Lower Returns On Your Investments
Bonds issued by the Treasury are typically seen as low-risk investments. When interest rates rise, the yield on these low-risk investments also rises, making them more attractive investments for income-minded investors over other riskier income-generating investments like corporate bonds.
This could leave companies that typically rely on bonds short on the loans they need to finance expansions and operations and translate into lower returns for equity investors when companies fail to meet revenue targets.
Solutions To Reduce The National Debt
76% of voters believe that the President and Congress should allocate more time and energy towards addressing the national debt. Americans care about the national debt, and some work has been done in order to address this issue. Solutions include raising revenue , cutting spending, and growing the countrys GDP.
Policy options such as the Simpson-Bowles plan and the Domenici-Rivlin Task Force have made efforts to create plans to reduce the national debt. Centers and institutes such as the American Enterprise Institute, Bipartisan Policy Center, Center for American Progress, and Economic Policy Institute all proposed things ranging from slow growth to reduction in benefits for high-income individuals.
Young people across America are getting educated about fiscal policy and making changes at their colleges and universities with Up to Us. Sign the pledge to let local representatives know that you are concerned about the nations fiscal future, or get involved by learning about how you can make a difference in your own community.
What Is Medical Debt
The SIPP shows that in 2017, 19% of U.S. households carried medical debt, defined as medical costs people were unable to pay up front or when they received care. Among households with medical debt, the median amount owed was $2,000, meaning half had more and half had less.
Like other debt, medical debt means that households have less money to spend on other essential items, such as food and housing. People with medical debt, or at risk of accumulating medical debt, may also forgo needed medical care or treatment. Medical debt can also lead to bankruptcy.
Recommended Reading: Bankruptcy Attorney Huntsville Al
How Does The National Debt Affect Me
Interest payments also have an important role as they grow in step with the national debt. As the government allocates more funds towards paying off interests, other investment areas could get crowded out. Areas such as education, research and development, and infrastructure may not progress at sufficient or adequate levels due to interest payments. Interest payments currently take many of the dollars that are raised through federal income, estate, and federal excise taxes. Net worth is also an important and interesting factor that can be affected by the national debt.The cost of borrowing money to purchase large assets such as homes will increase due to the Federal Reserves interest rates. Interest rates will push down the prices of homes as individuals will struggle to qualify for mortgage loans this will then lower prices on home values.
You May Like: Consolidate Debt Loans Bank Of America
What Will Happen To Our National Debt
U.S. spending is currently at an all-time high to combat the effects of COVID-19. The current level of debt-to-GDP is comparable to the period immediately after World War II. Despite the effort to reduce the national debt, it is apparent and crucial for the government to take on the debt during times of crisis. Being able to adequately and successfully respond to emergencies is one of the many reasons why the national debt should be reduced governments should respond to events in an appropriate and timely manner with its citizens in thought.
You May Like: Can You Pay Off Bankruptcy Chapter 13 Early
Current Foreign Ownership Of Us Debt
apan owned $1.23 trillion in U.S. Treasurys in June 2022, making it the largest foreign holder of the national debt. The second-largest holder is China, which owns $967.8 billion of U.S. debt. Both Japan and China want to keep the value of the dollar higher than the value of their own currencies. This helps to keep their exports to the U.S. affordable, which helps their economies grow.
China replaced the U.K. as the second-largest foreign holder in 2006 when it increased its holdings to $699 billion.
The U.K. is the third-largest holder with $615.4 billion. Its holdings have increased in rank as Brexit continues to weaken its economy. Luxembourg is next, holding $306.8 billion. The Cayman Islands, Switzerland, Ireland, Belgium, France, and Taiwan round out the top 10.
Types Of Debt In America
Consumer debt reached $14.56 trillion after the fourth quarter of 2020, according to the New York Federal Reserve.
The debt for Q4 was up $414 billion from the previous year and up nearly $1.9 trillion over the previous record high of $12.68 trillion in the third quarter of 2008.
There has been consistent growth in four main areas of debt home, auto, student loans and credit cards. Non-housing debt has risen faster, increasing 51% since 2013 compared with a 24% increase in mortgage debt.
