What Is The Current Us Debt Amount
Debt Held by the Public at the end of September 2021: $22.3 trillion. Debt Held by the Public at the end of September 2020: $21.0 trillion. The $2.8 trillion deficit in FY21 resulted in a $1.3 trillion increase in debt held by the public, with Treasury financing the rest of the deficit by drawing down existing cash balances.
Also Check: Debt Collection While On Disability
The Biggest Problem The Economy Faced Was Persistent High Inflation Which Remained Above The Reserve Banks Comfort Level For The Most Of The Year The Challenges Before The Government And The Reserve Bank In The New Year Would Be To Arrest Inflation Check Declining Value Of Rupee Against Us Dollar And Promote Private Investment And Growth With A View To Ensure That The Country Remains One The Fastest Growing Major Economies Of The World
Donât miss out on ET Prime stories! Get your daily dose of business updates on WhatsApp.
-
The Central Bureau of Investigation has widened its probe into the loans sanctioned by ICICI Bank to Videocon group companies, seeking details on 10 more such loans allegedly sanctioned between 2013 and 2016.
Read More News on
Debt By Year Compared To Nominal Gdp And Events
In the table below, the national debt is compared to GDP and influential events since 1929. The debt and GDP are given as of the end of the fourth quarter in each year to coincide with the end of the fiscal year. That’s the best way to accurately determine how spending in each fiscal year contributes to the debt and compare it to economic growth.
From 1947-1976, debt and GDP are given at the end of the second quarter since, during that time, the fiscal year ended on June 30. For years 1929 through 1946, debt is reported at the end of the second quarter, while GDP is reported annually, since quarterly figures are not available.
Also Check: Cheapest Way To File Bankruptcy Chapter 7
Concerns Over Chinese Holdings Of Us Debt
According to a 2013 Forbes article, many American and other economic analysts have expressed concerns on account of the People’s Republic of China’s “extensive” holdings of United States government debt as part of their reserves. The National Defense Authorization Act of FY2012 included a provision requiring the Secretary of Defense to conduct a “national security risk assessment of U.S. federal debt held by China.” The department issued its report in July 2012, stating that “attempting to use U.S. Treasury securities as a coercive tool would have limited effect and likely would do more harm to China than to the United States. An August 19, 2013 Congressional Research Service report said that the threat is not credible and the effect would be limited even if carried out. The report said that the threat would not offer “China deterrence options, whether in the diplomatic, military, or economic realms, and this would remain true both in peacetime and in scenarios of crisis or war.”
How Do You Calculate The Debt
To get the debt-to-GDP ratio, you divide a nations debt by its GDP.
You can use several sources to find the information you need to calculate a countrys GDP. For example, you can use the U.S. Treasurys Debt to the Penny website, which gives a complete breakdown of how much the government owes.
You can also use the Bureau of Economic Analysis National Income and Product Accounts to find GDP for recent periods.
Recommended Reading: Debt Collection For Small Business
Don’t Miss: How Does Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Work
What Is The Debt
The debt-to-GDP ratio is the metric comparing a countrys public debt to its gross domestic product . By comparing what a country owes with what it produces, the debt-to-GDP ratio reliably indicates that particular countrys ability to pay back its debts. Often expressed as a percentage, this ratio can also be interpreted as the number of years needed to pay back debt if GDP is dedicated entirely to debt repayment.
Definition Of Debt To Gdp Ratio
Debt to GDP ratio is defined as the ratio between total government/sovereign debts taken by a country to the total GDP of the country or the economic output for an entire year. A lower ratio of this number is always preferred as it means the economy is well balanced in terms of its total GDP when compared to debt. Similarly, a higher ratio may be alarming and may signal to the economy going to default.
A low debt GDP ratio is always preferable because it means a country is producing and selling goods and has sufficient ability to pay back its debt by taking any further debt. As the debt to gross domestic product ratio for a country rises, the risk of the country becoming default also rises. A study by World Bank shows that countries that have a debt-to-gross domestic product ratio of more than 77% for a longer period of time are expected to go through slowdowns in the growth of their economy.
