Raising Reserve Requirements And Full Reserve Banking
Two economists, Jaromir Benes and Michael Kumhof, working for the International Monetary Fund, published a working paper called The Chicago Plan Revisited suggesting that the debt could be eliminated by raising bank reserve requirements and converting from fractional-reserve banking to full-reserve banking. Economists at the Paris School of Economics have commented on the plan, stating that it is already the status quo for coinage currency, and a Norges Bank economist has examined the proposal in the context of considering the finance industry as part of the real economy. A Centre for Economic Policy Research paper agrees with the conclusion that “no real liability is created by new fiat money creation and therefore public debt does not rise as a result.”
The debt ceiling is a legislative mechanism to limit the amount of national debt that can be issued by the Treasury. In effect, it restrains the Treasury from paying for expenditures after the limit has been reached, even if the expenditures have already been approved and have been appropriated. If this situation were to occur, it is unclear whether Treasury would be able to prioritize payments on debt to avoid a default on its debt obligations, but it would have to default on some of its non-debt obligations.
Why The Deficit Is Less Than The Increase In The Debt
There’s an important difference between the deficit and debt. The deficit has been less than the increase in debt for years because Congress borrows from the Social Security Trust Fund surplus. The surplus emerged back in the 1980s when there were more people working than there were retirees. As such, payroll tax contributions were greater than Social Security spending, allowing the fund to invest the extra revenue in special Treasury bonds. Congress spent some of the surplus so it wouldn’t have to issue as many new Treasury bonds.
Why Do Governments Lower Interest Rates On Growing Economies
This knowledge in the financial community enables governments to lower the interest rates that it offers on its debt and reduce the cost of financing deficits.
Thanks to economic indicators, you can work out whether a countrys national debt will trigger a virtuous cycle of investment and expansion, or a destructive debt spiral.
Also Check: How To Clear Bankruptcy From Credit Report
Consequences Of Growing National Debt
Japan’s experience shows sovereigns can incur a surprising amount of debt if the country’s central bank is willing to monetize the borrowing, and so long as it doesn’t stoke inflation.
But even if we discount the remote risk of a default, rising debt imposes higher interest costs, especially when interest rates rise. The CBO expects the U.S. government’s net interest costs to triple over the next decade, reaching $1.2 trillion annually by 2032.
That will force lawmakers to decide between running even larger deficits just to keep spending and revenue constant, or some combination of spending cuts and revenue increases.
If the choice is even larger deficits, bond buyers might require higher yields to compensate them for the resulting increase in risk. Or they may not, if slowing economic growth prompts investment flows into fixed income amid expectations of lower interest rates.
The National Debt Today
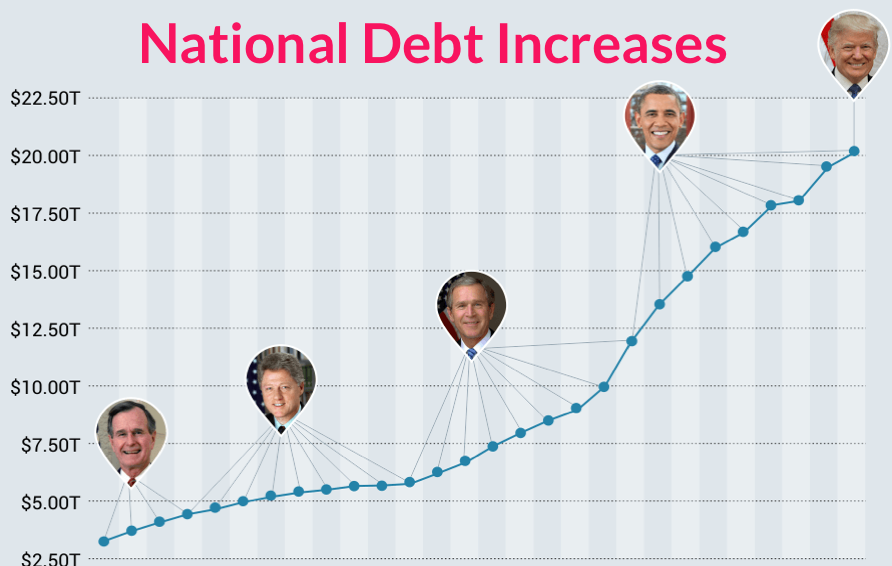
The COVID-19 pandemic damaged many areas of the global economy, forcing governments to drastically increase their spending. At the same time, many central banks once again reduced interest rates to zero.
This has resulted in a growing snowball of government debt that shows little signs of shrinking, even though the worst of the pandemic is already behind us.