Home Total mortgage debt rose to $10.4-trillion, an increase of $1 trillion from the same juncture in 2017.
But the increase is a good thing overall. The rise of mortgage debt is an indication of recovery in the housing market. Household debt has been growing for five years, but mortgage balance growth has been on a slower incline since it stopped declining in 2013.
Auto Total auto debt in Q4 of 2020 is $1.37 trillion, a jump of $100 billion from the same time in 2018.
When the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates in 2008 to fight the recession giving consumers more incentive to pursue the typical three-to-five year loan for autos it kick-started a trend that has held true today. Auto loans continue to increase because of low-interest rates.
Student Loans They continue to escalate, growing to a record $1.56 trillion in Q4 of 2020, up $100 billion from the same juncture in 2018. The average student debt in 2020 was $38,792.
Dont Miss: How To File Bankruptcy On Student Loans
Recommended Reading: Debt Sold To Collection Agency
Tracking The Federal Deficit: February 2019
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated a $227 billion deficit in February, the fifth month of Fiscal Year 2019, for a total deficit of $537 billion so far this fiscal year. Februarys deficit is 5 percent higher than the deficit recorded a year earlier in February 2018. Total revenues so far in Fiscal Year 2019 decreased by 0.3 percent , while spending increased by 8.5 percent , compared to the same period last year.
Analysis of Notable Trends this Fiscal Year to Date: Income tax refunds were down by 10 percent from October-February 2019 compared to the same period in Fiscal Year 2018, and corporate income tax receipts were down by 19 percent from October-February 2019 relative to the same period in Fiscal Year 2018. The dip in corporate revenues is primarily attributable to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. On the spending side, Department of Homeland Security outlays decreased by 31 percent due to a relative decrease in disaster spending versus last year. Conversely, net interest payments on the national debt were up 15 percent from October-February 2019 compared to the same period in Fiscal Year 2018.
Tracking The Federal Deficit: August 2020
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $198 billion in August, the eleventh month of fiscal year 2020. This deficitthe difference between $223 billion of revenues and $420 billion of outlaysis $3 billion less than last Augusts, although this apparent improvement is an illusion created by shifts in the timing of certain payments. Without these timing shifts, this Augusts deficit would have been $106 billion greater than last Augusts. The cumulative deficit in FY2020 has risen to $3.0 trillion, an increase of $1.9 trillion from this point last year.
Analysis of notable trends: Cumulative revenue for the fiscal year is down 1% from this point last year, while cumulative outlays are 46% higher. August repeated this asymmetry, with revenues 2% lower than last Augusts and outlaysnetting out the timing shifts described above27% higher.
Thanks to a strong economy, this years revenue through March had been running 6% above last years. Then COVID-19 hit, and revenues from April through August have come in 9% lower than last year, due to both the loss in economic activity and legislation responding to the pandemic.
CBO now projects that the total deficit this fiscal year will run to $3.3 trillion, more than triple last years and the largest deficit as a share of the economy since 1945.
Read Also: How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Job And Future Credit
Whom Does The United States Owe Nearly $31 Trillion In Debt
Proverbs 22:7 comes to mind. :
The U.S. has about $30.9 trillion in national debt, according to the latest data from Treasury Department, and that total will reach a record $31 trillion as early as later in the month.
Roughly $24.3 trillion of Americas total public debt outstanding consists of debt held by the public, and $6.6 trillion is intragovernmental holdings, according to Monday data from the Treasury Department.
Intragovernmental holdings include federal trust funds, revolving funds and special funds, as well as Federal Financing Bank securities, the Treasury Department said on its website.
You can be sure that nobody will pay this intragovermental holdings debt but you, dear reader.
Debt held by the public consists of all national debt held by any person or entity that is not a U.S. federal government agency, according to the Treasury Department. That includes corporations, domestic individual investors, local or state governments, Federal Reserve banks, foreign investors, foreign governments and other entities.
Read Also: Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Credit Rating
How Much Is The Us National Debt In 2021
On Dec. 31, 2021 the US national debt stood at $28.4T. That was relative to an economy that generated a gross domestic product of $23T. That made the debt-to-GDP ratio 1.05 Put another way, the national debt was around 105 percent of GDP.