You May Like: Foreclosure Homes For $1 000 Dollars
What The National Debt Means To You
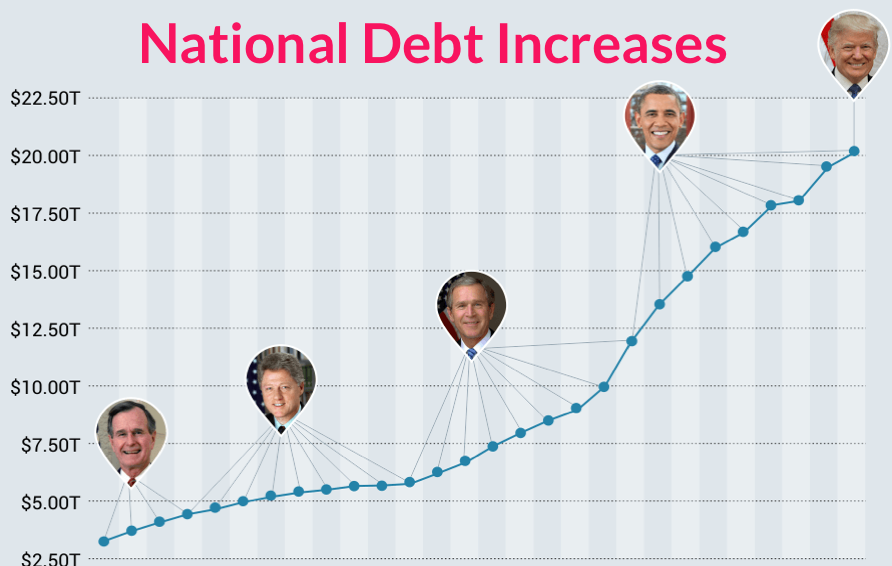
The U.S. national debt has long been the subject of significant political controversy. Given its rapid rise in recent years following federal spending increases tied to the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s easy to understand why the issue is drawing more attention from economists, financial markets participants, and critics of government policies.
Polls have long shown high levels of public unease with the U.S. government’s debt, which topped $31 trillion in October 2022. The debt has grown in nominal terms and also relative to the U.S. gross domestic product .
At the same time, large majorities of Americans backed the pandemic relief spending while opposing spending cuts for the costliest government programs. Most also believe they’re already paying too much in federal income tax, while increasingly backing tax increases for corporations and the rich.
The public debt people say makes them uncomfortable is the inevitable result of the tax and spending policies that continue to enjoy broad public support. A related problem is that many aren’t sure what effect the national debt has or might have on their own lives and finances.
How Is The Us Debt
The U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio is unique in two ways:
-
First, the U.S. dollar has been the worlds reserve currency since 1944.
-
The second way the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio is unique is tied to its use as global reserve currency: The United States has had the worlds largest and most dominant economy for years.
Because of the scale of the U.S. economy and the dominance of the U.S. dollar, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio is very important to the global economy. According to the World Bank, as of 2020 the United States made up approximately a quarter of global GDP. That means that the U.S. creates roughly 25% of all the goods and services produced and purchased around the worlda huge chunk of the worlds GDP.
The relationship between a countrys debt and its GDP is more complicated than it might seem at first, but it can still tell us a lot about that countrys economy. And as long as the United States continues to be one of the most dominant economies globally, the world will look to its debt-to-GDP ratio to predict which way the international economy is heading.
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Can You File Bankruptcy In Ga
Us National Debt To Gdp Ratio By Year
The national debt to GDP ratio therefore measures a countrys debt vs its total output. Economists disagree where the ideal range for this ratio is. Ideally this ratio would be as close to zero as possible . However, most economists agree that some public debt is necessary to spur growth and investment.