In the U.S., federal debt has reached or surpassed WWII levels. When excluding intragovernmental holdings, it now sits at 104% of GDPand including those holdings, it sits at 128% of GDP. But while the debt is expected to grow even further, the cost of servicing this debt has actually in recent years.
This is because existing government bonds, which were originally issued at higher rates, are now maturing and being refinanced to take advantage of todays lower borrowing costs.
The key takeaway from this is that the U.S. national debt will remain manageable for the foreseeable future. Longer term, however, interest expenses are expected to grow significantlyespecially if interest rates begin to rise again.
Read Also: Amazon Liquidation Pallets Houston
Wars In Iraq And Afghanistan
Overseas wars and military operations launched after the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks in the U.S., in combination with increased domestic security spending, interest costs, and long-term veterans funding obligations, has added about $8 trillion to the national debt since 2001, by one estimate.
Meanwhile, annual U.S. military spending exceeds that of the next nine highest spenders combined.
Examples Of Capital Expenditure
Examples of infrastructure spending that improve an economy are:
- The development of transport infrastructure, such as motorways and railways
- Investment in universities to create more educational institutions or crate centers of excellence from existing establishments.
- Improvements in communication infrastructure, such as a fibre optic backbone to expand the nations internet bandwidth availability and speed.
If you are thinking of investing in a countrys economy, or if you are considering moving there, researching the national debt of that place and how the government spends money may be insightful.
A countrys national debt is one of many economic indicators that interplay to create a judgment on a countrys prospects for success.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Bankruptcy Off Credit Report Early
Household Debt To Gdp For United States
Observation:
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Units: Ratio, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Quarterly
Notes:
The data for household debt comprise debt incurred by resident households of the economy only. This FSI measures the overall level of household indebtedness as a share of GDP.Copyright © 2016, International Monetary Fund. Reprinted with permission. Complete terms of use and contact details are available from the IMF.
Suggested Citation:
International Monetary Fund, Household Debt to GDP for United States , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/HDTGPDUSQ163N, November 1, 2022.
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Obligations Excluded
Under normal accounting rules, fully owned companies would be consolidated into the books of their owners, but the large size of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac has made the U.S. government reluctant to incorporate them into its own books. When the two mortgage companies required bail-outs, White House Budget Director Jim Nussle, on September 12, 2008, initially indicated their budget plans would not incorporate the government-sponsored enterprise debt into the budget because of the temporary nature of the conservator intervention. As the intervention has dragged out, pundits began to question this accounting treatment, noting that changes in August 2012 “makes them even more permanent wards of the state and turns the government’s preferred stock into a permanent, perpetual kind of security”.
Don’t Miss: How Many Times Has Donald Trump Filed Bankruptcy
A Long Wait For I Told You So
The simple truth is that U.S. national debt will almost certainly increase for the foreseeable future. Even at current interest rates, debt-fueled tax cuts and spending increases are popular with voters and politicians across the political spectrum, despite occasional rhetoric to the contrary. And why not? With foreign investors scooping up nearly a third of U.S. debt, as a nation the U.S. essentially exchanges slips of paper promising future payment for valuable goods and services today. Long-term rates of four percent are apparently insufficiently ominous compared to the temptations of current consumption.
This leads to longer-term outlooks that are frankly troubling. The baseline projection, for instance, from the Congressional Budget Office , a non-partisan economic forecasting agency, has nearly a third of government revenue dedicated to debt service by 2052 as accumulated government borrowing hits 185 percent of the economy. If future rates were to be only 1.8 percent higher than the baseline forecast, the CBO sees debt payments consuming nearly 80 percent of the governments revenue with a total government debt burden over 2.3x the size of the economy. It is difficult to see those numbers as sustainable, in our opinion.
Risks To Economic Growth
Debt levels may affect economic growth rates. In 2010, economists Kenneth Rogoff and Carmen Reinhart reported that among the 20 developed countries studied, average annual GDP growth was 34% when debt was relatively moderate or low , but it dips to just 1.6% when debt was high . In April 2013, the conclusions of Rogoff and Reinhart’s study came into question when a coding error in their original paper was discovered by Herndon, Ash and Pollin of the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Herndon, Ash and Pollin found that after correcting for errors and unorthodox methods used, there was no evidence that debt above a specific threshold reduces growth. Reinhart and Rogoff maintain that after correcting for errors, a negative relationship between high debt and growth remains. However, other economists, including Paul Krugman, have argued that it is low growth which causes national debt to increase, rather than the other way around.
Commenting on fiscal sustainability, former Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke stated in April 2010 that “Neither experience nor economic theory clearly indicates the threshold at which government debt begins to endanger prosperity and economic stability. But given the significant costs and risks associated with a rapidly rising federal debt, our nation should soon put in place a credible plan for reducing deficits to sustainable levels over time.”