This ratio is much higher than the US has seen for most of its history. The peak occurred just after World War II, when the ratio was 112 percent. In 2018, the US had the fourteenth highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the world.
In 2019, the government collected about $3.5T in revenue while spending $4.4T. Thus, there was a nearly $1T federal deficit in 2019, which was added to the national public debt.
Also Check: How To Avoid Credit Card Debt
You May Like: Do Employees Get Paid In Bankruptcy
Tracking The Federal Deficit: February 2021
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the federal government ran a deficit of $312 billion in February 2021, the fifth month of fiscal year 2021. This months deficitthe difference between $246 billion in revenue and $558 billion in spendingwas $77 billion more than last Februarys. The deficit so far in fiscal year 2021 has climbed to just over $1 trillion, an 83% year-over-year increase . Year-over-year, total spending has risen by 25% and revenues have increased by 5%.
Analysis of Notable Trends: Increased spending in February, and fiscal year 2021 as a whole, mostly resulted from pandemic relief legislation. For instance, the Small Business Administrations Paycheck Protection Program accounted for most of the $133 billion spending increase from last February to this one. SBA outlays soared to $91 billion this February compared to only $100 million in the same month last year. The other largest spending changes were greater outlays on unemployment compensation and $17 billion less in refundable tax credit payments because of a delayed start to the tax filing season this year.
Despite a historic recession, revenues were 5% higher in the first five months of fiscal year 2021 than during the same period last year . This healthy growth is surprising, especially when compared to the onset of the last major recession: In the first five months of fiscal year 2009, revenues plunged 11% year-over-year.
The Pandemic Impact On Debt
The less your income, the easier it is to pile up debt. That obvious lesson hit home in 2020.
The unemployment rate went from 3.5% pre-COVID to a peak of 14.8% in April 2020the highest level since 1948.
The total U.S. consumer debt balance grew $800 billion, according to Experian. That was an increase of 6% over 2019, the highest annual growth jump in over a decade.
Student loan debt increased the most , followed by mortgage debt and personal loan debt .
But dropped $73 billion, a 9% decrease from 2019 and the first annual drop in eight years.
A November 2020 Experian survey showed that 66% of consumers were spending the same or less during the pandemic than they had in 2019. About 33% of those surveyed said they put more in savings in 2020 than they did in the last year.
You May Like: How To Hide Assets From Bankruptcy
You May Like: How To File Bankruptcy On Student Loans
Jan How Much Debt Can The United States Handle
This morning I woke up and the first thing that I heard was that the Federal Government has started purchasing troubled mortgages to ease the credit crisis. Well, if it were that easy, we should have did it several months ago. Now I feel much better that the Federal Government is going to start helping people. Wait a minute, are they really helping people or helping financial institutions again? The blank checks just keep on getting issued. I believe that the Federal Government has either spent or guaranteed over seven trillion dollars of debt already. Of course, that number will never be shown to the American public.
This analysis comes with some assumptions. First, that the United States doesnt borrow any more money. Second, that we can pay it back at the rate of one billion dollars a day. Third, that the Asian countries will waive any and all interest. This last assumption is clearly a fallacy.
No Comments
Tracking The Federal Deficit: January 2020
The Congressional Budget Office reported that the federal government generated a $32 billion deficit in January, the fourth month of fiscal year 2020. Januarys deficit is a $40 billion change from the $9 billion surplus recorded a year earlier in January 2019. Januarys deficit brings the total deficit so far this fiscal year to $388 billion, which is 25% higher than the same period last year . Total revenues so far in FY2020 increased by 6% , while spending increased by 10% , compared to the same period last year. (After accounting for timing shifts, spending rose by 6% or $90 billion.
Analysis of Notable Trends in This Fiscal Year to Date: Through the first four months of FY2020, revenue from corporate income taxes rose by 27% . Additionally, Federal Reserve remittances increased by 14% partly due to lower short-term interest rates that reduced its interest expenses. On the spending side, after accounting for timing shifts, total Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid outlays rose by 6% . Outlays for the Department of Defense rose by 7% , largely for procurement and research and development.