The ideal range for this ratio is typically cited to be somewhere between 40-80%. Where a country falls on that scale depends on how developed they are, and what kind of debt is owed. After 80%, countries usually face a risk of adverse effects from the high levels of debt.
However, some debt is much more risky than others. For instance, foreign owed debt is much worse than internal debt Internal debt can be held by public citizens, but also can be held by social programs designed to pay citizens back .
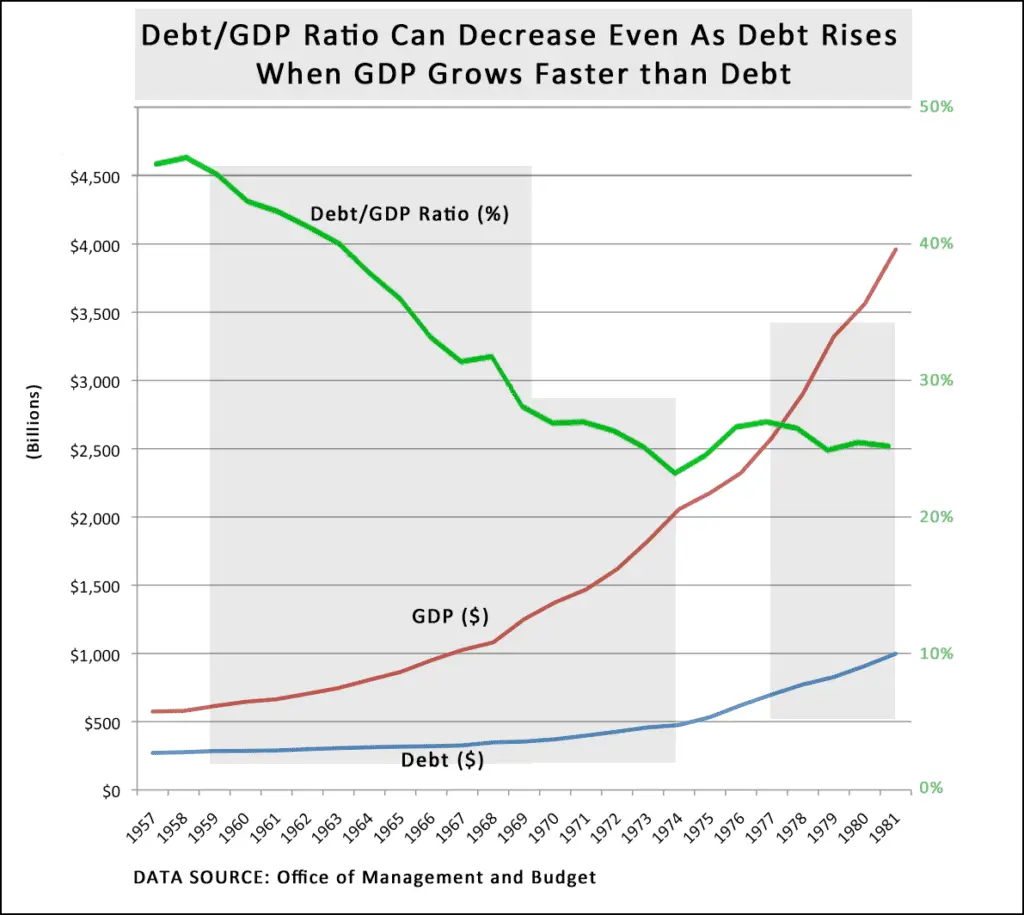
As you can see in the chart, the US ratio has varied greatly over the last century. During World War II the ratio skyrocketed due to higher government spending as well as efforts to rebuild Europe such as the . In the years following the ratio lowered due to spending cuts, as well as the US economys postwar boom.
In recent years the US ratio has greatly increased once again due to the 2008 global financial crisis and COVID-19 pandemic relief. This would suggest that in future years, taxes will need to increase, or spending lowered to help bring the ratio down to more reasonable levels.
