The Types Of Presidential Decisions That Impact National Debt
Presidents can have a tremendous impact on the national debt. They can also have an impact on the debt in another presidentâs term. When President Trump took office in January of 2017, for the first nine months of his presidency, he operated under President Obamaâs budget which didnât end until September, 2017. So for most of a new presidentâs first year in office, he isnât accountable for the spending that takes place. As strange as this may seem, itâs actually by design to allow time for the new president to put a budget together when in office.
What Is The National Debt
The national debt is the debt that the federal government holds which includes public debt, federal trust funds, and government accounts. As the total amount of deficit that the government has garnered, it is a number that encompasses what the government owes itself and others. The national debt is looked at in three parts: debt held by the public, gross federal debt, and debt subject to limit. Debt held by the public is the money gathered to fund activities and programs, with money borrowed from external lenders. The gross federal debt includes the public debt, but also adds federal trust funds and governments. Debt subject to limit is similar to gross federal debt, but only includes debt issued by the treasury and Federal Financing Bank.
As of July 2020, the national debt is more than $26.5 trillion. This number equates to $80,422 for every person living in the u.S., and is 123% of the U.S.’s annual economic output. As of June 2020 the debt-to-GDP ratio was 120.5%, due to the economic strain of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Beauty Pageant Of Money
While there is a diversity of opinion on how to think about the national debt, there is broad agreement that comparing it to household debt credit cards, mortgages or student loans, for example is the wrong way to think about it.
The important difference is that if you or I run out of dollars, we lack the ability to generate new ones. The government has no such encumbrance, and when it makes new dollars, people all over the world respect their value.
One perspective here is, we call it the national debt, but its not really debt, said David Andolfatto, senior vice president in the research division at the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Its actually part of the money supply that people find useful, the same way you and I find using money useful.
The government acquires more debt by issuing Treasury securities which come in the form of bills, notes or bonds which have different maturities and have a seemingly infinite market for buyers because they are regarded as the safest of assets. Investments go up or down in value T-bills do too, but theyre never worthless.
Because Treasuries are stable, retain value and are eminently marketable, banks are now required to hold some quantity of them at all times as a provision against the kind of market collapse that the banking system experienced in 2008.
The United States is not experiencing that pressure today far from it. China sold about $180 billion in Treasuries in 2015, and the market largely shrugged it off.
Don’t Miss: Do Lenders Look At Gross Or Net Income
Recovery From The Civil War
The Civil War alone is estimated to have cost $5.2 billion when it ended and government debt skyrocketed from $65 million to $2.6 billion. Post-Civil War inflation along with economic disturbance from Europes financial struggles contributed to the vulnerable economic climate of the late 19th century.
The collapse of Jay Cooke & Co., a major bank invested in railroading, caused the Panic of 1873. Nearly a quarter of the countrys railroads went bankrupt, more than 18,000 businesses closed, unemployment hit 14 percent and the New York Stock Exchange began sinking.
This period of deflation and low growth continued for 65 months making it the longest depression, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research. During this time the government collected less money in taxes and the national debt grew.
How Are Debt Clocks Calculated

Well use the United Kingdom as an example:
1 We obtain the latest data regarding the countrys national debt and the 10-year average interest rate they pay on it, like:
National Debt: $1,717,879,000,000 10-Year Interest Rate: 2.50
2 Using these two figures we can then calculate how much the debt increases per year and subsequently per second.
Increase per Year: $42,946,975,000 Increase per Second: $1,362
3 We then work out the time difference between when the data was obtained and when the debt clock is being viewed by a visitor.
Time Difference = Time and Date of Visit Time and Date of Official Figure
4 The current debt is then calculated by adding the increase over this time to the official figure.
Current National Debt = Official Figure +
5 The debt clock then updates every two seconds, increasing according to the figures calculated in step 2.
Current National Debt = ) x Exchange Rate
Contents
Recommended Reading: How Often Can You File Bankruptcy In Indiana
Examples Of Capital Expenditure
Examples of infrastructure spending that improve an economy are:
- The development of transport infrastructure, such as motorways and railways
- Investment in universities to create more educational institutions or crate centers of excellence from existing establishments.
