When You Declare Bankruptcy You Are Said To Be Insolvent
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Vs Chapter 7
| Chapter 11 | |
|---|---|
| Discharge takes four to six months | |
| Debtor retains assets and pays debts from future monthly income | Trustee sells assets to pay off debts |
| Debtor reorganizes debts and finances | Loan balances are not reduced |
| Very expensive | There are no monthly payments |
Chapter 11 bankruptcy allows a business to continue its operations while paying off its debts. This is in contrast to a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, also known as a “liquidation bankruptcy.” With Chapter 7, a business’s or individual’s assets are sold. The trustee uses the proceeds to pay debts, which often means ceasing operations for a business.
Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
Home > Bankruptcy > Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
This is the story for anyone who thinks a bankruptcy is a bankruptcy is a bankruptcy. Not so. In fact, bankruptcies are like Nike sneakers: They come in a variety of styles, each fashioned to meet the particular needs of the applicant.
Named for the chapter of the federal bankruptcy code that describes them, two of the most common varieties are Chapter 7 and Chapter 11. Which one is right for the applicant depends on the details of candidates bleak circumstances.
Know this going in: The consequences of bankruptcy will have a punishing effect in the short- and long-term. Your credit rating will take a severe hit youll have trouble financing any major purchases potential employers may find you too severe a risk to hire and your bankruptcy will stick to your credit history for at least seven years.
On the upside, bankruptcy overseen by specialized federal courts provides a civil and orderly resolution for individuals or businesses whose finances are a wreck. Bankruptcy is almost always painful. But its not the end of the world.
Bankruptcy is a fresh start for a debtor, says Cathy Peek McEwen, a Federal Bankruptcy Judge for the Middle District of Florida. Thats the pep talk I give my law students, and to everyone who comes into my courtroom.
Read Also: Does Claiming Bankruptcy Clear Student Loans
What Debts Can Be Included In Chapter 11
Most debts incurred prior to declaring bankruptcy can be discharged. These include, but are not limited to, business debts, back rent, and credit card bills.
Its easier to note what cant be done away with in Chapter 11 filings, beginning with this: A debtor who commits misconduct during the course of a bankruptcy proceeding will be denied discharge.
Otherwise, debts that cannot be discharged include certain tax claims and mortgages. These can be restructured, however, as part of a realistic repayment scheme that allows the business to endure.
Restructuring plans must survive a fair and equitable test, a key consideration of which is whether secured creditors will receive at least the value of their collateral.
Chapter 7 Title 11 United States Code

| This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. |
| Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| This article needs to be . Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
(
Chapter 7 of Title 11 of the United States Code governs the process of liquidation under the bankruptcy laws of the United States, in contrast to Chapters 11 and 13, which govern the process of reorganization of a debtor. Chapter 7 is the most common form of bankruptcy in the United States.
Also Check: Does Bankruptcy Pay Off Car Loans
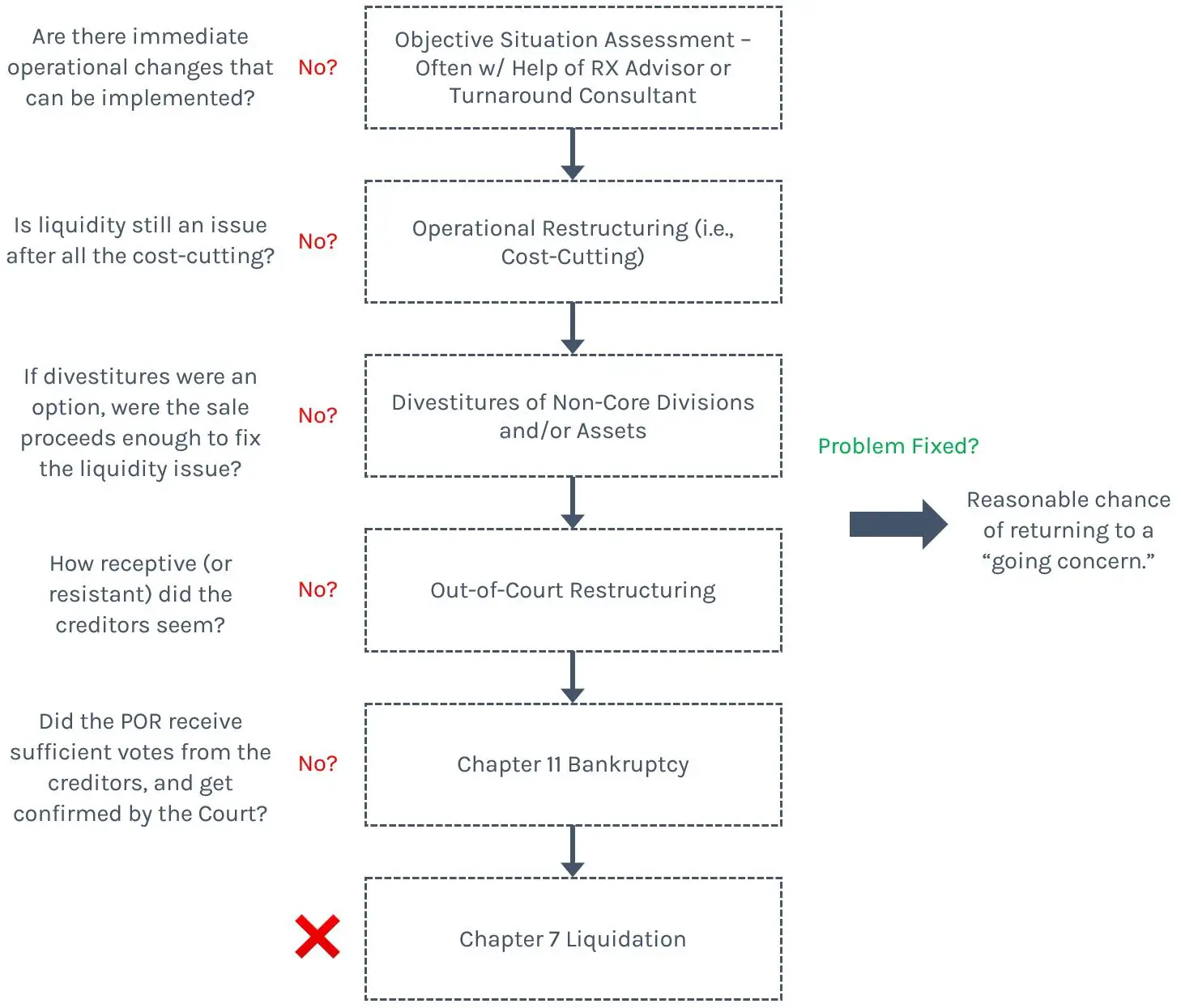
Chapter 11 Vs Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Introduction
Under the oversight of the Bankruptcy Court, the debtor has the opportunity to emerge from Chapter 11 as a viable business with a better-aligned capital structure.