United States Bond Rating
On August 5, 2011, the bond rating service Standard and Poors, a company which rates the ability of institutions to repay their debt, lowered the United States federal governments long-term debt rating from AAA to AA+ for the first time since their ratings began in the early 1940s and gave the governments credit a negative outlook, warning that unless the rate of new government spending were reduced, there would be grounds for lowering the rating again.
Don’t Miss: How Many Months Bank Statements For Bankruptcy
Notable Companies And Markets
According to Fortune Global 500 2011, the ten largest U.S. employers were Walmart, U.S. Postal Service, IBM, UPS, McDonalds, Target Corporation, Kroger, The Home Depot, General Electric, and Sears Holdings.
Apple Inc., , IBM, McDonalds, and Microsoft are the worlds five most valuable brands in an index published by Millward Brown.
A 2012 Deloitte report published in STORES magazine indicated that of the worlds top 250 largest retailers by retail sales revenue in fiscal year 2010, 32% of those retailers were based in the United States, and those 32% accounted for 41% of the total retail sales revenue of the top 250. is the worlds largest online retailer.
Half of the worlds 20 largest semiconductor manufacturers by sales were American-origin in 2011.
Most of the worlds largest charitable foundations were founded by Americans.
American producers create nearly all of the worlds highest-grossing films. Many of the worlds best-selling music artists are based in the United States. U.S. tourism sector welcomes approximately sixty million international visitors every year. In a recent study by Salam Standard, it has been reported that the United States is the biggest beneficiary of global Muslim tourism spend, enjoying 24 percent share of the total Muslimtravel spend worldwide or almost $35 billion.
Negative Real Interest Rates
Since 2010, the U.S. Treasury has been obtaining negative real interest rates on government debt, meaning the inflation rate is greater than the interest rate paid on the debt. Such low rates, outpaced by the inflation rate, occur when the market believes that there are no alternatives with sufficiently low risk, or when popular institutional investments such as insurance companies, pensions, or bond, money market, and balanced mutual funds are required or choose to invest sufficiently large sums in Treasury securities to hedge against risk. Economist Lawrence Summers states that at such low interest rates, government borrowing actually saves taxpayer money and improves creditworthiness.
In the late 1940s through the early 1970s, the U.S. and UK both reduced their debt burden by about 30% to 40% of GDP per decade by taking advantage of negative real interest rates, but there is no guarantee that government debt rates will continue to stay this low. Between 1946 and 1974, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio fell from 121% to 32% even though there were surpluses in only eight of those years which were much smaller than the deficits.
Recommended Reading: How To Purchase Foreclosed Homes
Budget Deficit By Year Since 1929
The deficit since 1929 is compared to the increase in the debt, nominal GDP, and national events in the table below.
The national debt and GDP are given as of the end of the third quarter of each year unless otherwise notedspecifically, September 30. The date coincides with the budget deficits fiscal year-end. GDP for years up to 1947 isnt available for the third quarter, so annual figures are used.
The first column represents the fiscal year, followed by the deficit for that year in billions. The next column is how much the debt increased for that fiscal year, also in billions. The third column calculates the deficit-to-GDP ratio. It indicates that there was a surplus if numbers are in parentheses. The fourth column describes events that affected the deficit and debt.
GDP is as of June 30, 2021, for 2021. The national debt increase is from October 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021. The estimated fiscal year budget deficit is from the CBO and was released on July 1, 2021.
| FY |
|---|
You May Like: Debt To Income Calculator Fha
Calculating The Annual Change In Debt
Conceptually, an annual deficit should represent the change in the national debt, with a deficit adding to the national debt and a surplus reducing it. However, there is complexity in the budgetary computations that can make the deficit figure commonly reported in the media considerably different from the annual increase in the debt. The major categories of differences are the treatment of the Social Security program, Treasury borrowing, and supplemental appropriations outside the budget process.