- Improvements in communication infrastructure, such as a fibre optic backbone to expand the nations internet bandwidth availability and speed.
If you are thinking of investing in a countrys economy, or if you are considering moving there, researching the national debt of that place and how the government spends money may be insightful.
A countrys national debt is one of many economic indicators that interplay to create a judgment on a countrys prospects for success.
Does The National Debt Affect American Citizens
The US national debt does have the potential for ramifications that individual citizens may be impacted by. According to the Congressional Budget Office, US citizens could feel the effects of a large national debt in higher taxes, lower ability to fund benefits and services, and less money to meet economic crises like wars or natural disasters like the coronavirus pandemic.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get A Copy Of A Bankruptcy Discharge
President Andrew Jackson Cuts Debt To Zero
The War of 1812 more than doubled the nations debt. It increased from $45.2 million to $119.2 million by September 1815. The Treasury Department issued bonds to pay a portion of the debt, but it was not until Andrew Jackson became president and determined to master the debt that this national curse, as he deemed it, was addressed.
The time of prosperity was short-lived, as state banks began printing money and offering easy credit, and land value dropped.
How Has The Covid
According to the Congressional Budget Office, debt held by the American public will rise to 98% of GDP due to the economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic and legislative actions taken as a result. The CBO says that the main driver of the increased debt is a federal budget shortfall of $3.3 trillion, the largest since 1945.
Read Also: What Are The Alternatives To Filing Bankruptcy
You May Like: How Many Times Can You File Bankruptcy In Ga
Who Is In Charge Of The Us National Debt
US government debt is the responsibility of the Treasury Department. Money is raised in the form of bonds, which are known as Treasury bonds, Treasury bills, or T-bills.
Bonds are sold in auctions, which are conducted by the Federal Financing Bank each sale event can raise a maximum of $15 billion.
Why Is This Important
Interests costs continue to rise, meaning that much of government spending may go towards paying it off. This means that areas of development such as education and infrastructure could receive less funding as more and more is allocated towards interest payments. In addition to this, higher interest rates create obstacles for private investments which affect economic growth. When the interest rate is high, it can be harder for businesses and individuals to receive funding and investments.
The national debt does not only affect the economy and its growth – it can also have a large effect on individuals and their livelihoods. As investments become harder to gain, businesses increase the costs of goods and services to balance out debt service obligations. In the long term, this can lead to lower investment returns. In addition to the possibility of paying more for goods and services, the average income for a family of four is projected to if debt continues to grow. This means that the money spent on necessities and luxuries will decrease. In addition to this, rising debt can equate to higher interest rates, meaning that houses, cars, and loans for college or businesses will become more expensive. In addition to this, the government may need to cut budgets around various programs which can affect those who rely on Medicare or Social Security to live.
Want to know more about how the debt is affecting our fiscal future? Check out our graphs and see it for yourself!
Also Check: How To Declare Bankruptcy In Toronto
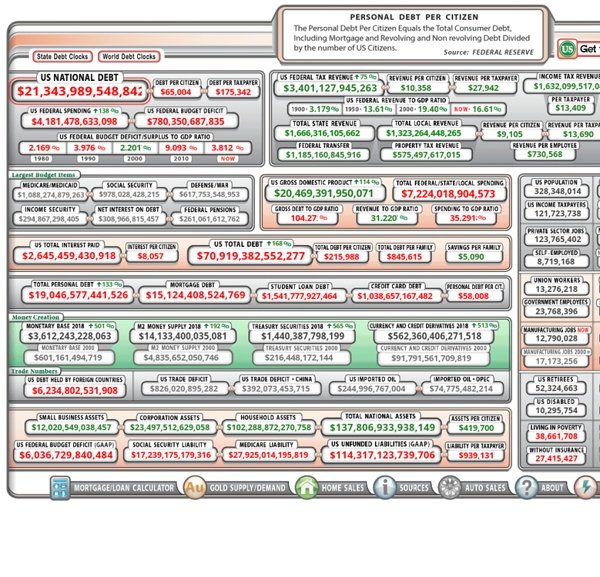
Us National Debt Clock
The US National Debt Clock covers the outstanding debt owed by the federal government. Two-thirds of the clock shows the public debt by way of treasury bills, notes, and bonds – this covers individuals, businesses, and foreign governments. The other third of the debt is what the government owes to itself – this covers federal programs like Social Security.