Read Also: How To Remove Bankruptcy Accounts From Credit Report
How To Look At The National Debt By Year
It’s best to look at a country’s national debt in context. During a recession, expansionary fiscal policy, such as spending and tax cuts, is often used to spur the economy back to health. If it boosts growth enough, it can reduce the debt. A growing economy produces more tax revenues to pay back the debt.
The theory of supply-side economics says the growth from tax cuts is enough to replace the tax revenue lost if the tax rate is above 50% of income. When tax rates are lower, the cuts worsen the national debt without boosting growth enough to replace lost revenue.
Major events, like wars and pandemics, can increase the national debt.
During national threats, the U.S. increases military spending. For example, the U.S. debt grew after the September 11, 2001, attacks as the country increased military spending to launch the War on Terror. Between fiscal years 2001 and 2020, those efforts cost $6.4 trillion, including increases to the Department of Defense and the Veterans Administration.
The national debt by year should be compared to the size of the economy as measured by the gross domestic product. That gives you the debt-to-GDP ratio. That ratio is important because investors worry about default when the debt-to-GDP ratio is greater than 77%that’s the tipping point.
You can also use the debt-to-GDP ratio to compare the national debt to other countries. It gives you an idea of how likely the country is to pay back its debt.
Forms Of Government Borrowing
In addition to selling Treasury bills, notes, and bonds, the U.S. government borrows by issuing Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities and Floating Rate Notes . Its borrowing instruments also include savings bonds as well as the government account securities representing intergovernmental debt.
Other nations have borrowed from international organizations like the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank as well as private financial institutions.
Don’t Miss: Can You File Irs Debt In Bankruptcy
Which Countries Have The Lowest National Debt
Does national debt matter? Is it an indication of financial stability? Not always.
There is only one debt-free country as per the IMF database. For many countries, the unusually low national debt could be due to failing to report actual figures to the IMF.
Another instance where low national debt might be a bad sign is if a countrys economy is so underdeveloped that nobody would want to lend to them.
Here the ten least indebted nations in the world in 2020 as per the IMFs reported data:
| Rank | |
|---|---|
| Congo, Dem. Rep. of the | 16.1% |
| 16.5% |
Calculating The Annual Change In Debt
Conceptually, an annual deficit should represent the change in the national debt, with a deficit adding to the national debt and a surplus reducing it. However, there is complexity in the budgetary computations that can make the deficit figure commonly reported in the media considerably different from the annual increase in the debt. The major categories of differences are the treatment of the Social Security program, Treasury borrowing, and supplemental appropriations outside the budget process.
Social Security payroll taxes and benefit payments, along with the net balance of the U.S. Postal Service, are considered “off-budget”, while most other expenditure and receipt categories are considered “on-budget”. The total federal deficit is the sum of the on-budget deficit and the off-budget deficit . Since FY1960, the federal government has run on-budget deficits except for FY1999 and FY2000, and total federal deficits except in FY1969 and FY1998FY2001.
You May Like: What Is Involved In Filing Personal Bankruptcy
Top 12 Countries With The Highest Debt
As of December 2020, the nation with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio is Venezuela, and by a considerable margin. The South American country has what may be the world’s largest reserves of oil, but the state-owned oil company is said to be poorly managed, and Venezuela’s GDP has plummeted in recent years. At the same time, Venezuela has taken out massive loans, adding to its debt burden, and president Nicolas Maduro has made questionable moves to slow the country’s rampant inflation.
Japan occupies the second slot with a ratio of 266%. In 1992, Japan’s Nikkei crashed. The government bailed out banks and insurance companies, providing them with low-interest credit. Banks were consolidated and nationalized, and other stimulus initiatives were used to help the struggling economy. However, these actions caused Japan’s debt to increase dramatically.
Another interesting entry on this list is the United States, whose debt-to-GDP ratio ranks 12th out of all the world’s countries. While the U.S. boasts the highest GDP in the world,, it nonetheless spends more than it earns. Major contributors to the national debt include the world’s largest military budget, tax cuts , COVID-19 relief efforts, and mandatory-but-underfunded programs such as Medicare.
What Other Factors Impact National Debt Rating
A countrys rating is also influenced by the:
- Rate of population growth
- Distribution of income in the country
- Levels of private debt
- Value of the housing stock
- Rate of homeownership
- Annual inward investment in a country
The above factors show whether the economy is likely to grow. A growing economy can bear the burden of tax that is needed to comfortably repay national debt.