You May Like: Debt To Income Calculation
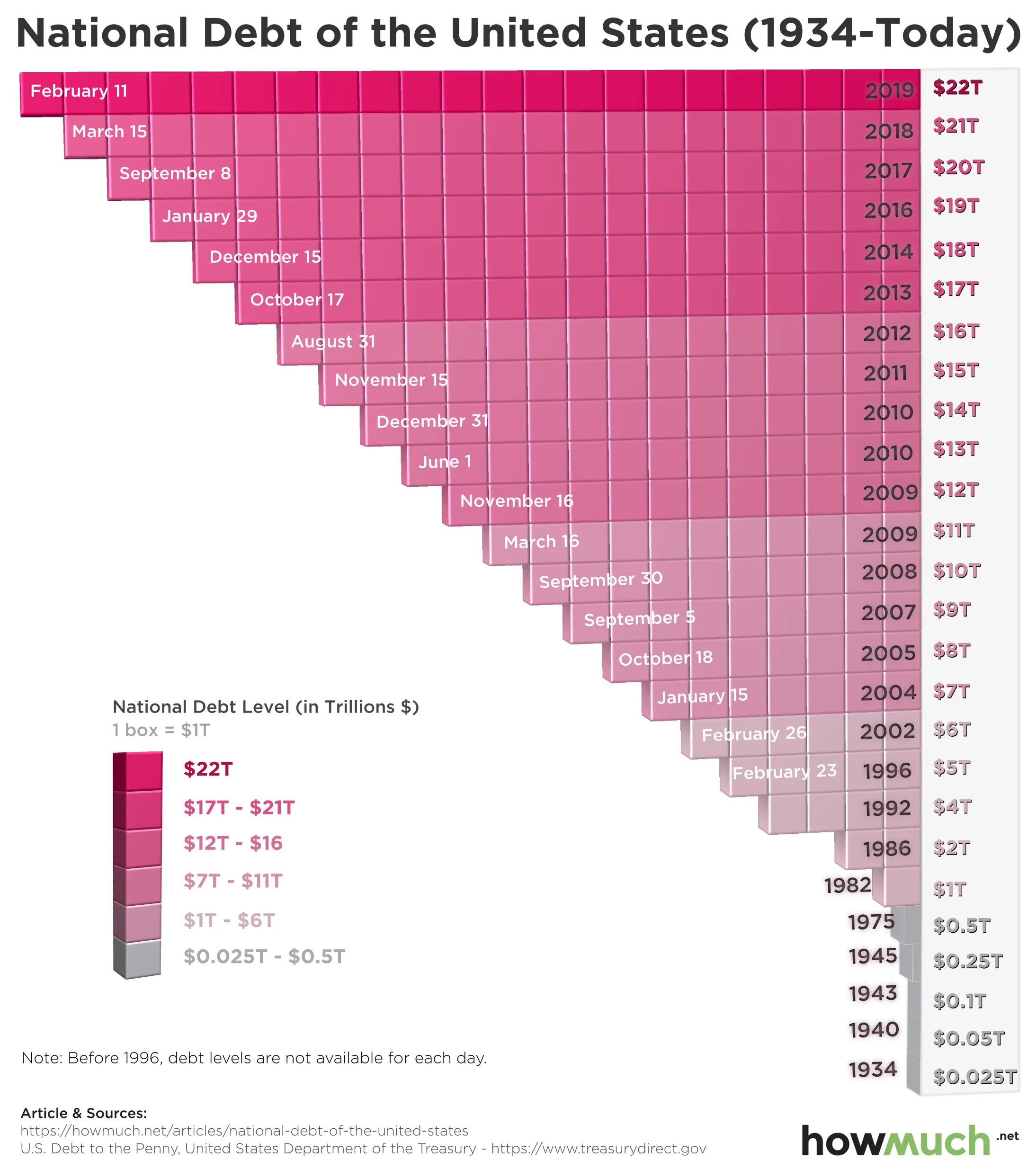
A Brief History Of Us Debt
Sabrina Jiang / Investopedia
Nearly all national governments borrow money. The U.S. has carried national debt throughout its history, dating back to the borrowing that financed the Revolutionary War. Since then, the debt has grown alongside the economy as a result of increased government responsibilities and in response to economic developments.