The largest budget items include: Medicare and Medicaid, Social Security, defense, and interest paid on the national debt. The former two items are a part of the mandatory programs that the government is required to fund with federal expenses. To give you an idea of how much more the U.S. spends compared to other countries, for the defense budget alone the U.S. spends more than China, India, Russia, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, and Brazil combined.
The Debt Clock also gives statistics on the demographics of the country, which is helpful in understanding where program funding may go. With a population of over 329 million, 60 million people are enrolled in Medicare and 79 million people receive Medicaid. In addition to this, there are currently 54 million retirees who seek Social Security benefits.
The National Debt Is Now More Than $31 Trillion What Does That Mean
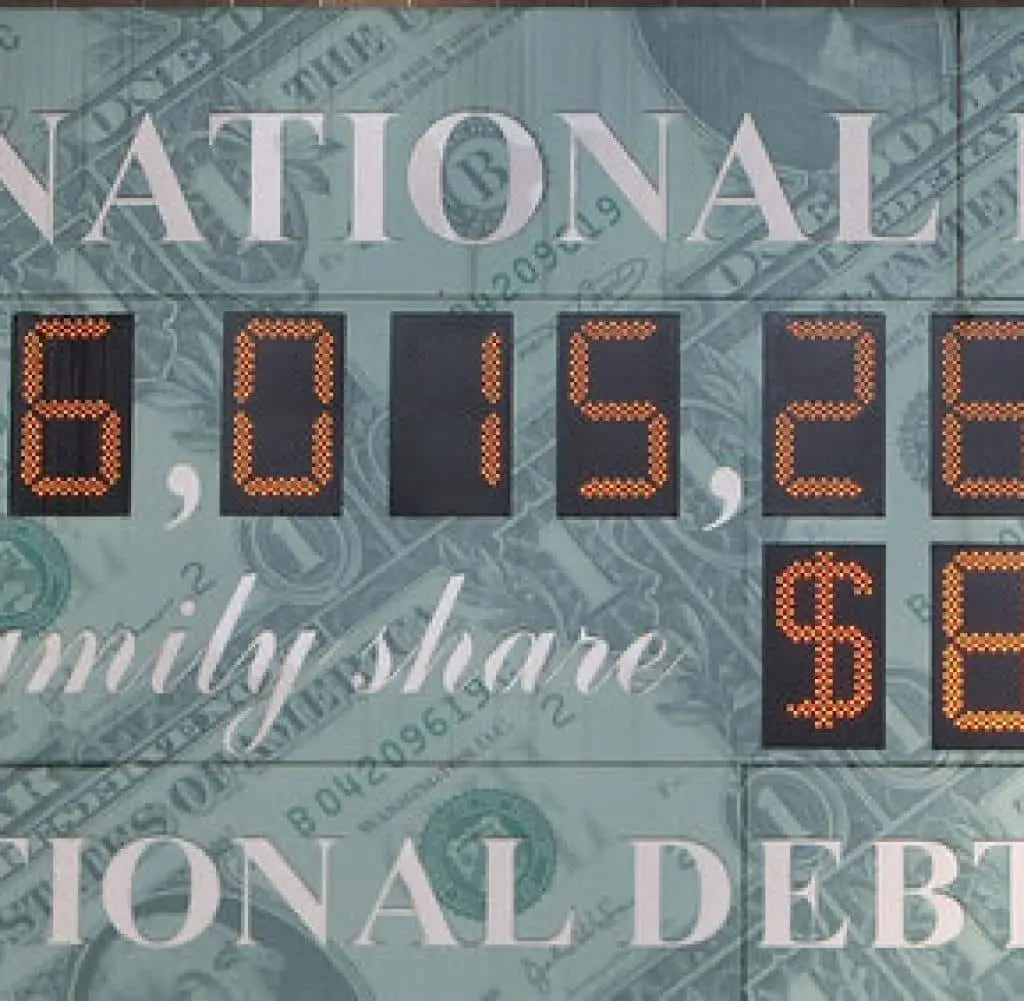
The gross federal debt of the United States has surpassed $31,000,000,000,000. Although the debt affects each of us, it may be difficult to put such a large number into perspective and fully understand its implications. The infographic below offers different ways of looking at the debt and its relationship to the economy, the budget, and American families.