Social Security payroll taxes and benefit payments, along with the net balance of the U.S. Postal Service, are considered “off-budget”, while most other expenditure and receipt categories are considered “on-budget”. The total federal deficit is the sum of the on-budget deficit and the off-budget deficit . Since FY1960, the federal government has run on-budget deficits except for FY1999 and FY2000, and total federal deficits except in FY1969 and FY1998FY2001.
Read Also: Liquidation Pallets San Francisco
National Debt Vs Budget Deficit: Whats The Difference
A budget deficit is when a nationâs annual budget spending is greater than its annual revenue from all sources. Meanwhile, the national debt is the total outstanding value of all treasury bonds issued by a government.
In the U.S., Congress has the responsibility of passing an annual budget for the federal government. The Treasuryâwhich is part of the executive branch controlled by the White Houseâgathers taxes, collects other revenue and sells U.S. government debt, known as Treasurys.
The U.S. has a budget deficit when Congressâs annual budget costs more than the Treasury raises in taxes and other revenue. When revenue exceeds spending, itâs called a budget surplus
To fund the budget, the Treasury sells bonds on a regular schedule. It sells a wide variety of debt securities with varying terms and maturities, but in each case, they are liabilities owed by the government. Investors expect to receive regular interest payments, plus the return of their principal when the securities mature.
The total of all outstanding Treasurys is considered to be the U.S. national debt. The connection between the national debt and budget deficits is somewhat indirect since the Treasury sells bonds no matter what shape the budget takes.
The budget deficit is paid for by revenue from the sale of Treasurys. Recently, that has amounted to trillions of dollars added to the national debt each year.
Recommended Reading: Debt Consolidation Vs Personal Loan
How To Look At The National Debt By Year
It’s best to look at a country’s national debt in context. During a recession, expansionary fiscal policy, such as spending and tax cuts, is often used to spur the economy back to health. If it boosts growth enough, it can reduce the debt. A growing economy produces more tax revenues to pay back the debt.
The theory of supply-side economics says the growth from tax cuts is enough to replace the tax revenue lost if the tax rate is above 50% of income. When tax rates are lower, the cuts worsen the national debt without boosting growth enough to replace lost revenue.
Don’t Miss: Government Help For Homeowners
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Obligations Excluded
Under normal accounting rules, fully owned companies would be consolidated into the books of their owners, but the large size of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac has made the U.S. government reluctant to incorporate them into its own books. When the two mortgage companies required bail-outs, White House Budget Director Jim Nussle, on September 12, 2008, initially indicated their budget plans would not incorporate the government-sponsored enterprise debt into the budget because of the temporary nature of the conservator intervention. As the intervention has dragged out, pundits began to question this accounting treatment, noting that changes in August 2012 “makes them even more permanent wards of the state and turns the government’s preferred stock into a permanent, perpetual kind of security”.
Us Will Hit Debt Limit On Thursday Yellen Tells Congress
The Treasury Department expects to begin taking extraordinary measures to continue paying the governments obligations before what is expected to be a big fight to raise the borrowing cap.
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this articleGive this articleGive this article
By Alan Rappeport and Jim Tankersley
WASHINGTON Treasury Secretary Janet L. Yellen warned on Friday that she would have to begin employing extraordinary measures on Thursday to continue paying the nations bills if lawmakers did not act to raise the statutory debt limit and that her powers to delay a default could be exhausted by early June.
Ms. Yellens letter to Congress was the first sign that resistance by House Republicans to lifting the borrowing cap could put the U.S. economy at risk and signals the beginning of an intense fight in Washington this year over spending and deficits.
Failure to meet the governments obligations would cause irreparable harm to the U.S. economy, the livelihoods of all Americans and global financial stability, Ms. Yellen wrote.
The letter is the beginning of what is expected to be a protracted and potentially damaging economic fight. Republicans, who assumed control of the House last week, have insisted that any increase to the debt limit be accompanied by significant spending curbs, most likely including cuts to both the military and domestic issues.
Don’t Miss: Are Foreclosures On Hold Right Now