The federal debt is held primarily by the American public, followed by foreign governments and U.S. banks and investors. Note that the portion of the federal debt held by the public is considered more meaningful than the overall national debt because it excludes intragovernmental debtthat is, it only accounts for U.S. debt held by entities other than the federal government. So, while national debt totaled $31.1 trillion as of October 2022, federal debt held by the public was $24.3 trillion and intragovernmental debt amounted to $6.9 trillion. Thus, while national debt-to-GDP was at 121% as of the second quarter of 2022, the ratio of federal debt to GDP counting only debt held by the public was 95%.
Why The Federal Reserve Owns Treasurys
As the nation’s central bank, the Federal Reserve is in charge of the country’s credit. It doesn’t have a financial reason to own Treasury notes. So why does it?
The Federal Reserve actually tripled its holdings between 2007 and 2014. The Fed had to fight the 2008 financial crisis, so it ramped up open market operations by purchasing bank-owned mortgage-backed securities. The Fed began adding U.S. Treasurys in 2009. It owned $1.6 trillion, by 2011, maxing out at $2.5 trillion in 2014.
This quantitative easing stimulated the economy by keeping interest rates low and infusing liquidity into the capital markets. It gave businesses continued access to low-cost borrowing for operations and expansion.
The Fed purchased Treasurys from its member banks, using credit that it created out of thin air. It had the same effect as printing money. By keeping interest rates low, the Fed helped the government avoid the high-interest-rate penalty it would incur for excessive debt.
Don’t Miss: Personal Debt To Income Ratio
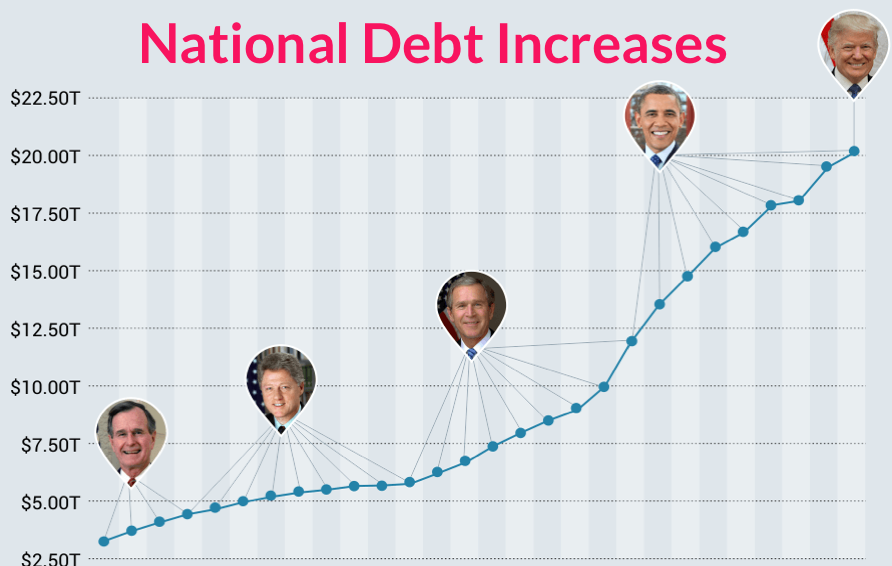
National Debt By President
The National Debt has always been an area of interest for the United States President George Washington appointed future President Alexander Hamilton to understand and solve the $80 million debtthat had accrued due to the Revolutionary War. Hamilton came up with the plan to pay off the debt through taxes and the creation of the national bank. Since then the United States has steadily increased its budget deficit, and the national debt has continued to rise.The first time that the national debt hit the $1 billion mark was in 1863 while the Civil War was occurring it hit the $2 billion was two years later when the civil war ended in 1865. As the country went to battle during World War I and World War II, the national debt hit the $10 billion mark and $100 billion marks respectively. By 1982 after the Vietnam War and the Cold War, the national debt hit the $1 trillion mark for the first time in history. By the 21st Century, the national debt got to $20 trillion after major events such as the War on Terror and the Great Recession. Today , the national debt stands at $30.2 trillion and public debt is roughly 100% of the country’s GDP.