The $31 trillion gross federal debt includes debt held by the public as well as debt held by federal trust funds and other government accounts. In very basic terms, this can be thought of as debt that the government owes to others plus debt that it owes to itself.
Americas high and rising debt matters because it threatens our economic future. The coronavirus pandemic rapidly accelerated our fiscal challenges, but we were already on an unsustainable path, with structural drivers that existed long before the pandemic. Putting our nation on a better fiscal path will help ensure a stronger and more resilient economy for the future.
Recommended Reading: Can You Rent With A Bankruptcy
A Blessing Or A Curse
The United States has had an up-and-down relationship with debt. One of Congresss first actions was to assume states Revolutionary War debt in exchange for moving the countrys permanent capital to Washington, D.C. Alexander Hamilton saw collective debt as a way to build the nation and its international credit and bind the several states together in common cause.
A national debt, if it is not excessive, will be to us a national blessing, he wrote in 1781. It will be a powerful cement of our Union.
President Andrew Jackson differed considerably in his opinion. He campaigned on the promise of eliminating the national debt, which he regarded as a tool empowering the federal government and thus centralizing power.
I believe it a national curse, Jackson said in 1824. My vow shall be to pay the national debt, to prevent a monied aristocracy from growing up around our administration that must bend it to its views, and ultimately destroy the liberty of our country.
Jackson followed through on his promise, vetoing virtually every spending bill and using federal funds to pay down the debt until it was fully paid off in 1837 right before a six-year economic depression that pumped it back up again.
World War II ballooned the debt as the nation ratcheted up defense spending to finance the war, causing the countrys debt to rise to more than 100% of gross domestic product.
The financial crisis was the appropriate time to borrow, just like it is now, she added.
What Other Factors Impact National Debt Rating
A countrys rating is also influenced by the:
- Rate of population growth
- Distribution of income in the country
- Levels of private debt
- Value of the housing stock
- Rate of homeownership
- Annual inward investment in a country
The above factors show whether the economy is likely to grow. A growing economy can bear the burden of tax that is needed to comfortably repay national debt.
Recommended Reading: What Happens After Bankruptcy Petition Is Filed
How Is The Debt Ceiling Raised
Inflation and legislation that expands government activities require the debt ceiling to be raised.
If the debt ceiling is not raised, the Treasury must resort to alternative measures to raise funds. Once those measures are exhausted, the government would go bankrupt. Politics can result in Congress refusing to raise the debt ceiling to gain concessions on other areas of policy.
The National Debt Is Big And Getting Bigger Does It Matter
WASHINGTON The United States national debt is nestled in a brick-laden underpass just a block away from Times Square. It ticks away, month after month, year after year, never getting smaller, never slowing down.