Conversely, during Chapter 7, the assets belonging to the debtor are liquidated to pay off liabilities owed to creditors in accordance with the absolute priority rule and the business ultimately ceases to exist.
Regardless of whether the corporation determines if Chapter 11 or Chapter 7 is the right course of action for its circumstances, the decision by the debtor is legally required to be in the best interests of the impaired creditors.
If an actual turnaround of the debtor seems plausible and the catalyst for the financial distress is deemed temporary and/or one that the company could adapt to, filing for Chapter 11 could be the right choice.
But liquidations under Chapter 7 can often be an unavoidable outcome, as not every company is suited for a reorganization. Instead, an irrational attempt at a turnaround could put the debtor in a worsened state and further reduce the recovery proceeds belonging to creditors.
The decisive factor for whether to file for Chapter 11 or Chapter 7 comes down to the perceived value of the enterprise post-reorganization.
What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
In this chapter 7 bankruptcy liquidation of assets takes place. The debtor pays his debts by selling his/her personal assets. The debtor pays his secured loan on a priority basis because creditors can claim for collateral like a car loan, home equity loan, mortgage, etc. After paying secured loansSecured LoansSecured loans refer to the type of loans approved and received against a guarantee or collateral. If they fail to do so, the lending institution acquires the collateral to compensate for the amount that the borrowers were allowed.read more if still some money is left to the debtor, he pays unsecured loans like a credit card, unsecured personal loan, etc.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be HyperlinkedFor eg:Source: Chapter 7 vs Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
Also Check: What Happens When You Declare Bankruptcy In Australia
Can A Small Business File For Chapter 7
Filing a Chapter 7 for small business may be a viable bankruptcy option depending on how your own business is organized.
If the business is a sole proprietorship, you must file for Chapter 7 in your own name, which allows you to protect your personal assets from seizure by business creditors. You will need to pass the means test unless your business debt exceeds your personal debt. You may be able to exempt certain property from your creditors, possibly allowing you to stay in business.
If your business is a partnership, corporation or limited liability company , it can file for bankruptcy as a separate entity and wont need to pass the means test. However, individual partners remain personally liable for partnership debts. If you co-signed or guaranteed a business debt, you are liable as well. Furthermore, there are no exemptions of property available to business entities. This means that all of the companys assets will be liquidated, leaving the business insolvent.
We can fully explain the consequences of Chapter 7 for you and your small business and advise you on the best course of action.
Consult With Our Portland Bankruptcy Attorneys Today
If you are dealing with crippling debt and youre considering filing for bankruptcy, deciding whether to file for bankruptcy under Chapter 7 vs Chapter 11 can be a tough decision to make. It can affect how you deal with home foreclosure, wage garnishment, or car repossession.
Not all types of bankruptcy are the same. Before proceeding with bankruptcy, it is best to review your financial situation with an experienced Portland bankruptcy attorney. Our Portland bankruptcy attorneys are experienced in both Chapter 7 and Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. Dont hesitate to contact our legal team at Michael D. OBrien & Associates PC today! We can help you assess your situation and give you a fresh start.
Don’t Miss: What Questions To Ask A Bankruptcy Lawyer
Individuals And Sole Proprietors In Chapter 7
These Chapter 7 filers can keep property using bankruptcy exemptions and discharge qualifying debt. It’s best suited for a low- or no-income debtor whose property is fully protected by bankruptcy exemptions and whose debts qualify for discharge. But as long as the debtor would come out ahead financially, meaning that the amount of erased debt would adequately exceed the value of property lost, Chapter 7 would likely make sense.
How Long Does It Take To Complete A Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 11 Case
The time to complete a Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 bankruptcy case is very different.
A Chapter 7 case for individuals can be completed in four to six months. Chapter 11 cases for individuals can last several years.
A business that files under Chapter 11 is in bankruptcy for several years in most cases. A Chapter 7 for a business could be completed in a year or two, depending on the size of the business.
Recommended Reading: How Long After Bankruptcy Can You Buy A Home
Bankruptcy Law Revision: The Bapcpa
On October 17, 2005, the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act went into effect. This legislation was the biggest reform to the bankruptcy laws since 1978. The legislation was enacted after years of lobbying efforts by banks and lending institutions and was intended to prevent abuses of the bankruptcy laws.
The changes to Chapter 7 were extensive.