Recommended Reading: Can You File Bankruptcy On Secured Loans
Social Security System Strains
For decades, payroll tax receipts earmarked for Social Security have exceeded benefit payments, producing system surpluses that have masked the structural U.S. budget deficit.
But those surpluses shrank before turning into a shortfall in 2021, and in the near future the deficits are expected to increase as Baby Boomer retirements swell the ranks of Social Security recipients.
The Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund funding the Social Security payments for retirees saw annual gains that peaked at about $180 billion in 2006-2008. Those surpluses are projected by the trust fund’s board of trustees to give way to growing deficits topping $200 billion annually by 2028 and $300 billion from 2031. In combination with payroll taxes, the $2.75 trillion trust fund is expected to finance full benefit payments until it is exhausted in 2034.
Growing life expectancy and reduced fertility rates are expected to reduce the share of working-age population from 58.3% in 2021 to 54.6% by 2050. Over the same span, the ratio of working-age Americans to those of retirement age is projected to drop from 3.4-to-1 to 2.6-to-1.
A Brief History Of Us Debt
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
Nearly all national governments borrow money. The U.S. has carried national debt throughout its history, dating back to the borrowing that financed the Revolutionary War. Since then the debt has grown alongside the economy, as a result of increased government responsibilities, and in response to economic developments.
Don’t Miss: Will Filing Bankruptcy Affect Student Loans
Why The Budget Deficit Matters
The federal deficit and debt are concerns for the country because the majority of the national debt is held by those who have purchased Treasury notes and other securities. A continuous deficit adds to the national debt, increasing the amount owed to security holders.
The concern is that the country won’t be able to pay its debt off. Debt holders demand higher interest to compensate for the higher risk when that happens. This increases the cost of all interest rates and can cause a recession.
Do Government Deficits Recover
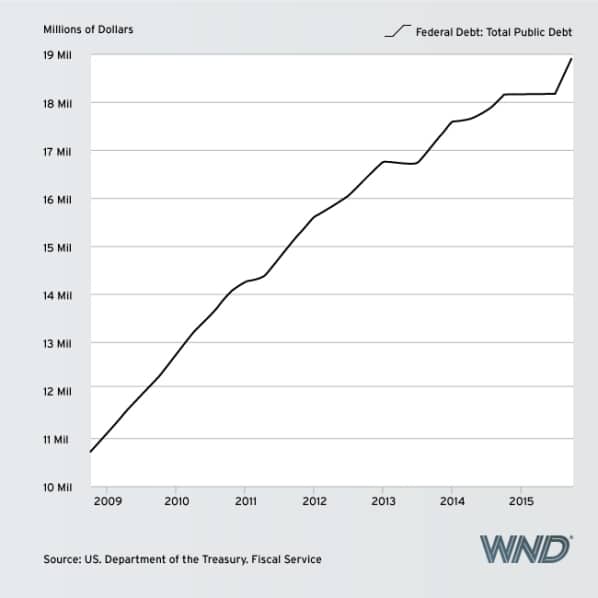
This situation creates an annual deficit that is unlikely to end until the accumulated debt becomes unsustainable and the governments finances collapse.
Other governments only borrow to stimulate the economy during a recession, calculating that they can repay that debt once expansion returns and produces a government budget surplus.
If the country and its government have a good reputation, the instruments that it issues in order to raise debt to cover a deficit represent a safe investment. See our example on foreign investors in U.S debt.
Governments that run constant deficits to buy votes find it difficult to attract loans.
Don’t Miss: How To View Foreclosed Homes
Public And Government Accounts
As of July 20, 2020, debt held by the public was $20.57 trillion, and intragovernmental holdings were $5.94 trillion, for a total of $26.51 trillion. Debt held by the public was approximately 77% of GDP in 2017, ranked 43rd highest out of 207 countries. The CBO forecast in April 2018 that the ratio will rise to nearly 100% by 2028, perhaps higher if current policies are extended beyond their scheduled expiration date.
The national debt can also be classified into marketable or non-marketable securities. Most of the marketable securities are Treasury notes, bills, and bonds held by investors and governments globally. The non-marketable securities are mainly the “government account series” owed to certain government trust funds such as the Social Security Trust Fund, which represented $2.82 trillion in 2017.
The non-marketable securities represent amounts owed to program beneficiaries. For example, in the cash upon receipt but spent for other purposes. If the government continues to run deficits in other parts of the budget, the government will have to issue debt held by the public to fund the Social Security Trust Fund, in effect exchanging one type of debt for the other. Other large intragovernmental holders include the Federal Housing Administration, the Federal Savings and Loan Corporation’s Resolution Fund and the Federal Hospital Insurance Trust Fund .