That national debt clock the brainchild of the real estate tycoon Seymour Durst, who installed it on West 43rdStreet in Manhattan in 1989 isnt actually the national debt. Its a representation of the national debt, a simple tally of how much money the federal government has borrowed from the public and has yet to pay back.
Durst said of the clock when it was installed that it was meant to strike anxiety if not fear into passersby. If it bothers people, he said, then its working.
When Durst died in 1995, the national debt totaled more than $4 trillion. In 2008, less than 20 years later, the debt clock ran out of digits, forcing the Durst Organization to add two more. The clock can now track our collective debt into the quadrillions.
The clock currently reads $28 trillion, give or take, and will grow rapidly in the coming years. The coronavirus pandemic has cost the U.S. economy $16 trillion, give or take, and Congress appropriated more than $3 trillion in aid in 2020.
Lawmakers have echoed Dursts distaste for the national debt for decades, with varying degrees of sincerity. And we are hearing them again, as Congress debates a nearly $2 trillion relief package to respond to the pandemic and its economic fallout.
Also Check: How To Stop A Garnishment Without Bankruptcy
Read Also: How Long Does Bankruptcy Stay On Credit Report In Australia
Why Does Larger National Debt Attract Bond Buyer
Having a large national debt doesnt always discourage buyers of bonds. For example, the United States has a debt to GDP ratio of 108% and a lot of people want to buy US Treasury bonds.
You can see this data summary of US Local & State Government Debt for more information.
Some countries, such as the USA are always considered a good place to invest, and the government bonds of those countries are always in high demand.
Social Security Trust Fund
Every president borrows from the Social Security Trust Fund. Over the years, the Fund has taken in more revenue than it needed through payroll taxes leveraged on the baby boomer generation.
Ideally, this money should have been invested to be available when members of that generation retire. Instead, the Fund was loaned to the government to finance increased spending. This interest-free loan helps keep Treasury bond interest rates low, allowing more debt financing. But, it must be repaid by increased taxes as more individuals retire.
Don’t Miss: How Does Filing Bankruptcy Affect Me
How Is National Debt Rated
Rating agencies score governments on a range of metrics. Countries with higher ratings can offer lower interest rates on their bonds because they are considered to be safe investments.
When investigating a countrys economy, the national debt is one metric that rating agencies note.
They also look at the debt-to-GDP ratio, the national debt per head of population, the interest rates on government debt, and the average bank lending rate.
Do Foreign Countries Own National Debt
For example, Japan owns $1.276 trillions worth of US government debt.
You can research the economies of the largest US national debt holders. See our economic overviews of Brazil, China, the UK, Belgium, and India.
The ten largest holding nations of US government debt as of September 2020 are shown in the table below:
| Rank |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Can A Probate Estate File Bankruptcy
How To Look At The National Debt By Year
It’s best to look at a country’s national debt in context. During a recession, expansionary fiscal policy, such as spending and tax cuts, is often used to spur the economy back to health. If it boosts growth enough, it can reduce the debt. A growing economy produces more tax revenues to pay back the debt.
The theory of supply-side economics says the growth from tax cuts is enough to replace the tax revenue lost if the tax rate is above 50% of income. When tax rates are lower, the cuts worsen the national debt without boosting growth enough to replace lost revenue.
Major events, like wars and pandemics, can increase the national debt.
During national threats, the U.S. increases military spending. For example, the U.S. debt grew after the September 11, 2001, attacks as the country increased military spending to launch the War on Terror. Between fiscal years 2001 and 2020, those efforts cost $6.4 trillion, including increases to the Department of Defense and the Veterans Administration.
The national debt by year should be compared to the size of the economy as measured by the gross domestic product. That gives you the debt-to-GDP ratio. That ratio is important because investors worry about default when the debt-to-GDP ratio is greater than 77%that’s the tipping point.
You can also use the debt-to-GDP ratio to compare the national debt to other countries. It gives you an idea of how likely the country is to pay back its debt.